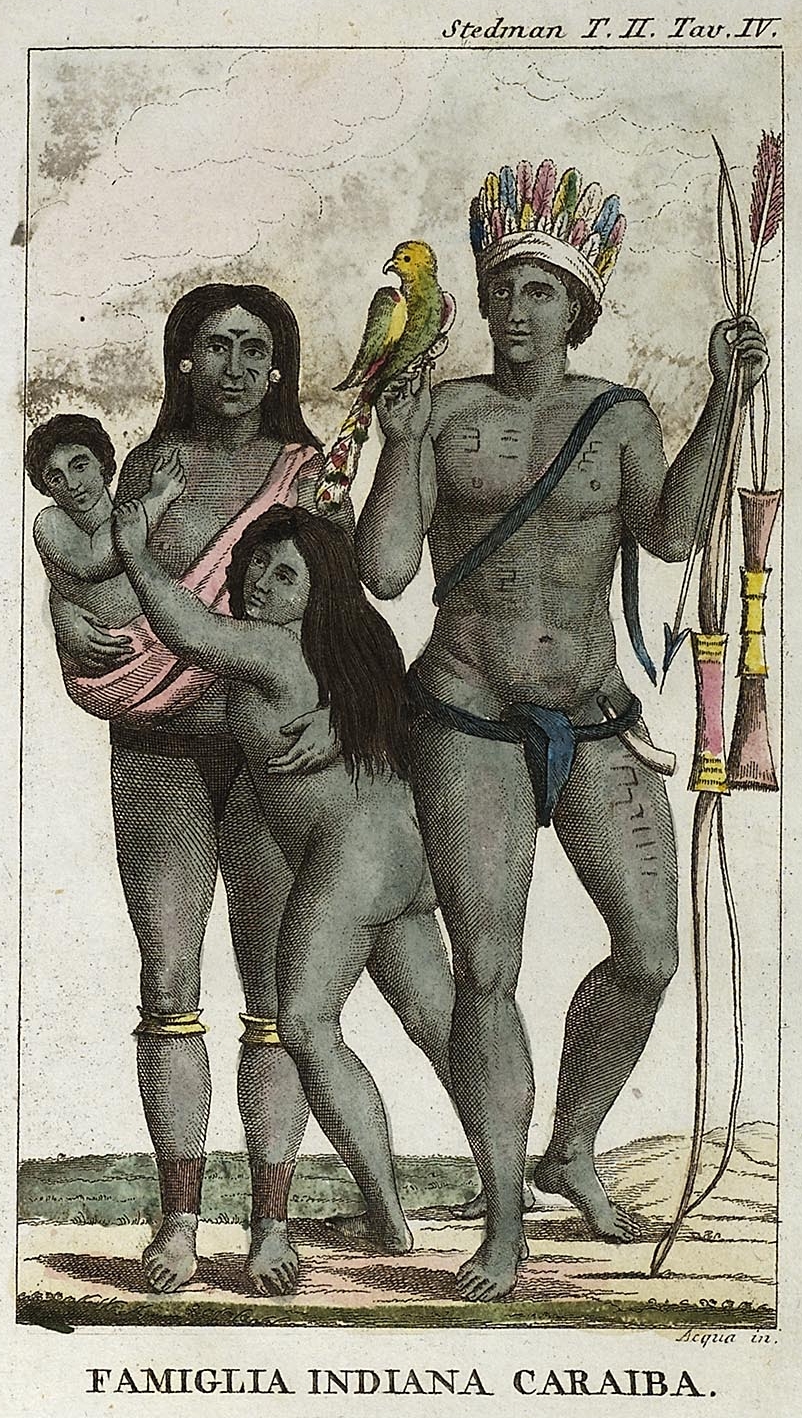|
Igneris
The Igneri were an indigenous Arawak people of the southern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. Historically, it was believed that the Igneri were conquered and displaced by the Island Caribs in an invasion some time before European contact. However, linguistic and archaeological studies in the 20th century have led scholars to more nuanced theories as to the fate of the Igneri. The Igneri spoke an Arawakan language, Iñeri, which transitioned into the Island Carib language. History The Caribbean was populated in various waves, several of which produced varying and often successive archaeological cultures. It is not clear which sites and cultures may be related to the Igneri. Archaeologist Irving Rouse associated them with the Suazoid culture, which emerged around AD 1000 in the Lesser Antilles as a continuation of the earlier Saladoid culture. Suazoid culture lasted until around 1450, which may reflect the transition from Igneri to Island Carib culture in the islands. Island Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneri Language
The Kalinago language, also known as Igneri (Iñeri, Inyeri, etc.), was an Arawakan language historically spoken by the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. Kalinago proper became extinct by about 1920 due to population decline and colonial period deportations resulting in language death, but an offshoot survives as Garifuna, primarily in Central America. Despite its name, Kalinago was not closely related to the Carib language of the mainland Caribs. Instead, it appears to have been a development of the Arawakan language spoken by the islands' earlier Igneri inhabitants, which incoming Caribs adopted in the pre-Columbian era. During the French colonial period, Carib men also spoke a Cariban-derived pidgin amongst themselves. History At the time of European contact, the Kalinago lived throughout the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, from Guadeloupe to Grenada. Contemporary traditions indicated the Caribs (or Kaliphuna) had conquered these islands from their pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural History Of Puerto Rico
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Caribbean
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Ciguayo and Macorix of parts of Hispaniola, and the Guanahatabey of western Cuba. The Kalinago have maintained an identity as an indigenous people, with a reserved territory in Dominica. Introduction Some scholars consider it important to distinguish the Taíno from the neo-Taíno nations of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Hispaniola, and the Lucayan of the Bahamas and Jamaica. Linguistically or culturally these differences extended from various cognates or types of canoe: canoa, piragua, cayuco to distinct languages. Languages diverged even over short distances. Previously these groups often had distinctly non-Taíno deities such as the goddess Jagua, strangely enough the god Teju Jagua is a major demon of indigenous Paraguayan mythology. Stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneri
The Igneri were an indigenous Arawak people of the southern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. Historically, it was believed that the Igneri were conquered and displaced by the Island Caribs in an invasion some time before European contact. However, linguistic and archaeological studies in the 20th century have led scholars to more nuanced theories as to the fate of the Igneri. The Igneri spoke an Arawakan language, Iñeri, which transitioned into the Island Carib language. History The Caribbean was populated in various waves, several of which produced varying and often successive archaeological cultures. It is not clear which sites and cultures may be related to the Igneri. Archaeologist Irving Rouse associated them with the Suazoid culture, which emerged around AD 1000 in the Lesser Antilles as a continuation of the earlier Saladoid culture. Suazoid culture lasted until around 1450, which may reflect the transition from Igneri to Island Carib culture in the islands. Island Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from several languages. It is most commonly employed in situations such as trade, or where both groups speak languages different from the language of the country in which they reside (but where there is no common language between the groups). Linguists do not typically consider pidgins as full or complete languages. Fundamentally, a pidgin is a simplified means of linguistic communication, as it is constructed impromptu, or by convention, between individuals or groups of people. A pidgin is not the native language of any speech community, but is instead learned as a second language. A pidgin may be built from words, sounds, or body language from a multitude of languages as well as onomatopoeia. As the lexicon of any pidgin will be limited to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariban
The Cariban languages are a Language family, family of languages indigenous to northeastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen, but most are spoken only by a few hundred people. Macushi language, Macushi is the only language among them with numerous speakers, estimated at 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family—Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject. Previous to their discovery of this, linguists believed that this order did not exist in any spoken natural language. In the 16th century, Cariban peoples expanded into the Lesser Antilles. There they killed or displaced, and also mixed with the Arawaks, Arawak peoples who already inhabited the islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawakan
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland Caribs
The Kalina, also known as the Caribs or mainland Caribs and by several other names, are an indigenous people native to the northern coastal areas of South America. Today, the Kalina live largely in villages on the rivers and coasts of Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Brazil. They speak a Cariban language known as Carib. They may be related to the Island Caribs of the Caribbean, though their languages are unrelated. Name The exonym ''Caribe'' was first recorded by Christopher Columbus. One hypothesis for the origin of ''Carib'' is that it means "brave warrior". Its variants, including the English ''Carib'', were then adopted by other European languages. Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and ''Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. The Kalina call themselves ''Kalina'' or ''Karìna'' , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Carib
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse and others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladoid Culture
The Saladoid culture is a pre-Columbian indigenous culture of territory in present-day Venezuela and the Caribbean that flourished from 500 BCE to 545 CE. The Saladoid were an Arawak people. Concentrated along the lowlands of the Orinoco River, the people migrated by sea to the Lesser Antilles, and then to Puerto Rico."Prehistory of the Caribbean Culture Area" Southeast Archaeological Center, National Park Service (retrieved 19 July 2013) Name This cultural classification comes from adding the suffix "oid" to the sites where these unique pottery styles were first recognised; thus the name Saladoid, from name of the modern settlement of Saladero, is used by archaeologists to identify the peoples of the early ceramic age.Chronology The Saladoid period includes ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irving Rouse
Benjamin Irving Rouse (August 29, 1913 – February 24, 2006) was an American archaeologist on the faculty of Yale University best known for his work in the Greater and Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean, especially in Haiti. He also conducted fieldwork in Florida and Venezuela. He made major contributions to the development of archaeological theory, with a special emphasis on taxonomy and classification of archaeological materials and studies of human migration. Early life Benjamin Irving Rouse was born on August 29, 1913 in Rochester, New York, the son of Louise Gillespie (Bohachek) and Benjamin Irving Rouse. His maternal grandfather was Czech. His family had been in the plant nursery industry for nearly a century, and Ben (as he was known to family and friends) was planning on continuing in the family business when he enrolled at Yale University in 1930 as a plant science major. His father had also attended Yale as an undergraduate. Education Irving Rouse began his academic care ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |