|
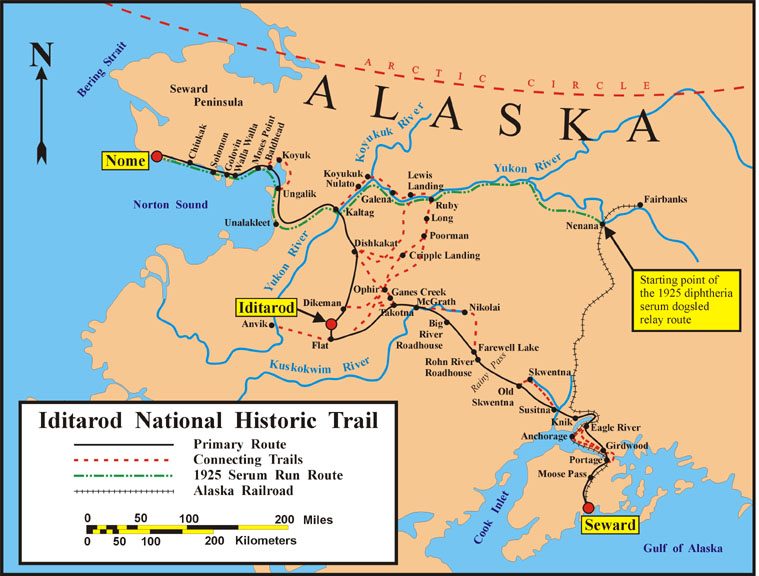
Iditarod Trail
The Iditarod Trail, also known historically as the Seward-to-Nome Trail, is a thousand-plus mile (1,600 km) historic and contemporary trail system in the US state of Alaska. The trail began as a composite of trails established by Alaskan native peoples. Its route crossed several mountain ranges and valleys and passed through numerous historical settlements en route from Seward to Nome. The discovery of gold around Nome brought thousands of people over this route beginning in 1908. Roadhouses for people and dog barns sprang up every 20 or so miles. By 1918 World War I and the lack of 'gold fever' resulted in far less travel. The trail might have been forgotten except for the 1925 diphtheria outbreak in Nome. In one of the final great feats of dog sleds, twenty drivers and teams carried the life-saving serum in 127 hours. Today, the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race serves to commemorate the part the trail and its dog sleds played in the development of Alaska, and the route an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iditarod Trail BLM Map
The Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, more commonly known as The Iditarod, is an annual long-distance sled dog race run in early March. It travels from Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage to Nome, Alaska, Nome, entirely within the US state of Alaska. Mushing, Mushers and a team of between 12 and 14 dogs, of which at least 5 must be on the towline at the finish line, cover the distance in 8–15 days or more. The Iditarod began in 1973 as an event to test the best sled dog mushers and teams but evolved into today's highly competitive race. Teams often race through blizzards causing whiteout (weather), whiteout conditions, sub-zero temperatures and gale-force winds which can cause the wind chill to reach . A ceremonial start occurs in the city of Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage and is followed by the official restart in Willow, Alaska, Willow, a city north of Anchorage. The restart was originally in Wasilla, Alaska, Wasilla through to 2007, but due to Climate change, too little snow, the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet ( tfn, Tikahtnu; Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage. The Cook Inlet watershed is the most populated watershed in Alaska. The watershed covers about of southern Alaska, east of the Aleutian Range, south and east of the Alaska Range, receiving water from its tributaries, the Knik River, the Little Susitna River, and the Susitna and Matanuska rivers. The watershed includes the drainage areas of Denali (formerly named Mount McKinley). Within the watershed there are several national parks and the active volcano Mount Redoubt, along with three other historically active volcanoes. Cook Inlet provides navigable access to the port of Anchorage at the northern end, and to the smaller Homer port fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula is a large peninsula on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska whose westernmost point is Cape Prince of Wales. The peninsula projects about into the Bering Sea between Norton Sound, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Sea, and Kotzebue Sound, just below the Arctic Circle. The entire peninsula is about long and wide. Like Seward, Alaska, it was named after William H. Seward, the United States Secretary of State who fought for the U.S. purchase of Alaska. The Seward Peninsula is a remnant of the Bering land bridge, a roughly thousand mile wide swath of land connecting Siberia with mainland Alaska during the Pleistocene Ice Age. This land bridge aided in the migration of humans, as well as plant and animal species, from Asia to North America. Excavations at sites such as the Trail Creek Caves and Cape Espenberg in the Bering Land Bridge National Preserve as well as Cape Denbigh to the south have provided insight into the timeline of prehistorical migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norton Sound
Norton Sound (russian: Нортон-Саунд) is an inlet of the Bering Sea on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, south of the Seward Peninsula. It is about 240 km (150 mi) long and 200 km (125 mi) wide. The Yukon River delta forms a portion of the south shore and water from the Yukon influences this body of water. It is ice-free from June to October. Norton Sound was explored by Captain James Cook in September 1778. He named the body of water after Sir Fletcher Norton, then Speaker of the British House of Commons. The Norton Sound area has been home to Yup'ik and Inupiat for many centuries. It is the boundary between the two peoples; the Inupiat live to the north and the Yup'ik to the south. The town of Nome is along the northern edge of Norton Sound. The villages of Elim, Golovin, Stebbins, White Mountain, Koyuk, Shaktoolik, St. Michael, and Unalakleet are on the shores or waterways flowing into Norton Sound. The Iditarod Trail Sled Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unalakleet, Alaska
Unalakleet ( ; ik, Uŋalaqłiq, ; russian: Уналаклит) is a city in Nome Census Area, Alaska, United States, in the western part of the state. At the 2010 census the population was 688, down from 747 in 2000. Unalakleet is known in the region and around Alaska for its salmon and king crab harvests; the residents rely for much of their diet on caribou, ptarmigan, ''oogruk'' (bearded seal), and various salmon species. Unalakleet is also known for its aesthetic value. It is located next to the Bering Sea and the large, clean Unalakleet River. The landscape also has trees, tundra, and hills behind it. History ''Unalakleet'' is an adaptation of the Iñupiaq word ''"Una-la-thliq"'',Community Information Summaries: "Unalakleet." Alaska Community Database Online, Alaska Department of Commerce, Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaltag, Alaska
Kaltag (Koyukon: ; ik, Qałtaq) is a city and village in Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 190, down from 230 in 2000. History Kaltag was a Koyokon Athabascan area used as a cemetery for surrounding villages. It is located on an old portage trail which led west through the mountains to Unalakleet. The Athabascans had seasonal camps in the area and moved as the wild game migrated. There were 12 summer fish camps located on the Yukon River between the Koyukuk River and the Nowitna River. Kaltag was named by Russians for a Koyokon man named Kaltaga. There was a smallpox epidemic in 1839 that killed a large part of the population of the area. After the Alaska Purchase, a United States military telegraph line was constructed along the north side of the Yukon River. A trading post opened around 1880, just before the gold rush of 1884–85. Steamboats on the Yukon, which supplied gold prospectors ran before and after 1900 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuskokwim Mountains
The Kuskokwim Mountains is a range of mountains in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States, west of the Alaska Range and southeast of the Yukon River. The Kuskokwim Mountains begin in the interior west of Fairbanks. The mountain range extend from Canyon Creek and Chikuminuk Lake in the southwest over a distance of about long to the Tanana River in the northeast and reach a width of up to . The southeast flank of the Kuskokwim Mountains borders the rivers Kantishna, Kuskokwim, Holitna and Kogrukluk. In the northwest lie the Kaiyuh, Russian and Kilbuck Mountains as well as the rivers Innoko, Dishna and Iditarod. The range takes its name from the Kuskokwim River, which flows through the mountains, as well as Aniak and Nowitna rivers. Reported and defined in 1898 by Josiah Edward Spurr of the USGS. Spurr applied the name "Tanana Hills" to the low mountains at the northeast end of what are now the Kuskokwim Mountains. Sub-ranges * Ahklun Mountains * Eek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophir, Alaska
Ophir is an unincorporated area located in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area in the U.S. state of Alaska. It was named by miners after the wealthy land of Ophir mentioned in the Old Testament. The area was the site of a gold rush in 1906. Ophir reached a peak population of 122 in 1910. Ophir is now abandoned, but serves as a checkpoint in the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race. An airport with a single gravel runway exists at the village, built prior to 1949. It is currently in disuse and unmaintained. There are a number of creeks near Ophir, all on the west bank of the Innoko, where gold placers were located starting about 1906. Yankee Creek is the closest to the source of the river, then , Little and Spruce Creeks, all above Ophir Creek. The original Iditarod trail ran above Ganes Creek in the summer, down the Innoko valley in the winter; the current race trail goes through the old townsite, which was destroyed in a brush fire started by a camper in the 1970s, and is a rest stop. Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innoko River
The Innoko River (; (Deg Xinag: ''Yooniq'') is a tributary of the Yukon River in the U.S. state of Alaska. It flows north from its origin south of Cloudy Mountain in the Kuskokwim Mountains and then southwest to meet the larger river across from Holy Cross. Most of its upper portion flows through the Innoko National Wildlife Refuge. The entire river is within the Yukon–Koyukuk Census Area. Innoko is a Deg Hit’an name for the river. The Russian colonial administrators also called the river ''Shiltonotno'', ''Legon'' or ''Tlegon'', ''Chagelyuk'' or ''Shageluk'' and ''Ittege'' at various times in the 19th century. See also *List of rivers of Alaska This is a List of rivers in Alaska, which are at least fifth-order according to the Strahler method of stream classification, and an incomplete list of otherwise-notable rivers and streams. Alaska has more than 12,000 rivers, and thousands more st ... References External links * Rivers of Alaska Rivers of Yukon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGrath, Alaska
McGrath (''Tochak’'' in Upper Kuskokwim, ''Digenegh'' in Deg Xinag) is a city and village on the Kuskokwim River in Alaska, United States. The population was 301 at the 2020 census. Despite its small population, the village is an important transportation and economic hub for the area. History The Old Town McGrath site, across the river from present-day McGrath, was a meeting and trading place for Big River, Nikolai, Telida, and Lake Minchumina villagers. In 1904, Abraham Appel established a trading post in Old Town. In 1906, gold was discovered in the Innoko District, and in 1907, and at . Since McGrath was the northernmost point on the Kuskokwim River accessible by large riverboats, it became a regional supply center. A town was established at the site of Old McGrath in 1907, and was named for Peter McGrath, a local United States Marshal. The Iditarod Trail also contributed to McGrath's role as a supply center. From 1911 to 1920, hundreds of people walked and mushed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuskokwim River
The Kuskokwim River or Kusko River (Yup'ik: ''Kusquqvak''; Deg Xinag: ''Digenegh''; Upper Kuskokwim: ''Dichinanek' ''; russian: Кускоквим (''Kuskokvim'')) is a river, long, in Southwest Alaska in the United States. It is the ninth largest river in the United States by average discharge volume at its mouth and seventeenth largest by basin drainage area. The Kuskokwim River is the longest river system contained entirely within a single U.S. state. The river provides the principal drainage for an area of the remote Alaska Interior on the north and west side of the Alaska Range, flowing southwest into Kuskokwim Bay on the Bering Sea. The highest point in its watershed is Mount Russell. Except for its headwaters in the mountains, the river is broad and flat for its entire course, making it a useful transportation route for many types of watercraft, as well as road vehicles during the winter when it is frozen over. It is the longest free flowing river in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Range
The Alaska Range is a relatively narrow, 600-mile-long (950 km) mountain range in the southcentral region of the U.S. state of Alaska, from Lake Clark at its southwest endSources differ as to the exact delineation of the Alaska Range. ThBoard on Geographic Namesentry is inconsistent; part of it designates Iliamna Lake as the southwestern end, and part of the entry has the range ending at the Telaquana and Neacola Rivers. Other sources identify Lake Clark, in between those two, as the endpoint. This also means that the status of the Neacola Mountains is unclear: it is usually identified as the northernmost subrange of the Aleutian Range, but it could also be considered the southernmost part of the Alaska Range. to the White River in Canada's Yukon Territory in the southeast. The highest mountain in North America, Denali, is in the Alaska Range. It is part of the American Cordillera. The Alaska range is one of the higher ranges in the world after the Himalayas and the Andes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





