|
Ideal Observer Analysis
Ideal observer analysis is a method for investigating how information is processed in a perceptual system. It is also a basic principle that guides modern research in perception. The ''ideal observer'' is a theoretical system that performs a specific task in an optimal way. If there is uncertainty in the task, then perfect performance is impossible and the ideal observer will make errors. ''Ideal performance'' is the theoretical upper limit of performance. It is theoretically impossible for a real system to perform better than ideal. Typically, real systems are only capable of sub-ideal performance. This technique is useful for analyzing psychophysical data (see psychophysics). Definition Many definitions of this term have been offered. Geisler (2003) (slightly reworded): The central concept in ideal observer analysis is the ''ideal observer'', a theoretical device that performs a given task in an optimal fashion given the available information and some specified constrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptual System
A perceptual system is a computational system (biological or artificial) designed to make inferences about properties of a physical environment based on scenes. In this context, a scene is defined as sensory information that can flow from a physical environment into a computational system via sensory transduction. A sensory organ (biological or artificial) is used to capture this information. Therefore, a perceptual system must incorporate input from at least one sensory organ. Examples of perceptual systems include: * The visual system * The auditory system * The olfactory system * The somatosensory system * A bat's sonar/ echolocation system * A man-made light meter * A man-made motion detector Research in the field of perceptual systems focuses on computational aspects of perception. For this reason, there is significant overlap with neuroscience, sensor design, natural scene statistics, and computer science. References Further reading * {{cite book , author=Gibson, James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scene Statistics
Scene statistics is a discipline within the field of perception. It is concerned with the statistical regularities related to scenes. It is based on the premise that a perceptual system is designed to interpret scenes. Biological perceptual systems have evolved in response to physical properties of natural environments. Therefore natural scenes receive a great deal of attention. Natural scene statistics are useful for defining the behavior of an ideal observer in a natural task, typically by incorporating signal detection theory, information theory, or estimation theory Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such .... Within-domain versus across-domain Geisler (2008) distinguishes between four kinds of domains: (1) Physical environments, (2) Images/Scenes, (3) Neural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receiver Operating Characteristic
A receiver operating characteristic curve, or ROC curve, is a graph of a function, graphical plot that illustrates the performance of a binary classifier model (can be used for multi class classification as well) at varying threshold values. ROC analysis is commonly applied in the assessment of diagnostic test performance in clinical epidemiology. The ROC curve is the plot of the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR) at each threshold setting. The ROC can also be thought of as a plot of the statistical power as a function of the Type I Error of the decision rule (when the performance is calculated from just a sample of the population, it can be thought of as estimators of these quantities). The ROC curve is thus the sensitivity as a function of false positive rate. Given that the probability distributions for both true positive and false positive are known, the ROC curve is obtained as the cumulative distribution function (CDF, area under the probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
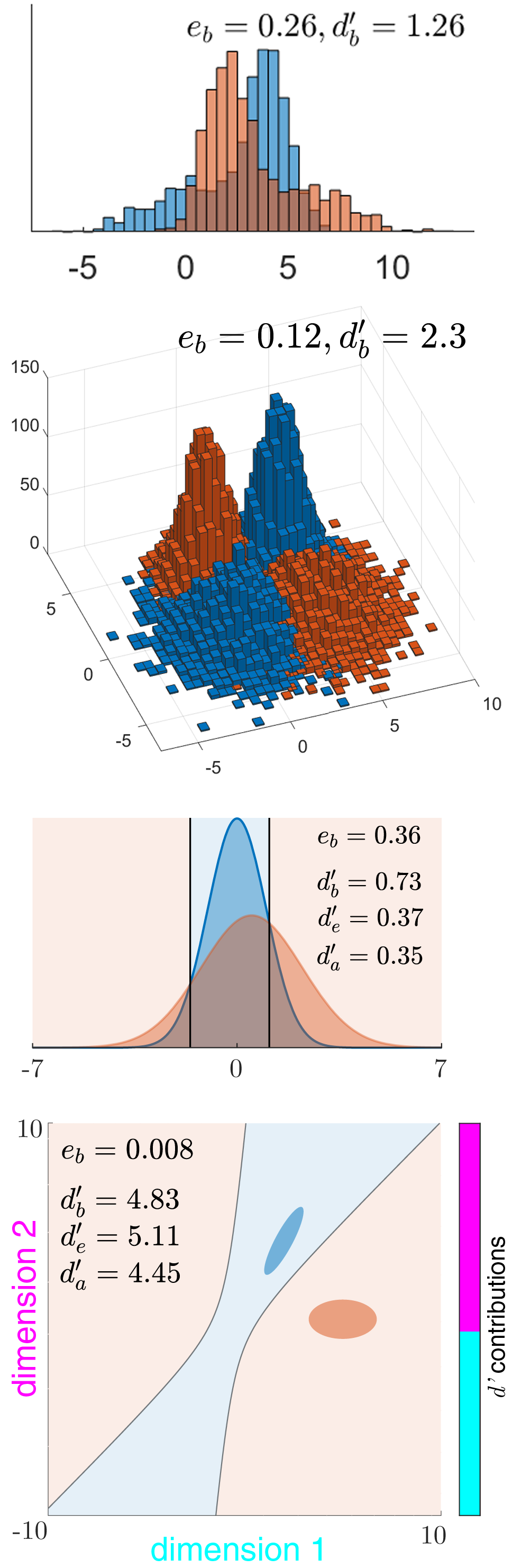
Sensitivity Index
The sensitivity index or discriminability index or detectability index is a dimensionless statistic used in signal detection theory. A higher index indicates that the signal can be more readily detected. Definition The discriminability index is the separation between the means of two distributions (typically the signal and the noise distributions), in units of the standard deviation. Equal variances/covariances For two univariate distributions a and b with the same standard deviation, it is denoted by d' ('dee-prime'): : d' = \frac. In higher dimensions, i.e. with two multivariate distributions with the same variance-covariance matrix \mathbf, (whose symmetric square-root, the standard deviation matrix, is \mathbf), this generalizes to the Mahalanobis distance between the two distributions: : d'=\sqrt = \lVert \mathbf^(\boldsymbol_a-\boldsymbol_b) \rVert = \lVert \boldsymbol_a-\boldsymbol_b \rVert /\sigma_, where \sigma_ = 1/ \lVert\mathbf^\boldsymbol\rVert is the 1d slice of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-alternative Forced Choice
Two-alternative forced choice (2AFC) is a method for measuring the sensitivity of a person or animal to some particular sensory input, stimulus, through that observer's pattern of choices and response times to two versions of the sensory input. For example, to determine a person's sensitivity to dim light, the observer would be presented with a series of trials in which a dim light was randomly either in the top or bottom of the display. After each trial, the observer responds "top" or "bottom". The observer is not allowed to say "I do not know", or "I am not sure", or "I did not see anything". In that sense the observer's choice is forced between the two alternatives. Both options can be presented concurrently (as in the above example) or sequentially in two intervals (also known as two-interval forced choice, 2IFC). For example, to determine sensitivity to a dim light in a two-interval forced choice procedure, an observer could be presented with series of trials comprising two su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confusion Matrix
In the field of machine learning and specifically the problem of statistical classification, a confusion matrix, also known as error matrix, is a specific table layout that allows visualization of the performance of an algorithm, typically a supervised learning one; in unsupervised learning it is usually called a matching matrix. Each row of the matrix represents the instances in an actual class while each column represents the instances in a predicted class, or vice versa – both variants are found in the literature. The diagonal of the matrix therefore represents all instances that are correctly predicted. The name stems from the fact that it makes it easy to see whether the system is confusing two classes (i.e. commonly mislabeling one as another). It is a special kind of contingency table, with two dimensions ("actual" and "predicted"), and identical sets of "classes" in both dimensions (each combination of dimension and class is a variable in the contingency table). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimation Theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the measured data. An ''estimator'' attempts to approximate the unknown parameters using the measurements. In estimation theory, two approaches are generally considered: * The probabilistic approach (described in this article) assumes that the measured data is random with probability distribution dependent on the parameters of interest * The set estimation, set-membership approach assumes that the measured data vector belongs to a set which depends on the parameter vector. Examples For example, it is desired to estimate the proportion of a population of voters who will vote for a particular candidate. That proportion is the parameter sought; the estimate is based on a small random sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detection Theory
Detection theory or signal detection theory is a means to measure the ability to differentiate between information-bearing patterns (called stimulus in living organisms, signal in machines) and random patterns that distract from the information (called noise, consisting of background stimuli and random activity of the detection machine and of the nervous system of the operator). In the field of electronics, signal recovery is the separation of such patterns from a disguising background. According to the theory, there are a number of determiners of how a detecting system will detect a signal, and where its threshold levels will be. The theory can explain how changing the threshold will affect the ability to discern, often exposing how adapted the system is to the task, purpose or goal at which it is aimed. When the detecting system is a human being, characteristics such as experience, expectations, physiological state (e.g. fatigue) and other factors can affect the threshold app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scene (perception)
In the field of perception, a scene is information that can flow from a physical environment into a perceptual system via sensory transduction. A perceptual system is designed to interpret scenes. Examples of scenes include * Still images * Binocular still images * Moving images (movies) * Binocular moving images (~ 3D movies) * Sounds of a local environment (audio recording Sound recording and reproduction is the electrical, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording t ...s) * Tactile properties of a local environment. A natural scene is a scene that a perceptual system would typically encounter in a natural mode of operation. Therefore, a very relevant area of research is natural scene statistics. References Perception {{psych-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Acoustical Society Of America
The ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America'' (JASA) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of acoustics. It is published by the Acoustical Society of America. The editor-in-chief is James F. Lynch (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution). ''JASA'' contains news items, book reviews, references to contemporary papers, reviews of acoustical patents, and standards news. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 2.1. History In 1929, the newly formed Acoustical Society of America Publication Committee began investigating how to start a journal. The first issue of the ''Journal of the Acoustical Society of America'' (JASA) was published in October 1929 and contained 8 papers. The cover featured the 1929 logo designed by Wallace Waterfall. In May 1932, publication of JASA was transferred to the American Institute of Physics (AIP). In 1957 the publication frequency of the journal went from bimonthly to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Validity
External validity is the validity of applying the conclusions of a scientific study outside the context of that study. In other words, it is the extent to which the results of a study can generalize or transport to other situations, people, stimuli, and times.Aronson, E., Wilson, T. D., Akert, R. M., & Fehr, B. (2007). Social psychology. (4 ed.). Toronto, ON: Pearson Education. Generalizability refers to the applicability of a predefined sample to a broader population while transportability refers to the applicability of one sample to another target population. In contrast, internal validity is the validity of conclusions drawn ''within'' the context of a particular study. Mathematical analysis of external validity concerns a determination of whether generalization across heterogeneous populations is feasible, and devising statistical and computational methods that produce valid generalizations. In establishing external validity, scholars tend to identify the "scope" of the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |