|
Ichirai HЕҚshi
Ichirai (дёҖжқҘ, died 1180) was a Japanese warrior monk who supported the Minamoto clan of samurai against their rivals, the Taira clan. Ichirai-hЕҚshi is best known for his part in the battle of Uji. He was fighting behind Tsutsui JЕҚmyЕҚ MeishЕ« Tsutsui no JЕҚmyЕҚ MeishЕ« (зӯ’дә•жө„еҰҷжҳҺз§Җ) was a warrior monk (''sЕҚhei'') from Mii-dera who fought alongside Minamoto no Yorimasa and his fellow monks at the Battle of Uji in 1180, defending the ByЕҚdЕҚ-in and Prince Mochihito from the Taira ... on the Uji bridge, but as the beams were so narrow he could not come alongside his ally. He is said to have leapt over the other monk, taken over the brunt of the fighting, and continued until he fell. References *Turnbull, Stephen. ''Warriors of Medieval Japan.'' Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2005 Japanese warrior monks 1180 deaths People of Heian-period Japan Heian period Buddhist clergy Year of birth unknown {{Japan-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SЕҚhei
were Buddhist warrior monks of both classical and feudal Japan. At certain points in history, they held considerable power, obliging the imperial and military governments to collaborate. The prominence of the ''sЕҚhei'' rose in parallel with the ascendancy of the Tendai school's influence between the 10th and 17th centuries. The warriors protected land and intimidated rival schools of Buddhism, becoming a significant factor in the spread of Buddhism and the development of different schools during the Kamakura period. The ''sЕҚhei'' shared many similarities with the European lay brothers, members of a monastic order who might not have been ordained. Much like the Teutonic Order, the warrior monks of Holy Roman Empire, and the crusading orders, ''sЕҚhei'' did not operate as individuals, or even as members of small, individual temples, but rather as warriors in a large extended brotherhood or monastic order. The home temple of a ''sЕҚhei'' monastic order might have had severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto Clan
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were excluded from the line of succession and demoted into the ranks of the nobility from 1192 to 1333. The practice was most prevalent during the Heian period (794вҖ“1185 AD), although its last occurrence was during the Sengoku period. The Taira were another such offshoot of the imperial dynasty, making both clans distant relatives. The Minamoto clan is also called the , or less frequently, the , using the on'yomi reading for Minamoto. The Minamoto were one of four great clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian periodвҖ”the other three were the Fujiwara, the Taira, and the Tachibana. History The first emperor to grant the surname Minamoto was Minamoto no Makoto, seventh son of Emperor Saga. The most prominent of the several Minamoto families, the Seiwa Genji, descended from Minamoto no Tsunemoto (897вҖ“961), a grandson of Emperor Seiwa. Tsunemoto went to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They had high prestige and special privileges such as wearing two swords and ''Kiri-sute gomen'' (right to kill anyone of a lower class in certain situations). They cultivated the '' bushido'' codes of martial virtues, indifference to pain, and unflinching loyalty, engaging in many local battles. Though they had predecessors in earlier military and administrative officers, the samurai truly emerged during the Kamakura shogunate, ruling from 1185 to 1333. They became the ruling political class, with significant power but also significant responsibility. During the 13th century, the samurai proved themselves as adept warriors against the invading Mongols. During the peaceful Edo period (1603 to 1868), they became the stewards and chamberlains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira Clan
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history вҖ“ the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the emperor they descended from: Kanmu Heishi, NinmyЕҚ Heishi, Montoku Heishi, and KЕҚkЕҚ Heishi. The clan is commonly referred to as or , using the character's On'yomi for ''Taira'', while means " clan", and is used as a suffix for "extended family". History Along with the Minamoto, Taira was one of the honorary surnames given by the emperors of the Heian Period (794вҖ“1185 CE) to their children and grandchildren who were not considered eligible for the throne. The clan was founded when the Imperial Court grew too large, and the emperor ordered that the descendants of previous emperors from several generations ago would no longer be princes, but would instead be given noble surnames and ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
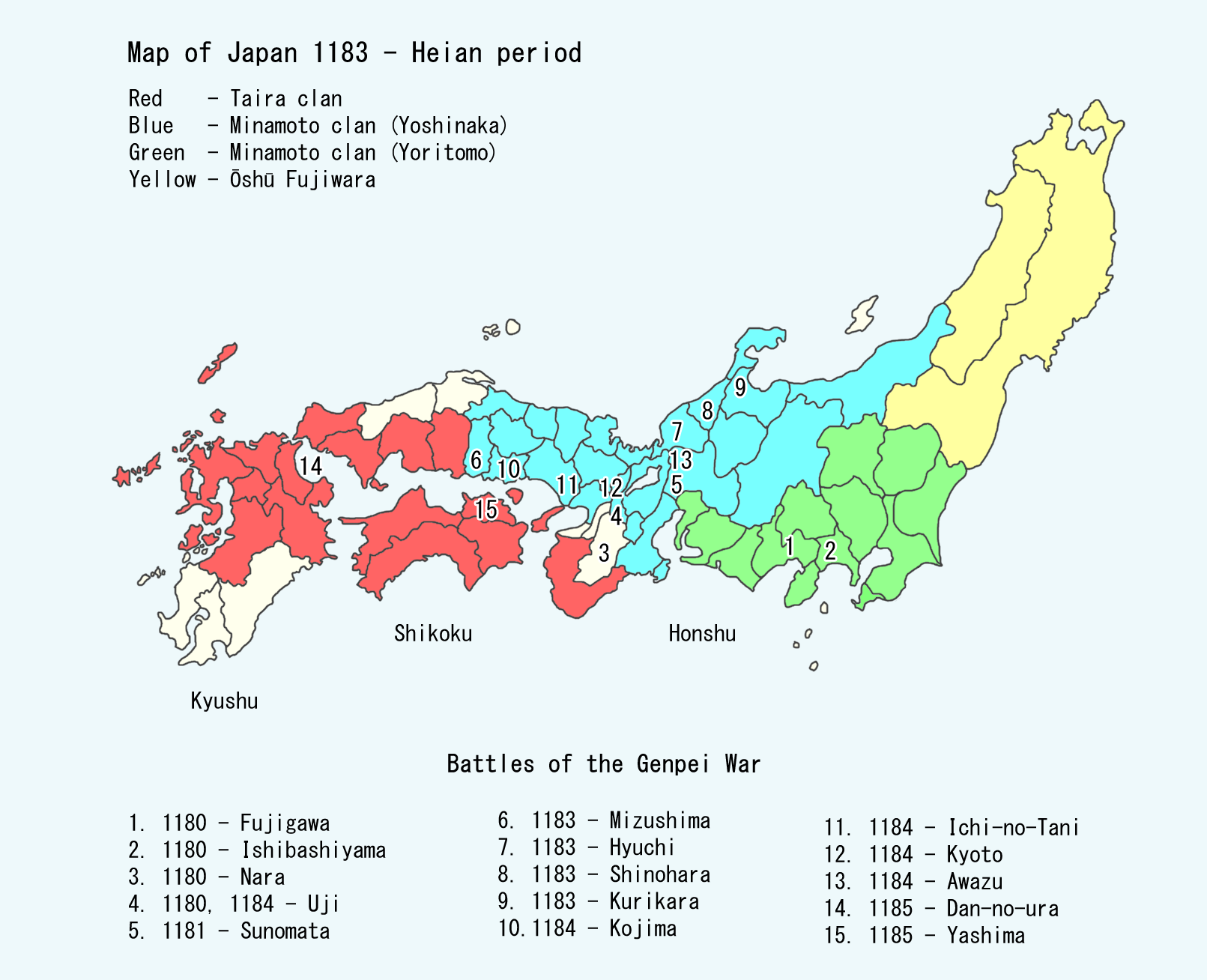
Battle Of Uji (1180)
The first battle of Uji is famous and important for having opened the Genpei War. In early 1180, Prince Mochihito, the Minamoto Clan's favored claimant to the Imperial Throne, was chased by Taira forces to the Mii-dera, a temple just outside Kyoto. Due to the interference of a Mii-dera monk with Taira sympathies, the Minamoto army arrived too late to help defend the temple. Minamoto no Yorimasa and Prince Mochihito, along with a force of about fifteen hundred men including the warrior monks of Mii-dera and the Watanabe clan, fled south towards Nara. They crossed the Uji River, just outside the ByЕҚdЕҚ-in, and tore up the planks of the bridge behind them to prevent the Taira from following. Three warrior monks in particular are named in the ''Heike Monogatari'': Gochi-in no Tajima, Tsutsui JЕҚmyЕҚ MeishЕ«, and Ichirai HЕҚshi. These three, along with the other monks of Mii-dera, fought with bow and arrow, a variety of swords, daggers and naginata. As for the Taira troops, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsutsui JЕҚmyЕҚ MeishЕ«
Tsutsui no JЕҚmyЕҚ MeishЕ« (зӯ’дә•жө„еҰҷжҳҺз§Җ) was a warrior monk (''sЕҚhei'') from Mii-dera who fought alongside Minamoto no Yorimasa and his fellow monks at the Battle of Uji in 1180, defending the ByЕҚdЕҚ-in and Prince Mochihito from the Taira clan. Later, in the same account, Gochi-in no Tajima is replaced on the bridge by his comrade, Tsutsui. Standing upon the broken bridge of Uji, Kyoto, Tsutsui fought off the Taira samurai with bow and arrow, ''naginata'', sword, and dagger. According to ''The Tale of the Heike is an epic poetry, epic account compiled prior to 1330 of the struggle between the Taira clan and Minamoto clan for control of Japan at the end of the 12th century in the Genpei War (1180вҖ“1185). Heike () refers to the Taira (), ''hei'' being ...'': References *Turnbull, Stephen. ''Japanese Warrior Monks AD 949вҖ“1603.'' Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2003. {{DEFAULTSORT:Tsutsui, Jomyo Meishu Japanese warrior monks Heian period Buddhist clergy People of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Warrior Monks
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1180 Deaths , synthetic chemical element with atomic number 118
{{Numberdis ...
118 may refer to: *118 (number) *AD 118 *118 BC *118 (TV series) *118 (film) *118 (Tees) Corps Engineer Regiment *118 (Tees) Field Squadron, Royal Engineers See also *11/8 (other) *Oganesson Oganesson is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Og and atomic number 118. It was first synthesized in 2002 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, near Moscow, Russia, by a joint team of Russian and American scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of Heian-period Japan
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Period Buddhist Clergy
The Japanese word Heian (е№іе®ү, lit. "peace") may refer to: * Heian period, an era of Japanese history * Heian-kyЕҚ, the Heian-period capital of Japan that has become the present-day city of Kyoto * Heian series, a group of karate kata (forms) * Heian Shrine, a large shrine in the city of Kyoto * "Heian", a song from the 2016 Momus album ''Scobberlotchers'' See also * Ping'an (other), the Chinese pinyin transliteration of е№іе®ү * Pyongan, the Korean hanja transliteration of е№іе®ү {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)