|
Ichibengops
''Ichibengops'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids known from the type species ''Ichibengops munyamadziensis'', which lived in what is now Zambia during the Late Permian. ''Ichibengops'' was named in 2015 on the basis of fossils found in the Wuchiapingian-age Madumabisa Mudstone Formation in the Luangwa Basin. Therocephalians have been known from the Luangwa Basin for decades, yet ''Ichibengops'' was the first endemic Zambian therocephalian to have been described in detail. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that it is a basal member of the clade Eutherocephalia, lying just outside a clade containing hofmeyriids, whaitsiids, and baurioids. ''Ichibengops'' is the sister taxon of the Russian therocephalian ''Chthonosaurus''; together they form one of several known African-Russian sister taxon pairs of eutherocephalians, which indicate that eutherocephalians could freely disperse across most of Pangea during the Late Permian. Like the fellow therocephalian ''Euchambersia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therocephalia Genera
Therocephalia is an extinct suborder of eutheriodont therapsids (mammals and their close relatives) from the Permian and Triassic. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals. This relationship takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. The fossils of therocephalians are numerous in the Karoo of South Africa, but have also been found in Russia, China, Tanzania, Zambia, and Antarctica. Early therocephalian fossils discovered in Middle Permian deposits of South Africa support a Gondwanan origin for the group, which seems to have spread quickly across Earth. Although almost every therocephalian lineage ended during the great Permian–Triassic extinction event, a few represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct suborder of eutheriodont therapsids (mammals and their close relatives) from the Permian and Triassic. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their teeth, suggest that they were carnivores. Like other non-mammalian synapsids, therocephalians were once described as "mammal-like reptiles". Therocephalia is the group most closely related to the cynodonts, which gave rise to the mammals. This relationship takes evidence in a variety of skeletal features. The fossils of therocephalians are numerous in the Karoo of South Africa, but have also been found in Russia, China, Tanzania, Zambia, and Antarctica. Early therocephalian fossils discovered in Middle Permian deposits of South Africa support a Gondwanan origin for the group, which seems to have spread quickly across Earth. Although almost every therocephalian lineage ended during the great Permian–Triassic extinction event, a few represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutherocephalia
Eutherocephalia ("true beast head") is an extinct clade of advanced therocephalian therapsids. Eutherocephalians are distinguished from the lycosuchids and scylacosaurids, two early therocephalian families. While lycosuchids and scyalosaurids became extinct by the end of the Permian period, eutherocephalians survived the Permian–Triassic extinction event. The group eventually became extinct in the Middle Triassic. Characteristics The Eutherocephalians evolved several mammal-like traits through convergent evolution with Cynodontia. Among those traits were the loss of palatine teeth and the reduction of the parietal eye. The latter organ is instrumental in thermoregulation among lizards and snakes, indicating both eutherocephalians and cynodonts were evolving toward a more active, homeothermic lifestyle, though the eye never fully disappeared in the eutherocephalians. Classification The clade Eutherocephalia contains the majority of therocephalians, yet the phylogenetic rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutherocephalians
Eutherocephalia ("true beast head") is an extinct clade of advanced therocephalian therapsids. Eutherocephalians are distinguished from the lycosuchids and scylacosaurids, two early therocephalian families. While lycosuchids and scyalosaurids became extinct by the end of the Permian period, eutherocephalians survived the Permian–Triassic extinction event. The group eventually became extinct in the Middle Triassic. Characteristics The Eutherocephalians evolved several mammal-like traits through convergent evolution with Cynodontia. Among those traits were the loss of palatine teeth and the reduction of the parietal eye. The latter organ is instrumental in thermoregulation among lizards and snakes, indicating both eutherocephalians and cynodonts were evolving toward a more active, homeothermic lifestyle, though the eye never fully disappeared in the eutherocephalians. Classification The clade Eutherocephalia contains the majority of therocephalians, yet the phylogenetic rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euchambersia
''Euchambersia'' is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids that lived during the Late Permian in what is now South Africa and China. The genus contains two species. The type species ''E. mirabilis'' was named by paleontologist Robert Broom in 1931 from a skull missing the lower jaw. A second skull, belonging to a probably immature individual, was later described. In 2022, a second species, ''E. liuyudongi'', was named by Jun Liu and Fernando Abdala from a well-preserved skull. It is a member of the family Akidnognathidae, which historically has also been referred by as the synonymous Euchambersiidae (named after ''Euchambersia''). ''Euchambersia'' was a small and short-snouted therocephalian, possessing large canines as is typical of the group. However, it is notable among therocephalians for possessing ridges on its canines and a large indentation in the side of the skull. It has been proposed that these structures supported a venom delivery mechanism. If this statement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofmeyriid
Hofmeyriidae is a family of therocephalian therapsids. It includes the genus ''Ictidostoma''. References External links Hofmeyriidaein the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Eutherocephalians Permian first appearances Permian extinctions Prehistoric therapsid families {{paleo-Therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopingian Synapsids Of Africa
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic. The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal terms late Permian or upper Permian. The name was introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1931 and derives from Leping, Jiangxi in China. It consists of two stages/ages. The earlier is the Wuchiapingian and the later is the Changhsingian. The International Chronostratigraphic Chart (v2018/07) provides a numerical age of 259.1 ±0.5 Ma. If a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) has been approved, the lower boundary of the earliest stage determines numerical age of an epoch. The GSSP for the Wuchiapingian has a numerical age of 259.8 ± 0.4 Ma. Evidence from Milankovitch cycles suggests that the length of an Earth day during this epoch was approximately 22 hours. The Lopingian ended with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Daily
''Science Daily'' is an American website launched in 1995 that aggregates press releases and publishes lightly edited press releases (a practice called churnalism) about science, similar to Phys.org and EurekAlert!. The site was founded by married couple Dan and Michele Hogan in 1995; Dan Hogan formerly worked in the public affairs department of Jackson Laboratory writing press releases. The site makes money from selling advertisements. As of 2010, the site said that it had grown "from a two-person operation to a full-fledged news business with worldwide contributors". At the time, it was run out of the Hogans' home, had no reporters, and only reprinted press releases. In 2012, Quantcast Quantcast is an American technology company, founded in 2006, that specializes in AI-driven real-time advertising, audience insights and measurement. It has offices in the United States, Canada, Australia, Singapore, United Kingdom, Ireland, Fran ... ranked it at 614 with 2.6 million U.S. vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
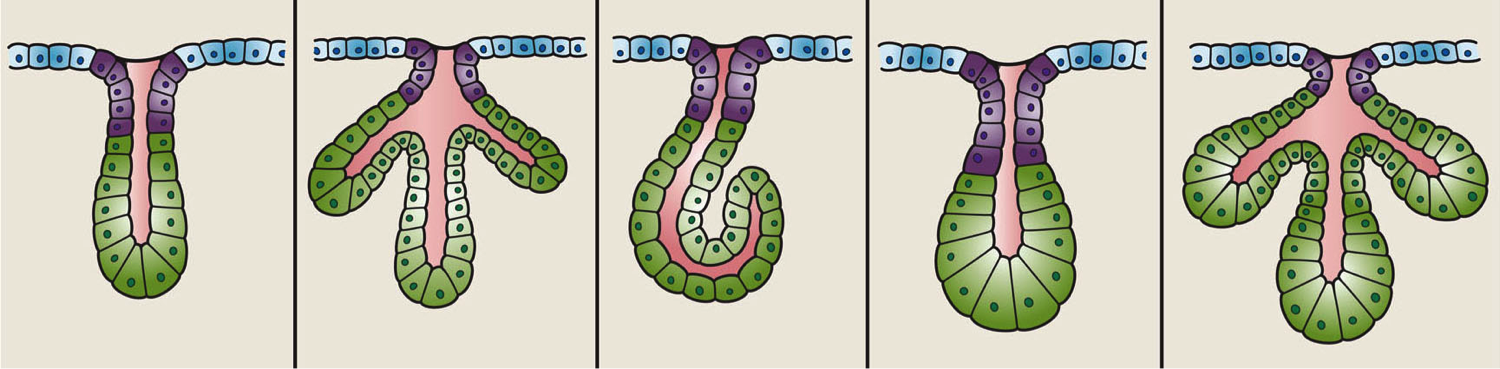
Glands
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Vertebrate Paleontology
The ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1980 by Jiri Zidek (University of Oklahoma). It covers all aspects of vertebrate paleontology, including vertebrate origins, evolution, functional morphology, taxonomy, biostratigraphy, paleoecology, paleobiogeography, and paleoanthropology. The journal is published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.190. References External links * Paleontology journals Publications established in 1980 Quarterly journals English-language journals Taylor & Francis academic journals {{paleontology-jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and '' Gaia'' or Gaea (, " Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents once formed a contiguous land mass was hypothesised, with corroborating evidence, by Alfred Wegener, the originator of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chthonosaurus
''Chthonosaurus'' is an extinct genus of eutherocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian Kutulukskaya Formation of Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the .... The type species ''Chthonosaurus velocidens'' was named in 1955. References Eutherocephalians Therocephalia genera Lopingian synapsids of Europe Fossils of Russia Fossil taxa described in 1955 {{paleo-therapsid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |