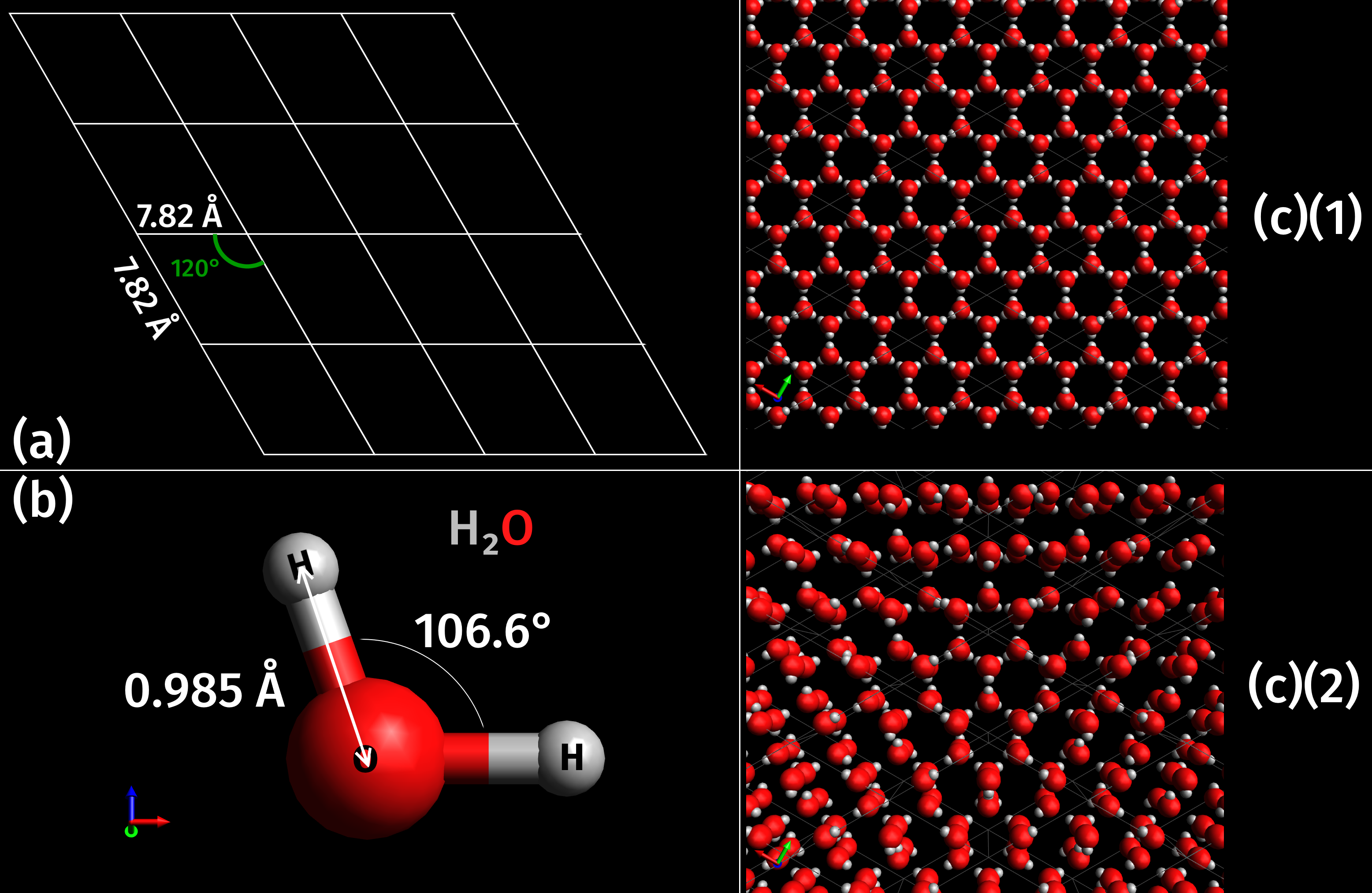
|
Iceboxes
An icebox (also called a cold closet) is a compact non-mechanical refrigerator which was a common early-twentieth-century kitchen appliance before the development of safely powered refrigeration devices. Before the development of electric refrigerators, iceboxes were referred to by the public as "refrigerators". Only after the invention of the modern Electricity, electric refrigerator did early non-electric refrigerators become known as iceboxes. The terms ''ice box'' and ''refrigerator'' were used interchangeably in advertising as long ago as 1848. Origin The first recorded use of refrigeration technology dates back to 1775 BC in the Sumerian city of Terqa. It was there that the region's King, Zimri-Lim, Zimri-lim, began the construction of an elaborate Ice house (building), ice house fitted with a sophisticated drainage system and shallow pools to freeze water in the night. Using ice for cooling and preservation was not new at that time; the ice house was an introductory mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerator
A refrigerator, commonly shortened to fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermal insulation, thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential Food preservation, food storage technique around the world. The low temperature reduces the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator lowers the rate of Food spoilage, spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable food storage is .Keep your fridge-freezer clean and ice-free ''BBC''. 30 April 2008 A freezer is a specialized refrigerator, or portion of a refrigerator, that maintains its contents’ temperature below the freezing point of water. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a common househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Box Used In Cafes Of Paris In Late 1800s
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. Virtually all of the ice on Earth is of a hexagonal crystalline structure denoted as ''ice Ih'' (spoken as "ice one h"). Depending on temperature and pressure, at least nineteen phases ( packing geometries) can exist. The most common phase transition to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below (, ) at standard atmospheric pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching), up to three types of amorphous ice can form. Interstellar ice is overwhelmingly low-density amorphous ice (LDA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Cooler (cabinet)
A California cooler, also known as a cooler cabinet, is a type of cabinet used for the cool storage of food items that was popular in the western United States, in the late 19th and early 20th century. Construction The California cooler is constructed simply as an interior cabinet with slatted or screened shelves. Vents near the top and bottom allow outside air to circulate by the principle of natural convection. This results in convective cooling, which keeps perishable food items fresh. The outside vents are separated from the outside by a screen, preventing the incursion of insects, and downward slanting slats shut out rain. Often on a wall away from sun, they tend to be located near where food is prepared, such as in the kitchen. Modifications to work in more variable climates, such as a trap door to selectively draw air from a cellar, are possible. Usage These coolers are most commonly found on the west coast of the United States because they function particularly well in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pot-in-pot Refrigerator
A pot-in-pot refrigerator, clay pot cooler or zeer () is an evaporative cooling refrigeration device which does not use electricity. It uses a porous outer clay pot (lined with wet sand) containing an inner pot (which can be ceramic glaze, glazed to prevent penetration by the liquid) within which the food is placed. The evaporation of the outer liquid draws heat from the inner pot. The device can cool any substance, and requires only a flow of relatively dry air and a source of water. History Many clay pots from around 3000 BC were discovered in the Indus Valley civilization and are considered to have been used for cooling as well as storing water. The pots are similar to the present-day ''ghara'' and ''Matki (earthen pot), matki'' used in India and Pakistan. There is evidence that evaporative cooling may have been used in North Africa as early as the Old Kingdom of Egypt, circa 2500 BC. Frescoes show slaves fanning water jars, which would increase air flow around porous jar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meat Safe
A pie safe, also called a pie chest, pie cupboard, kitchen safe, and meat safe, is a piece of furniture designed to store pies and other food items. This was a normal household item before iceboxes came into regular use, and it was an important part of the American household starting in the 1700s and continuing through the 1800s. The pie safe was used to store not only pies, but bread, meat, and other perishables as well, to protect them from insects and vermin. Origins The origin of the pie safe can be traced back to the early 1700s in America. It was likely introduced by German immigrants to the country, who typically settled in the Pennsylvania area. These people later become known as the Pennsylvania Dutch. The pie safe was introduced to protect perishables and other ingredients from vermin and pests. Their popularity meant that most American homes during this period possessed a pie safe, or similar regional variation. Design A common pie safe is made of wood, is around th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolgardie Safe
The Coolgardie safe is a low-tech food storage unit, using evaporative cooling to prolong the life of whatever edibles are kept in it. It applies the basic principle of heat transfer which occurs during evaporation of water (see latent heat and heat of evaporation). It was named after the place where it was invented – the small mining town of Coolgardie, Western Australia, near Kalgoorlie-Boulder. History Coolgardie was the site of a gold rush in the early 1890s, before the Kalgoorlie-Boulder gold rush. For the prospectors who had rushed here to find their fortune, one challenge was to extend the life of their perishable foods – hence the invention of the Coolgardie safe. The safe was invented in the late 1890s by Arthur Patrick McCormick, who used the same principle as explorers and travellers in the Outback used to cool their canvas water bags: when the canvas bag is wet the fibres expand and it holds water. Some water seeps out and evaporates. It is most effective when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooler
A cooler, portable ice chest, ice box, cool box, chilly bin (in New Zealand), or esky (Australia) is an insulated box used to keep food or drink cool. Ice cubes are most commonly placed in it to help the contents inside stay cool. Ice packs are sometimes used, as they either contain the melting water inside or have a gel sealed inside that stays cold longer than plain ice (absorbing heat as it changes phase). Coolers are often taken on picnics and on vacation or holidays. When summers are hot, they may also be used just to get cold groceries home from the store, such as keeping ice cream from melting in a sizzling automobile. Even without adding ice, this can be helpful, particularly if the trip home will be lengthy. Some coolers have built-in cupholders in the lid. They are usually made with interior and exterior shells of plastic, with a hard foam in between. They come in sizes from small personal ones to large family ones with wheels. Disposable ones are made solely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofluorocarbon
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are synthetic organic compounds that contain fluorine and hydrogen atoms, and are the most common type of organofluorine compounds. Most are gases at room temperature and pressure. They are frequently used in air conditioning and as refrigerants; R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane) is one of the most commonly used HFC refrigerants. In order to aid the recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer, HFCs were adopted to replace the more potent chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) such as R-12, which were phased out from use by the Montreal Protocol, and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) such as R-21 which are presently being phased out. HFCs are also used in insulating foams, aerosol propellants, as solvents and for fire protection. HFCs may not harm the ozone layer as much as the compounds they replace, but they still contribute to global warming – with some like trifluoromethane (CHF3 or R-23) having 11,700 times the warming potential of carbon dioxide. HFC atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. The most common example of a CFC is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12). R-12, also commonly called Freon, is used as a refrigerant. Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), gaseous fire suppression systems, and solvents. As a result of CFCs contributing to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) including R-410A, R-134a and R-1234yf. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbons in CFCs bond with tetrahedral symmetry. Because the fluorine and chlorine atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. The most common example of a CFC is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12). R-12, also commonly called Freon, is used as a refrigerant. Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), gaseous fire suppression systems, and solvents. As a result of CFCs contributing to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) including R-410A, R-134a and 2,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene, R-1234yf. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbons in CFCs bond with tetrahe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |