|
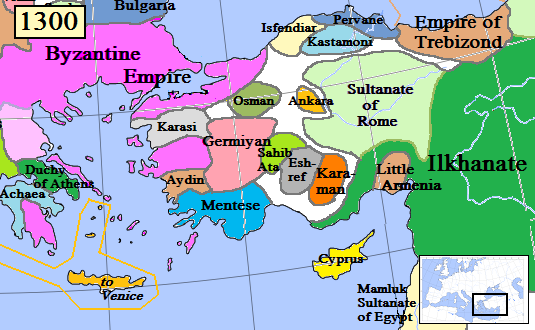
Ibrahim I Of Karaman
Ibrahim I, a.k.a. Bedrettin Ibrahim , was a bey of the Karamanids, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 14th century. His father was Mahmut Bey. His elder brother Musa had succeeded Mahmut in 1312.Prof. Yaşar Yüce-Prof. Ali Sevim: ''Türkiye tarihi Cilt I'', AKDTYKTTK Yayınları, İstanbul, 1991 p 245 But soon Ibrahim laid claim to throne and rebelled in 1318. Although the details of the civil war are not known, according to Ibn Battuta, the famous Arabian traveller who acted as Ibrahim's envoy to Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt, he won the throne with the help of Mamluks. Between 1332 and 1340 he abdicated on behalf of his brother Halil Halil is a common Turkish male given name. It is equivalent to the Arabic given name and surname Khalil or its variant Khaleel. Notable persons with the name include: * Halil Akbunar (born 1993), Turkish footballer * Halil Akkaş (born 1983), .... Upon Halil's death however, he resumed his former title. His death date is not certain. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karamanids
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the middle 1300s until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sofi, Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (Caucasus), Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of The Mongol Invasions, the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu and others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jones-Williams (New York: Taplinger, 1968), pp. 281–2. which participated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish People
The Turkish people, or simply the Turks ( tr, Türkler), are the world's largest Turkic ethnic group; they speak various dialects of the Turkish language and form a majority in Turkey and Northern Cyprus. In addition, centuries-old ethnic Turkish communities still live across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. Article 66 of the Turkish Constitution defines a "Turk" as: "Anyone who is bound to the Turkish state through the bond of citizenship." While the legal use of the term "Turkish" as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition, the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70 to 75 percent) are of Turkish ethnicity. The vast majority of Turks are Muslims and follow the Sunni and Alevi faith. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups. In particular, the culture of the Anatolian Turks in Asia Minor has underlied and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmut Of Karaman
Mahmut of Karaman was a bey of Karaman Beylik, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 14th century. His father was Karaman Bey, who succeeded his elder brother Güneri in 1300. Although he is known to have participated in the campaign to Alaiye during Güneri's reign, the details of his reign are not known. After the death of Hethum II in 1307, he took advantage of the weakened Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia and captured some of their territories. But when Seljuk sultan Mesud II died in 1308, he turned back and saw his chance to capture Konya, the Seljuk capital. He died in 1312. His tomb is in village at |
Musa Of Karaman
Musa of Karaman, a.k.a. Hacı Sufi Burhanettin Musa, was a bey of Karaman Beylik, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 14th century. His father was Mahmut Bey. He succeeded his father in 1312.Prof. Yaşar Yüce-Prof. Ali Sevim: ''Türkiye tarihi Cilt I'', AKDTYKTTK Yayınları, İstanbul, 1991 p 244 Although he appointed his brother Yahşi as the governor of Konya, the Seljuk capital, Emir Coban, the Mongol commander, captured the city and Musa had to be contended with the former possessions of his beylik. However, he even lost Karaman, his capital city (ancient Larende) to his rebelling brother İbrahim, who was backed by the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt. According to Ibn Batuta, in 1332 he was ruling only in Ermenek. But in 1352, after a chaos period in the beylik, he was invited to Karaman, where he ruled till 1356. In his last days, he went to battle with the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim world. He travelled more than any other explorer in pre-modern history, totalling around , surpassing Zheng He with about and Marco Polo with . Over a period of thirty years, Ibn Battuta visited most of southern Eurasia, including Central Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, China, and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, he dictated an account of his journeys, titled ''A Gift to Those Who Contemplate the Wonders of Cities and the Marvels of Travelling'', but commonly known as ''The Rihla''. Name Ibn Battuta is a patronymic literally meaning "son of the duckling". His most common full name is given as Kunya (Arabic), Abu Abdullah (name), Abdullah Muhammad (name), Muhammad ibn Battuta. In his travel literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamluk Sultanate Of Egypt
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16th centuries. It was ruled by a military caste of mamluks (manumitted slave soldiers) headed by the sultan. The Abbasid caliphs were the nominal sovereigns. The sultanate was established with the overthrow of the Ayyubid dynasty in Egypt in 1250 and was conquered by the Ottoman Empire in 1517. Mamluk history is generally divided into the Turkic or Bahri period (1250–1382) and the Circassian or Burji period (1382–1517), called after the predominant ethnicity or corps of the ruling Mamluks during these respective eras.Levanoni 1995, p. 17. The first rulers of the sultanate hailed from the mamluk regiments of the Ayyubid sultan as-Salih Ayyub (), usurping power from his successor in 1250. The Mamluks under Sultan Qutuz and Baybars rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halil Of Karaman
Halil, a.k.a. Alaattin Halil, was a bey of Karaman Beylik, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 14th century. His father was Mahmut Bey. He succeeded his elder brothers Musa and İbrahim in 1332. He wasn't active in military campaigns. But he commissioned some mosques and other social buildings in Ermenek Ermenek is a town and district of Karaman Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. As ancient Germanicopolis (in Isauria; has namesakes), a former bishopric, it remains a Latin Catholic titular see. The district forms the core of the plate ... during his reign. He died in 1340.Prof. Yaşar Yüce-Prof. Ali Sevim: ''Türkiye tarihi Cilt I'', AKDTYKTTK Yayınları, İstanbul, 1991 p 245 References Karamanids 1340 deaths 14th-century rulers in Asia Year of birth unknown Ethnic Afshar people {{Turkey-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Kingdom Of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, Կիլիկիայի հայկական իշխանութիւն), was an Armenians, Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian refugees fleeing the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk invasion of Armenia., pp. 630–631. Located outside the Armenian Highlands and distinct from the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia of classical antiquity, antiquity, it was centered in the Cilicia region northwest of the Gulf of Alexandretta. The kingdom had its origins in the principality founded c. 1080 by the Rubenid dynasty, an alleged offshoot of the larger Bagratuni dynasty, which at various times had held the throne of Armenia. Their capital was originally at Tarsus (city), Tarsus, and later became Sis (ancient city), Sis. Cilicia wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmet Of Karaman
Ahmet of Karaman, was a short term bey of Karaman Beylik, a Turkish principality in Anatolia in the 14th century. He succeeded his father İbrahim Bey. But his succession date is not known. According to one source, he fell during a battle against Mongols The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ... in 1350.Prof. Yaşar Yüce-Prof. Ali Sevim: ''Türkiye tarihi Cilt I'', AKDTYKTTK Yayınları, İstanbul, 1991 p 245 References Karamanids 1350 deaths Year of birth unknown 14th-century monarchs in the Middle East Ethnic Afshar people {{turkey-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1350 Deaths
135 may refer to: *135 (number) * AD 135 * 135 BC *135 film 135 film, more popularly referred to as 35 mm film or 35 mm, is a format of photographic film used for still photography. It is a film with a film gauge of loaded into a standardized type of magazine – also referred to as a casse ..., better known as 35 mm film, is a format of photographic film used for still photography * 135 (New Jersey bus) {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |