|
IRT Lexington Avenue Line
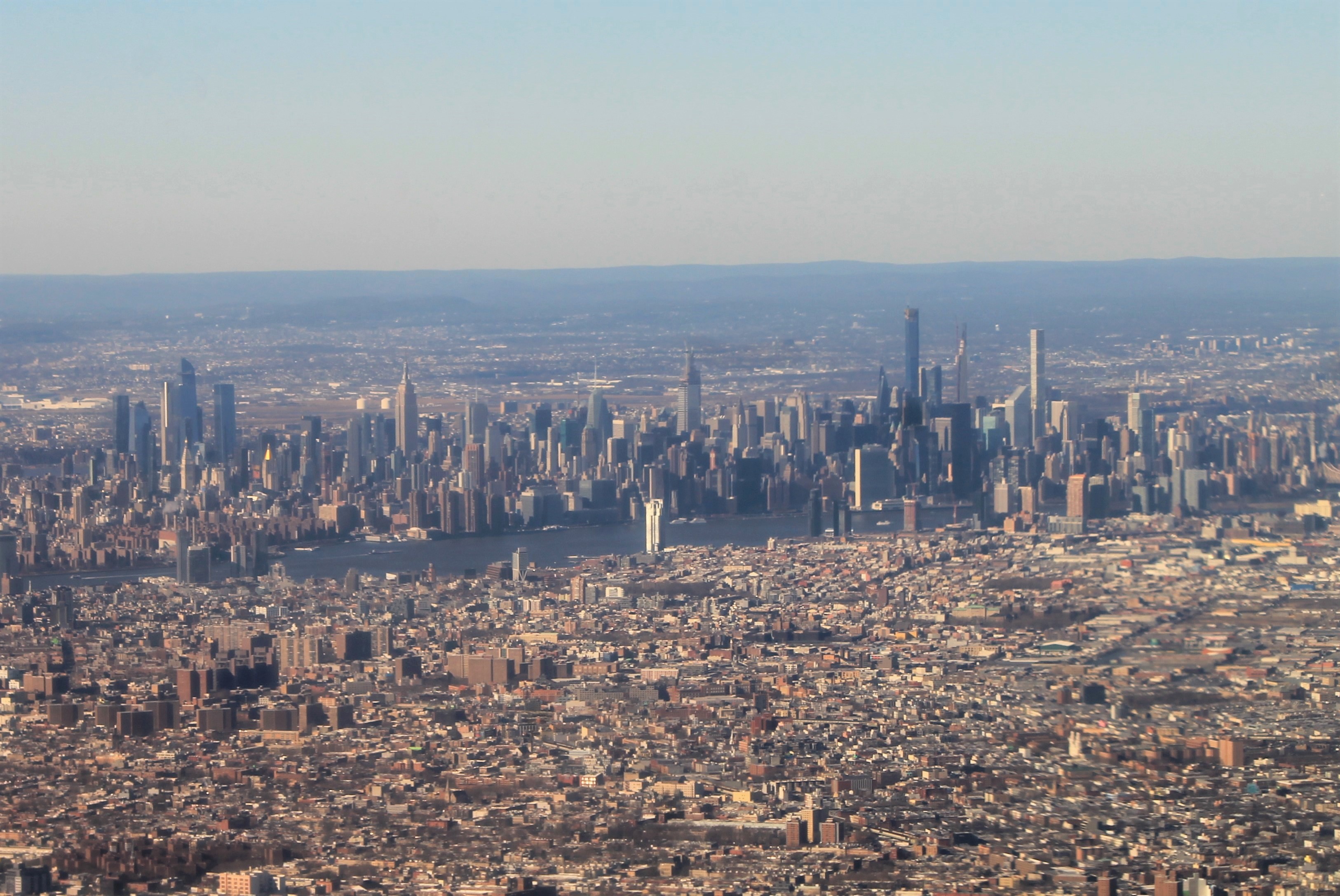
The IRT Lexington Avenue Line (also known as the IRT East Side Line and the IRT Lexington–Fourth Avenue Line) is one of the lines of the A Division of the New York City Subway, stretching from Lower Manhattan north to 125th Street in East Harlem. The line is served by the . The line was constructed in two main portions by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT), a private operator. The first portion, from City Hall north to 42nd Street, was opened between 1904 and 1908, and is part of the first subway line in the city. The original subway turned west across 42nd Street at the Grand Central station, then went north at Broadway, serving the present-day IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line. The second portion of the line, north of 42nd Street, was constructed as part of the Dual Contracts, which were signed between the IRT; the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company, via a subsidiary; and the City of New York. For decades, the Lexington Avenue Line was the only line in Manhattan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 (New York City Subway Service)
The 4 Lexington Avenue Express is a rapid transit service in the A Division of the New York City Subway. Its route emblem, or "bullet", is colored since it uses the IRT Lexington Avenue Line in Manhattan. The 4 operates at all times. Daytime service operates between Woodlawn in the Bronx and Utica Avenue in Crown Heights, Brooklyn, via the IRT Jerome Avenue Line in the Bronx, express via the Lexington Avenue Line in Manhattan, and the IRT Eastern Parkway Line in Brooklyn; limited rush hour service, as well as late night service, is extended beyond Utica Avenue to/from New Lots Avenue in East New York, Brooklyn via the IRT New Lots Line. During rush hours in the peak direction, 4 trains skip 138th Street–Grand Concourse. Late night service makes all stops except for Hoyt Street. For up to an hour after evening events that are held at Yankee Stadium, a special downtown-only express service runs between and . Until 1983, rush hour 4 trains originated and terminated at Fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Hall (IRT Lexington Avenue Line)
The City Hall station, also known as City Hall Loop, was a terminal station on the IRT Lexington Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. It was under City Hall Park next to New York City Hall in Civic Center, Manhattan. The City Hall station was constructed for the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) as the southern terminal of the city's first subway line, which was approved in 1900. Construction of the segment of the line that includes the City Hall station started on September 12 of the same year. The station opened on October 27, 1904, as one of the original 28 stations of the New York City Subway. As ridership grew, it was deemed infeasible to lengthen the original platform to accommodate ten-car trains. The station was closed on December 31, 1945, because of its proximity to the Brooklyn Bridge station. The City Hall station, with its single track and curved side platform, was the showpiece of the original IRT subway. The single platform and mezzanine feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MBTA Subway
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates rapid transit (heavy rail), light rail, and bus rapid transit services in the Boston metropolitan area, collectively referred to as the rapid transit, subway, or the T system. The color-branded lines consist of three heavy rail lines (Red, Orange, and Blue), one branched light rail system (Green), and a short light rail line (the Ashmont–Mattapan High-Speed Line, colored as part of the Red Line). All except the Ashmont–Mattapan line operate in tunnels in the downtown area, but no route operates entirely underground, and only 31 out of the system's 147 stations are located underground. The five branches of the Silver Line bus rapid transit network are also shown as part of the rapid transit system. Three branches operate underground and charge rapid transit fares; two branches operate entirely on the surface and charge lower bus fares. In , the heavy rail lines had rides, or about per weekday in , and compris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago 'L'
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Area Rapid Transit
Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) is a rapid transit system serving the San Francisco Bay Area in California. BART serves 50 stations along six routes on of rapid transit lines, including a spur line in eastern Contra Costa County which uses diesel multiple-unit trains and a automated guideway transit line to the Oakland International Airport. With an average of weekday passengers as of and annual passengers in , BART is the fifth-busiest heavy rail rapid transit system in the United States. BART is operated by the San Francisco Bay Area Rapid Transit District which formed in 1957. The initial system opened in stages from 1972 to 1974. The system was extended most recently in 2020, when Milpitas and Berryessa/North San José stations opened as part of the Silicon Valley BART extension in partnership with the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA). Services BART serves large portions of its three member counties – San Francisco, Alameda, and Contra Costa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of United States Rapid Transit Systems By Ridership
The following is a list of all heavy rail rapid transit systems in the United States. It does not include statistics for bus or light rail systems (see: List of United States light rail systems by ridership for the latter). All ridership figures represent "unlinked" passenger trips (i.e. line transfers on multi-line systems register as separate trips). The data is provided by the American Public Transportation Association's Ridership Reports. See also * List of metro systems *List of North American rapid transit systems by ridership *List of tram and light rail transit systems *List of suburban and commuter rail systems *List of United States light rail systems by ridership *List of North American light rail systems by ridership *List of United States commuter rail systems by ridership * List of United States local bus agencies by ridership Notes References {{reflist, 2 Rapid transit systems These lists of rapid transit systems are sorted by the type of system: * List ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midtown (Manhattan)
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the Chrysler Building, the Hudson Yards Redevelopment Project, the headquarters of the United Nations, Grand Central Terminal, and Rockefeller Center, as well as tourist destinations such as Broadway, Times Square, and Koreatown. Penn Station in Midtown Manhattan is the busiest transportation hub in the Western Hemisphere. Midtown Manhattan is the largest central business district in the world and ranks among the most expensive locations for real estate; Fifth Avenue in Midtown Manhattan commands the world's highest retail rents, with average annual rents at US in 2017. However, due to the high price of retail spaces in Midtown, there are also many vacant storefronts in the neighborhood. Midtown is the country's largest commercial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper East Side
The Upper East Side, sometimes abbreviated UES, is a neighborhood in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 96th Street to the north, the East River to the east, 59th Street to the south, and Central Park/Fifth Avenue to the west. The area incorporates several smaller neighborhoods, including Lenox Hill, Carnegie Hill, and Yorkville. Once known as the Silk Stocking District,The City Review Upper East Side, the Silk Stocking District it has long been the most affluent neighborhood in New York City. The Upper East Side is part of Manhattan Community District 8, and its primary ZIP Codes are 10021, 10028, 10065, 10075, and 10128 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company
The Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT) was a public transit holding company formed in 1896 to acquire and consolidate railway lines in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States. It was a prominent corporation and industry leader using the single-letter symbol B on the New York Stock Exchange. It operated both passenger and freight services on its rail rapid transit, elevated and subway network, making it unique among the three companies which built and operated subway lines in New York City. It became insolvent in 1919 and was restructured and released from bankruptcy as the Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation in 1923. Consolidation The BRT was incorporated January 18, 1896, and took over the bankrupt Long Island Traction Company in early February acquiring the Brooklyn Heights Railroad and the lessee of the Brooklyn City Rail Road. It then acquired the Brooklyn, Queens County and Suburban Railroad leased on July 1, 1898. The BRT took over the property of a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Contracts
The Dual Contracts, also known as the Dual Subway System, were contracts for the construction and/or rehabilitation and operation of rapid transit lines in the City of New York. The contracts were signed on March 19, 1913, by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company. As part of the Dual Contracts, the IRT and BRT would build or upgrade several subway lines in New York City, then operate them for 49 years. Most of the lines of the present-day New York City Subway were built or reconstructed under these contracts. The contracts were "dual" in that they were signed between the City and two separate private companies. Both the IRT and BRT (later Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation, or BMT) worked together to make the construction of the Dual Contracts possible. Background In the late 19th century and for most of the 20th century, New York was host to millions of immigrants each year. Many of the immigrants crowded into tenements and other ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line
The IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line (also known as the IRT Seventh Avenue Line or the IRT West Side Line) is a New York City Subway line. It is one of several lines that serves the A Division, stretching from South Ferry in Lower Manhattan north to Van Cortlandt Park–242nd Street in Riverdale, Bronx. The Brooklyn Branch, known as the Wall and William Streets Branch during construction, from the main line at Chambers Street southeast through the Clark Street Tunnel to Borough Hall in Downtown Brooklyn, is also part of the Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line. The IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line is the only line to have elevated stations in Manhattan, with two short stretches of elevated track at 125th Street and between Dyckman and 225th Streets. The line was constructed in two main portions by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT), a private operator. The first portion, north of 42nd Street, was opened between 1904 and 1908, and is part of the first subway line in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadway (Manhattan)
Broadway () is a road in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Broadway runs from State Street (Manhattan), State Street at Bowling Green (New York City), Bowling Green for through the Boroughs of New York City, borough of Manhattan and through the Bronx, exiting north from New York City to run an additional through the Westchester County, New York, Westchester County municipalities of Yonkers, New York, Yonkers, Hastings-on-Hudson, New York, Hastings-On-Hudson, Dobbs Ferry, New York, Dobbs Ferry, Irvington, New York, Irvington, and Tarrytown, New York, Tarrytown, and terminating north of Sleepy Hollow, New York, Sleepy Hollow.There are four other streets named "Broadway" in New York City's remaining three boroughs: one each in Brooklyn (Broadway (Brooklyn), see main article) and Staten Island, and two in Queens (one running from Astoria, Queens, Astoria to Elmhurst, Queens, Elmhurst, and the other in Hamilton Beach, Queens, Hamilton Beach). Each borough therefore has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

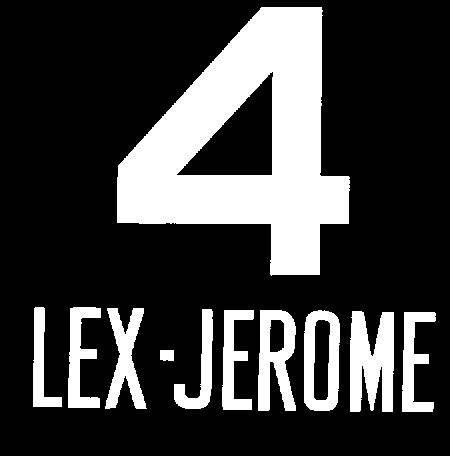




.jpg)


