|
IRF-3
Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor. Function IRF3 is a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF3 was originally discovered as a homolog of IRF1 and IRF2. IRF3 has been further characterized and shown to contain several functional domains including a nuclear export signal, a DNA-binding domain, a C-terminal IRF association domain and several regulatory phosphorylation sites. IRF3 is found in an inactive cytoplasmic form that upon serine/threonine phosphorylation forms a complex with CREBBP. The complex translocates into the nucleus for the transcriptional activation of interferons alpha and beta, and further interferon-induced genes. IRF3 plays an important role in the innate immune system's response to viral infection. Aggregated MAVS have been found to activate IRF3 dimerization. A 2015 study shows phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING and TRIF at a conserved pLxI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF7
Interferon regulatory factor 7, also known as IRF7, is a member of the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Function IRF7 encodes interferon regulatory factor 7, a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF7 has been shown to play a role in the transcriptional activation of virus-inducible cellular genes, including the type I interferon The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T cell, T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p2 ... genes. In particular, IRF7 regulates many interferon-alpha genes. Constitutive expression of IRF7 is largely restricted to lymphoid tissue, largely plasmacytoid dendritic cells, whereas IRF7 is inducible in many tissues. Multiple IRF7 transcript variants have been identified, although the functional consequences of these have not yet been e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Immune System
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms (see Beyond vertebrates).. The major functions of the innate immune system are to: * recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines * activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells * identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells * activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation * act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon Regulatory Factor
Interferon regulatory factors (IRF) are proteins which regulate transcription of interferons (see regulation of gene expression). Interferon regulatory factors contain a conserved N-terminal region of about 120 amino acids, which folds into a structure that binds specifically to the IRF-element (IRF-E) motifs, which is located upstream of the interferon genes. Some viruses have evolved defense mechanisms that regulate and interfere with IRF functions to escape the host immune system. For instance, the remaining parts of the interferon regulatory factor sequence vary depending on the precise function of the protein. The Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus, KSHV, is a cancer virus that encodes four different IRF-like genes; including vIRF1, which is a transforming oncoprotein that inhibits type 1 interferon activity. In addition, the expression of IRF genes is under epigenetic regulation by promoter DNA methylation. Role in IFN Signaling IRFs primarily regulate type I IFNs in the host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homolog
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching primord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF1
Interferon regulatory factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRF1'' gene. Function Interferon regulatory factor 1 was the first member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family identified. Initially described as a transcription factor able to activate expression of the cytokine Interferon beta, IRF-1 was subsequently shown to function as a transcriptional activator or repressor of a variety of target genes. IRF-1 regulates expression of target genes by binding to an interferon stimulated response element (ISRE) in their promoters. The IRF-1 protein binds to the ISRE via an N-terminal helix-turn-helix DNA binding domain, which is highly conserved among all IRF proteins. Beyond its function as a transcription factor, IRF-1 has also been shown to trans-activate the tumour suppressor protein p53 through the recruitment of its co-factor p300. IRF-1 has been shown to play roles in the immune response, regulating apoptosis, DNA damage and tumo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF2
Interferon regulatory factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRF2'' gene. Function IRF2 encodes interferon regulatory factor 2, a member of the interferon regulatory transcription factor (IRF) family. IRF2 competitively inhibits the IRF1-mediated transcriptional activation of interferons alpha and beta, and presumably other genes that employ IRF1 for transcription activation. However, IRF2 also functions as a transcriptional activator of histone H4. See also *IRF1 *Interferon regulatory factors Interactions IRF2 has been shown to interact with BRD7, EP300 and PCAF P300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF), also known as K(lysine) acetyltransferase 2B (KAT2B), is a human gene and transcriptional coactivator associated with p53. Structure Several domains of PCAF can act independently or in unison to enable its funct .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * Transcription factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
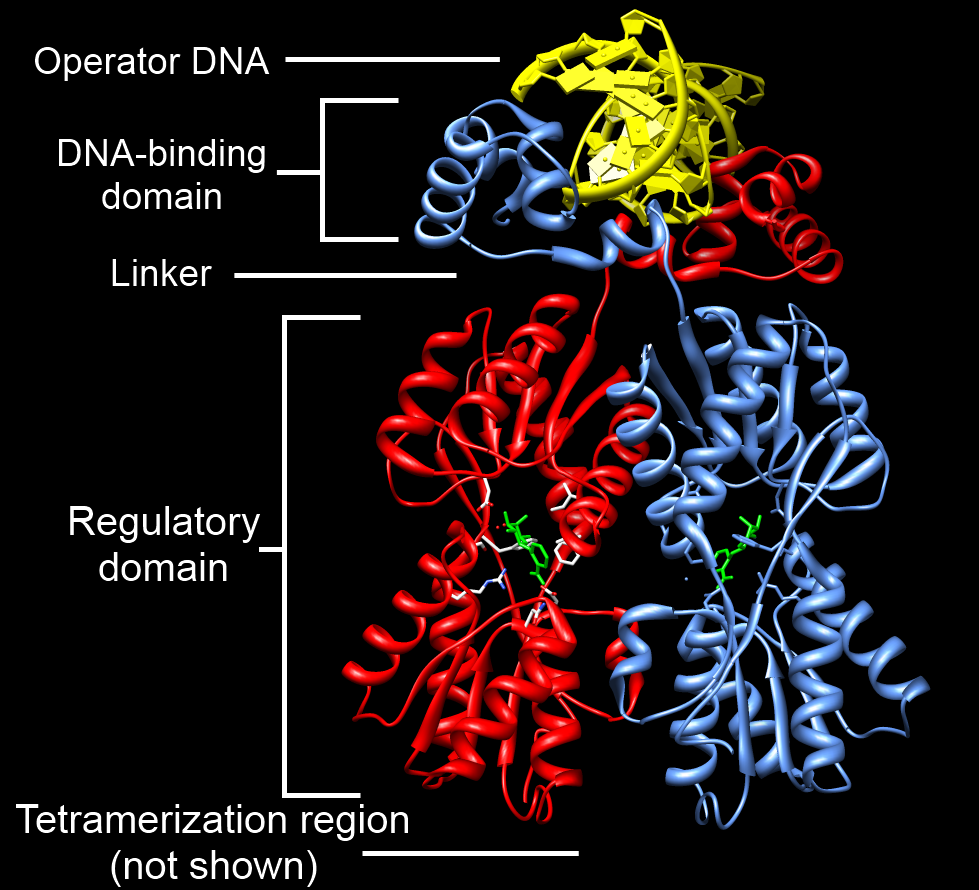
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CREB Binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Targeting
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells. Structural Characteristics Basic structural characteristics, such as genome type, virion shape and replication site, generally share the same features among virus species within the same family. * Double-stranded DNA families: three are non-enveloped (''Adenoviridae'', ''Papillomaviridae'' and ''Polyomaviridae'') and two are enveloped (''Herpesviridae'' and ''Poxviridae''). All of the non-enveloped families have icosahedral capsids. * Partly double-stranded DNA viruses: ''Hepadnaviridae''. These viruses are enveloped. * One family of single-stranded DNA viruses infects humans: ''Parvoviridae''. These viruses are non-enveloped. * Positive single-stranded RNA families: three non-enveloped (''Astroviridae'', ''Caliciviridae'' and ''Picornaviridae'') and four enveloped (''Coronaviridae'', ''Flaviviridae' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |