|
IEEE Annals Of The History Of Computing
The ''IEEE Annals of the History of Computing'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by the IEEE Computer Society. It covers the history of computing, computer science, and computer hardware. It was founded in 1979 by the AFIPS, in particular by Saul Rosen, who was an editor until his death in 1991. The journal publishes scholarly articles, interviews, "think pieces," and memoirs by computer pioneers, and news and events in the field. It was established in July 1979 as ''Annals of the History of Computing'', with Bernard Galler as editor-in-chief. The journal became an IEEE publication in 1992, and was retitled to ''IEEE Annals of the History of Computing''. The 2020 impact factor was 0.741. The current editor in chief is Gerardo Con Diaz with the University of California, Davis. See also * ''Technology and Culture'' * ''Information & Culture'' * Computer History Museum * Charles Babbage Institute The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing
The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables. Concrete devices Digital computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers. But long before abstractions like ''the number'' arose, there were mathematical concepts to serve the purposes of civilization. These concepts are implicit in concrete practices such as: *''One-to-one correspondence'', a rule to count ''how many'' items, e.g. on a tally stick, eventually abstracted into ''numbers''. *''Comparison to a standard'', a method for assuming ''reproducibility'' in a measurement, for example, the number of coins. *The ''3-4-5'' right triangle was a device for assuring a ''right angle'', using ropes with 12 evenly spaced knots, for example. Numbers Eventually, the concept of numbers became concrete and familiar enough for counting to arise, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Editor-in-chief
An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing editor, or executive editor, but where these titles are held while someone else is editor-in-chief, the editor-in-chief outranks the others. Description The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accountable for delegating tasks to staff members and managing them. The term is often used at newspapers, magazines, yearbooks, and television news programs. The editor-in-chief is commonly the link between the publisher or proprietor and the editorial staff. The term is also applied to academic journals, where the editor-in-chief gives the ultimate decision whether a submitted manuscript will be published. This decision is made by the editor-in-chief after seeking input from reviewers selected on the basis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarterly Journals
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combination of the three. Definition In the technical sense a '' journal'' has continuous pagination throughout a volume. Thus '' Business Week'', which starts each issue anew with page one, is a magazine, but the ''Journal of Business Communication'', which continues the same sequence of pagination throughout the coterminous year, is a journal. Some professional or trade publications are also peer-reviewed, for example the '' Journal of Accountancy''. Non-peer-reviewed academic or professional publications are generally ''professional magazines''. That a publication calls itself a ''journal'' does not make it a journal in the technical sense; ''The Wall Street Journal'' is actually a newspaper. Etymology The word "magazine" derives from Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science Journals
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Academic Journals
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Babbage Institute
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, it advises historians, promotes collaboration among academic organizations and museums, and assists IT corporations in preparing and archiving their histories for future studies. Activities The IT History Society provides background information to those with an interest in the history of Information Technology, including papers that provide advice on how to perform historical work and how historical activities can benefit private sector organizations. It tracks historical projects seeking funding as well as projects underway and completed. It maintains online, publicly available, lists of events pertaining to IT history, IT history resources, an IT Honor Roll acknowledging more than 700 individuals who have made a noteworthy contribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum of computer history, located in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the information age, and explores the computing revolution and its impact on society. History The museum's origins date to 1968 when Gordon Bell began a quest for a historical collection and, at that same time, others were looking to preserve the Whirlwind computer. The resulting ''Museum Project'' had its first exhibit in 1975, located in a converted coat closet in a DEC lobby. In 1978, the museum, now ''The Digital Computer Museum'' (TDCM), moved to a larger DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts. Maurice Wilkes presented the first lecture at TDCM in 1979 – the presentation of such lectures has continued to the present time. TDCM incorporated as '' The Computer Museum'' (TCM) in 1982. In 1984, TCM moved to Boston, locating on Museum Wharf. In 1996/1997, the TCM History Center (TCMHC) was established; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information %26 Culture
''Information & Culture'' is an academic journal devoted to the study of the history of information, and any topic that would fall under the purview of the modern interdisciplinary schools of information creation, organization, preservation, or utilization. In addition, the ''Journal'' honors its 50+ year heritage by continuing to publish in the areas of archival, museum, conservation, and library history as well. It is edited at the University of Texas at Austin School of Information Established in 1966 as ''The Journal of Library History'', the journal was edited and published at Florida State University School of Library Science until it moved to the University of Texas at Austin in 1976. It was briefly known as ''Journal of Library History, Philosophy, and Comparative Librarianship'' before returning to ''Journal of Library History''. In 1988, the title was changed to ''Libraries & Culture'', and changed again to ''Libraries and the Cultural Record'' in 2006. In 2012, the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology And Culture
''Technology and Culture'' is a quarterly academic journal founded in 1959. It is an official publication of the Society for the History of Technology (SHOT), whose members routinely refer to it as "T&C." Besides scholarly articles and critical essays, the journal publishes reviews of books and museum exhibitions. Occasionally, the journal publishes thematic issues; topics have included patents, gender and technology, and ecology. ''Technology and Culture'' has had three past editors-in-chief: Melvin Kranzberg (1959–1981), Robert C. Post (1982–1995), and John M. Staudenmaier (1996–2010). Since 2011 the journal has been edited at the University of Oklahoma by Prof. Suzanne Moon. Managing editors have included Joan Mentzer, Joseph M. Schultz, David M. Lucsko, and Peter Soppelsa. In its inaugural issue, editor Melvin Kranzberg set out a threefold educational mission for the journal: "to promote the scholarly study of the history of technology, to show the relations between te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
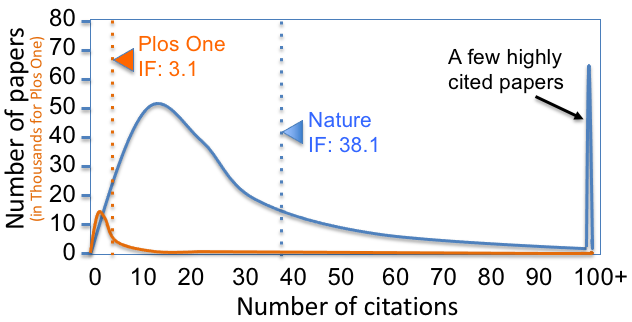
Impact Factor
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. As a journal-level metric, it is frequently used as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its field; journals with higher impact factor values are given the status of being more important, or carry more prestige in their respective fields, than those with lower values. While frequently used by universities and funding bodies to decide on promotion and research proposals, it has come under attack for distorting good scientific practices. History The impact factor was devised by Eugene Garfield, the founder of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) in Philadelphia. Impact factors began to be calculated yearly starting from 1975 for journals listed in the ''Journal Citatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Galler
Bernard A. Galler ( in Chicago – in Ann Arbor, Michigan) was an American mathematician and computer scientist at the University of Michigan who was involved in the development of large-scale operating systems and computer languages including the MAD programming language and the Michigan Terminal System operating system. Education and career Galler attended the University of Chicago where he earned a B.Sc. in mathematics at the University of Chicago (1947), followed by a M.Sc. from UCLA and a Ph.D. from the University of Chicago (1955), advised by Paul Halmos and Marshall Stone. He joined the mathematics department at the University of Michigan (1955) where he taught the first programming course (1956) using an IBM 704. Galler helped to develop the computer language called the Michigan Algorithm Decoder (1959-) in use at several universities. He formed the Communication Sciences dept (1965), renamed Computer Sciences (CS), which became the Computer and Communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |