|
IBM 2501
The IBM 2501 is a punched-card reader from IBM with models for the System/360 and System/370 mainframe systems and for the IBM System/360 Model 20, the IBM 1130 and IBM System/3 minicomputers. 2501 models can read 80-column cards at either 600 or 1000 cards per minute (CPM). The 2501 is no longer sold, but is simulated in software on current IBM systems. Models The 2501 comes in four models depending on speed and attachment features. Models for mainframe use come with an ''integrated control unit'' that performs the functions of a control unit required by other devices. The A1 and A2 are for the IBM 1130. Usage The 2501 uses a photoelectric sensor to read the data punched in the card. Cards are read ''serially'' (column by column) and the reader uses a simplified "straight through" card path. "Each column is read twice and the two readings are compared to check reading accuracy." In a mainframe environment the 2501 was frequently used for mainframe input in an "open shop" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 1402
The IBM 1402 was a high speed card reader/punch introduced on October 5, 1959 as a peripheral input/output device for the IBM 1401 computer. It was later used with other computers of the IBM 1400 series and IBM 7000 series product lines. It was adapted as the IBM 1622 Card Read-Punch for the IBM 1620 and provided the basic design for the models 2501, 2520 and 2540 equipment used with the IBM System/360 product line. Specifications Card reader * Card read speed up to 800 punched cards per minute (models 1, 2 and 3) or 450 cards per minute (models 4, 5 and 6). * Card input file for 3,000 cards (models 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6) or feed hopper for 1,200 cards (model 5). * Three stackers (NR, 1, 2/8) with approximately 1,000-card capacity hold cards after they are read. Card punch * Card punch speed up to 250 cards per minute (all models). * Feed hopper for 1,200 cards (all models). * Three stackers (NP, 4, 2/8) of approximately 1,000-card capacity after cards are punched. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 2821 Control Unit
The IBM 2821 Control Unit attaches card readers and card punches, and line printers to the IBM System/360 and IBM System/370 families of computers. The devices attached may be a combination of: * The IBM 2540 card reader and card punch; * The IBM 1403 models 2, 3, 7 and N1 line printer; and * The IBM 1404 model 2 line printer and bill feed printer. The 2821 was originally advertised—in 1964, before System/360 shipped—as a controller for the IBM 1402 card reader/punch and the IBM 1403 and IBM 2201 printers. Six models of the IBM 2821 Control Unit were available, as follows: * Model 1 attaches one IBM 2540 and one IBM 1403; * Model 2 attaches one IBM 1403; * Model 3 attaches two or three IBM 1403s; * Model 4 attaches one IBM 2540 and one IBM 1404, but only on IBM System/360 models 25, 30, 40 and 50; * Model 5 attaches one IBM 2540 and two or three IBM 1403s; and * Model 6 attaches one IBM 2540. The 2821 is fully buffered, that is it has buffers large enough to hold an entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Peripherals
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the computer system, but they are not the core components of the computer, such as the CPU or power supply unit. In other words, peripherals can also be defined as devices that can be easily removed and plugged into a computer system. Several categories of peripheral devices may be identified, based on their relationship with the computer: *An ''input device'' sends data or instructions to the computer, such as a mouse, keyboard, graphics tablet, image scanner, barcode reader, game controller, light pen, light gun, microphone and webcam; *An ''output device'' provides output data from the computer, such as a computer monitor, projector, printer, headphones and computer speaker; *An ''input/output device'' performs both input and output func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Programming In The Punched Card Era
From the invention of computer programming languages up to the mid-1970s, most computer programmers created, edited and stored their programs line by line on punch cards. Punched cards A punched card is a flexible write-once medium that encodes data, most commonly 80 characters. Groups or "decks" of cards form programs and collections of data. The term is often used interchangeably with ''punch card'', the difference being that an unused card is a "punch card," but once information had been encoded by punching holes in the card, it was now a "punched card." For simplicity, this article will use the term ''punched card'' to refer to either. Often programmers first wrote their program out on special forms called coding sheets, taking care to distinguish the digit zero from the letter ''O'', the digit one from the letter ''I'', eight from ''B'', two from ''Z'', and so on using local conventions such as the "slashed zero". These forms were then taken by keypunch operators, who usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card Input/output
A computer punched card reader or just computer card reader is a computer input device used to read computer programs in either source or executable form and data from punched cards. A computer card punch is a computer output device that punches holes in cards. Sometimes computer punch card readers were combined with computer card punches and, later, other devices to form multifunction machines. It is a input device and also an output device. Most early computers, such as the ENIAC, and the IBM NORC, provided for punched card input/output. Card readers and punches, either connected to computers or in off-line card to/from magnetic tape configurations, were ubiquitous through the mid-1970s. Punched cards had been in use since the 1890s; their technology was mature and reliable. Card readers and punches developed for punched card machines were readily adaptable for computer use. Businesses were familiar with storing data on punched cards and keypunch machines were widely employe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
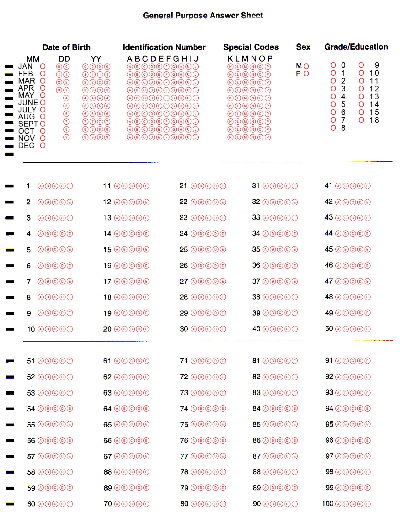
Optical Mark Recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the form of shaded areas. OMR background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word processor or computer and print them on a laser laser printer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request Price Quotation
Request price quotation or RPQ is a long-standing IBM designation for a product or component that is potentially available, but that is not on the "standard" price list. Typical RPQ offerings are custom interfaces, hardware modifications, research or experimental systems, or variable-cost items. In the days of IBM's large mainframes, e.g. the System/360 and System/370 series, many unusual features were flagged as "RPQ". A special-order software item is known as a Programming Request Price Quotation or PRPQ. Examples The standard punched card code for the groupmark character on the IBM 1401 computer system used punches in rows 12, 7, and 8 of a card column (written as 12-7-8). The older IBM 705 computer used 12-5-8 for this character. An RPQ was available for the 1401 for compatibility that allowed the system to read or punch the 705 code rather than the standard code. Since not all 1401 users would need this feature it was marketed as an RPQ. The features used by the Compati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 1442
IBM 1442 is a combination IBM card reader and card punch. It reads and punches 80-column IBM-format punched cards and is used on the IBM 1440, the IBM 1130, the IBM 1800 and System/360 and is an option on the IBM System/3. Overview The 1442 can read up to 400 cards per minute. Cards are read and punched one column at a time and binary cards are permitted. Cards are read using photocells, illuminated by fiber optics, unlike the IBM 1402, which uses wire brushes to read cards. It is even possible to create (but not read, except in Binary Mode) " IBM Doilies," cards with every possible hole punched. Few other pieces of IBM equipment could do this without sustaining damage. There are two output stackers, located in the photo on the left lower side. One could program to select the output stacker for each card read, so it is possible to read cards and separate them into two groups. Cards are placed in the top hopper ("face down, nine-edge leading") and a plate is added on the top of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectric
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid state and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the light's intensity or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, ''The New York Times'' suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than (), with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC. The class formed a distinct group with its own software architectures and operating systems. Minis were designed for control, instrumentation, human interaction, and communication switching as distinct from calculation and record keeping. Many were sold indirectly to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) for final end use application. During the two decade lifetime of the minicomputer class (1965–1985), almost 100 companies formed and only a half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punch Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to directly control automated machinery. Punched cards were widely used through much of the 20th century in the data processing industry, where specialized and increasingly complex unit record machines, organized into semiautomatic data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, output, and storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and data. While punched cards are now obsolete as a storage medium, as of 2012, some voting machines still used punched cards to record votes. They also had a significant cultural impact. History The idea of control and data storage via punched holes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/3
The IBM System/3 was an IBM midrange computer introduced in 1969, and marketed until 1985. It was produced by IBM Rochester in Minnesota as a low-end business computer aimed at smaller organizations that still used IBM 1400 series computers or unit record equipment. The first member of what IBM refers to as their "midrange" line, it also introduced the RPG II programming language. It is the first ancestor in the product line whose current version is the IBM i series and includes the highly successful AS/400. History At its launch in 1969 it was available for $1000/month — less than half cost of an IBM System/360 Model 20; the smallest member of the IBM System/360 family. Many of the original System/3 model 10 units were shipped diskless, with only the new IBM 5424 Multifunction Card Unit (MFCU) which read, punched, printed on and sorted the new, smaller 96-column punched cards introduced at the same time. IBM delivered the following models: * 1969 — IBM 5410, or System/3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)