|
Hyperprior
In Bayesian statistics, a hyperprior is a prior distribution on a hyperparameter, that is, on a parameter of a prior distribution. As with the term ''hyperparameter,'' the use of ''hyper'' is to distinguish it from a prior distribution of a parameter of the model for the underlying system. They arise particularly in the use of hierarchical models. For example, if one is using a beta distribution to model the distribution of the parameter ''p'' of a Bernoulli distribution, then: * The Bernoulli distribution (with parameter ''p'') is the ''model'' of the underlying system; * ''p'' is a ''parameter'' of the underlying system (Bernoulli distribution); * The beta distribution (with parameters ''α'' and ''β'') is the ''prior'' distribution of ''p''; * ''α'' and ''β'' are parameters of the prior distribution (beta distribution), hence ''hyperparameters;'' * A prior distribution of ''α'' and ''β'' is thus a ''hyperprior.'' In principle, one can iterate the above: if the hyperprior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperparameter
In Bayesian statistics, a hyperparameter is a parameter of a prior distribution; the term is used to distinguish them from parameters of the model for the underlying system under analysis. For example, if one is using a beta distribution to model the distribution of the parameter ''p'' of a Bernoulli distribution, then: * ''p'' is a parameter of the underlying system (Bernoulli distribution), and * ''α'' and ''β'' are parameters of the prior distribution (beta distribution), hence ''hyper''parameters. One may take a single value for a given hyperparameter, or one can iterate and take a probability distribution on the hyperparameter itself, called a hyperprior. Purpose One often uses a prior which comes from a parametric family of probability distributions – this is done partly for explicitness (so one can write down a distribution, and choose the form by varying the hyperparameter, rather than trying to produce an arbitrary function), and partly so that one can ''vary'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prior Distribution
In Bayesian statistical inference, a prior probability distribution, often simply called the prior, of an uncertain quantity is the probability distribution that would express one's beliefs about this quantity before some evidence is taken into account. For example, the prior could be the probability distribution representing the relative proportions of voters who will vote for a particular politician in a future election. The unknown quantity may be a parameter of the model or a latent variable rather than an observable variable. Bayes' theorem calculates the renormalized pointwise product of the prior and the likelihood function, to produce the '' posterior probability distribution'', which is the conditional distribution of the uncertain quantity given the data. Similarly, the prior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the unconditional probability that is assigned before any relevant evidence is taken into account. Priors can be created using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Statistics
Bayesian statistics is a theory in the field of statistics based on the Bayesian interpretation of probability where probability expresses a ''degree of belief'' in an event. The degree of belief may be based on prior knowledge about the event, such as the results of previous experiments, or on personal beliefs about the event. This differs from a number of other interpretations of probability, such as the frequentist interpretation that views probability as the limit of the relative frequency of an event after many trials. Bayesian statistical methods use Bayes' theorem to compute and update probabilities after obtaining new data. Bayes' theorem describes the conditional probability of an event based on data as well as prior information or beliefs about the event or conditions related to the event. For example, in Bayesian inference, Bayes' theorem can be used to estimate the parameters of a probability distribution or statistical model. Since Bayesian statistics treats probabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multilevel Model
Multilevel models (also known as hierarchical linear models, linear mixed-effect model, mixed models, nested data models, random coefficient, random-effects models, random parameter models, or split-plot designs) are statistical models of parameters that vary at more than one level. An example could be a model of student performance that contains measures for individual students as well as measures for classrooms within which the students are grouped. These models can be seen as generalizations of linear models (in particular, linear regression), although they can also extend to non-linear models. These models became much more popular after sufficient computing power and software became available. Multilevel models are particularly appropriate for research designs where data for participants are organized at more than one level (i.e., nested data). The units of analysis are usually individuals (at a lower level) who are nested within contextual/aggregate units (at a higher le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the beta distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval , 1in terms of two positive parameters, denoted by ''alpha'' (''α'') and ''beta'' (''β''), that appear as exponents of the random variable and control the shape of the distribution. The beta distribution has been applied to model the behavior of random variables limited to intervals of finite length in a wide variety of disciplines. The beta distribution is a suitable model for the random behavior of percentages and proportions. In Bayesian inference, the beta distribution is the conjugate prior probability distribution for the Bernoulli, binomial, negative binomial and geometric distributions. The formulation of the beta distribution discussed here is also known as the beta distribution of the first kind, whereas ''beta distribution of the second kind'' is an alternative name for the beta prime distribution. The generalization to mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Bernoulli distribution, named after Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli,James Victor Uspensky: ''Introduction to Mathematical Probability'', McGraw-Hill, New York 1937, page 45 is the discrete probability distribution of a random variable which takes the value 1 with probability p and the value 0 with probability q = 1-p. Less formally, it can be thought of as a model for the set of possible outcomes of any single experiment that asks a yes–no question. Such questions lead to outcomes that are boolean-valued: a single bit whose value is success/ yes/true/ one with probability ''p'' and failure/no/ false/zero with probability ''q''. It can be used to represent a (possibly biased) coin toss where 1 and 0 would represent "heads" and "tails", respectively, and ''p'' would be the probability of the coin landing on heads (or vice versa where 1 would represent tails and ''p'' would be the probability of tails). In particular, unfair coins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixture Density
In probability and statistics, a mixture distribution is the probability distribution of a random variable that is derived from a collection of other random variables as follows: first, a random variable is selected by chance from the collection according to given probabilities of selection, and then the value of the selected random variable is realized. The underlying random variables may be random real numbers, or they may be random vectors (each having the same dimension), in which case the mixture distribution is a multivariate distribution. In cases where each of the underlying random variables is continuous, the outcome variable will also be continuous and its probability density function is sometimes referred to as a mixture density. The cumulative distribution function (and the probability density function if it exists) can be expressed as a convex combination (i.e. a weighted sum, with non-negative weights that sum to 1) of other distribution functions and density func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Set
In geometry, a subset of a Euclidean space, or more generally an affine space over the reals, is convex if, given any two points in the subset, the subset contains the whole line segment that joins them. Equivalently, a convex set or a convex region is a subset that intersects every line into a single line segment (possibly empty). For example, a solid cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary of a convex set is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval with the property that its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
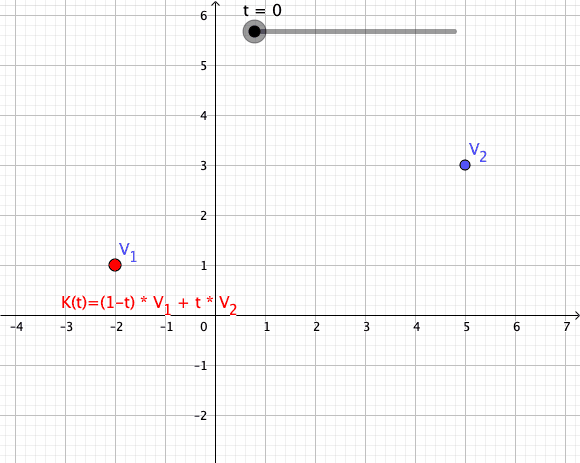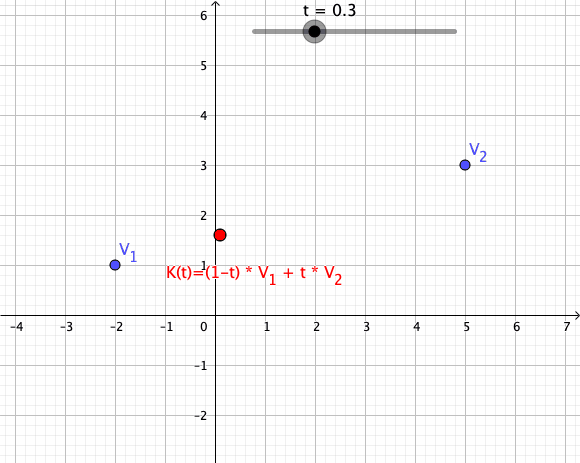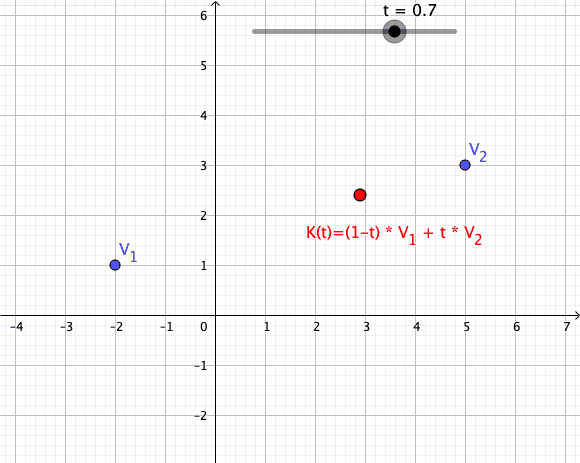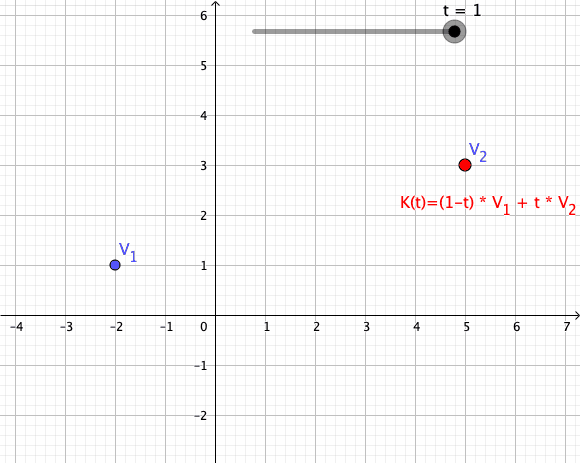
Convex Combination
In convex geometry and vector algebra, a convex combination is a linear combination of points (which can be vectors, scalars, or more generally points in an affine space) where all coefficients are non-negative and sum to 1. In other words, the operation is equivalent to a standard weighted average, but whose weights are expressed as a percent of the total weight, instead of as a fraction of the ''count'' of the weights as in a standard weighted average. More formally, given a finite number of points x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n in a real vector space, a convex combination of these points is a point of the form :\alpha_1x_1+\alpha_2x_2+\cdots+\alpha_nx_n where the real numbers \alpha_i satisfy \alpha_i\ge 0 and \alpha_1+\alpha_2+\cdots+\alpha_n=1. As a particular example, every convex combination of two points lies on the line segment between the points. A set is convex if it contains all convex combinations of its points. The convex hull of a given set of points is identical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogy With Eigenfunctions
Analogy (from Greek ''analogia'', "proportion", from ''ana-'' "upon, according to" lso "against", "anew"+ ''logos'' "ratio" lso "word, speech, reckoning" is a cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject (the analog, or source) to another (the target), or a linguistic expression corresponding to such a process. In a narrower sense, analogy is an inference or an argument from one particular to another particular, as opposed to deduction, induction, and abduction, in which at least one of the premises, or the conclusion, is general rather than particular in nature. The term analogy can also refer to the relation between the source and the target themselves, which is often (though not always) a similarity, as in the biological notion of analogy. Analogy plays a significant role in problem solving, as well as decision making, argumentation, perception, generalization, memory, creativity, invention, prediction, emotion, explanation, concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, fluid dynamics, the flow of water in a pipe, the Brownian motion, random motion of particles in the air, and population dynamics, the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real number, real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a Set (mathematics), set, without the need of a Differentiability, smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |