|
Hurricane Humberto (2019)
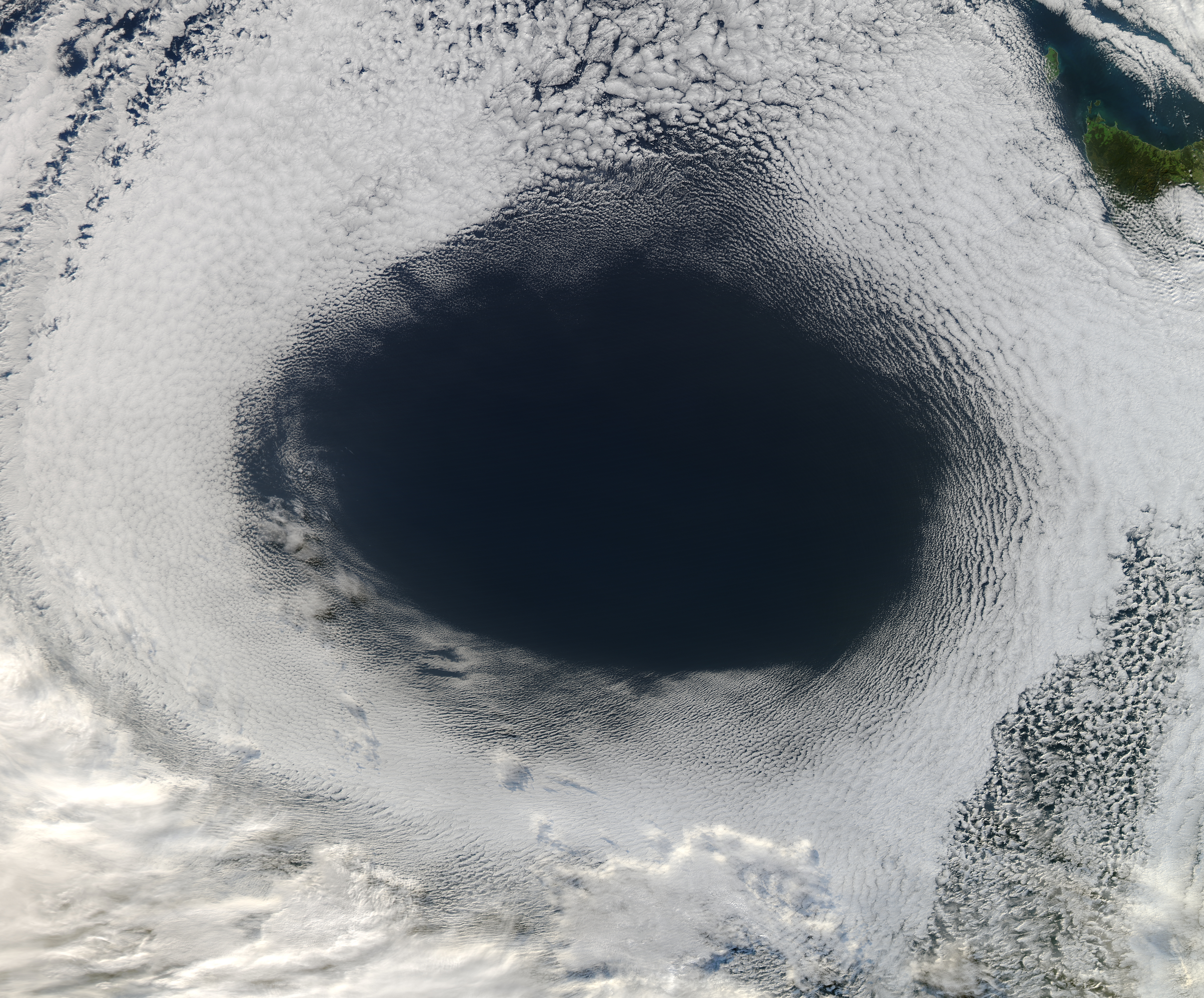
Hurricane Humberto was a large and powerful tropical cyclone that caused extensive wind damage in Bermuda during September 2019. It was the eighth named storm, third hurricane, and second major hurricane – Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale – of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season. Humberto formed on September 13 from the prolonged interaction of a tropical wave and an upper-level trough, then paralleled the eastern coastline of Florida through September 16 before turning sharply northeastward. A generally favorable environment allowed Humberto to become a hurricane that day, and the storm further strengthened to reach peak intensity as a Category 3 hurricane on September 18. After its center passed within 65 miles (100 km) of Bermuda around 00:00 UTC on September 19, the system encountered stronger wind shear and drier air. Stripped of its deep thunderstorm activity, the system transitioned to a potent extratropical cyclone ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
) , anthem = "God Save the King" , song_type = National song , song = " Hail to Bermuda" , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , mapsize2 = , map_caption2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title2 = English settlement , established_date2 = 1609 (officially becoming part of the Colony of Virginia in 1612) , official_languages = English , demonym = Bermudian , capital = Hamilton , coordinates = , largest_city = Hamilton , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2016 , government_type = Parliamentary dependency under a constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Rena Lalgie , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Edward David Burt , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Senate , lower_house = House of Assembly , area_km2 = 53.2 , area_sq_mi = 20.54 , area_rank = , percent_water = 27 , elevation_max_m = 79 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rip Currents
A rip current, often simply called a rip (or misleadingly a ''rip tide''), is a specific kind of water current that can occur near beaches with breaking waves. A rip is a strong, localized, and narrow current of water which moves directly away from the shore, cutting through the lines of breaking waves like a river running out to sea. The current in a rip is strongest and fastest next to the surface of the water. Rip currents can be hazardous to people in the water. Swimmers who are caught in a rip current and who do not understand what is happening, or who may not have the necessary water skills, may panic, or they may exhaust themselves by trying to swim directly against the flow of water. Because of these factors, rip currents are the leading cause of rescues by lifeguards at beaches, and in the United States, they are the cause of an average of 46 deaths by drowning per year. A rip current is not the same thing as undertow, although some people use the term incorrectly whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Tropical Cyclone
The following is a glossary of tropical cyclone terms. A ;Advisory: Official information issued by tropical cyclone warning centers describing all tropical cyclone watches and warnings in effect along with details concerning tropical cyclone locations, intensity and movement, and precautions that should be taken. Advisories are also issued to describe: (a) tropical cyclones prior to issuance of watches and warnings and (b) subtropical cyclones. B ;Bar: This is used to describe a dark layer of clouds that precedes the approach of a tropical cyclone. It is usually followed by heavy precipitation, and can also been seen in the eyewall of a cyclone. The arrival of the storm is often determined by this bar, as barometric pressure begins to fall and conditions begin to deteriorate following its passage. ;Best track: A subjectively-smoothed representation of a tropical cyclone's location and intensity over its lifetime. The best track contains the cyclone's latitude, longitude, maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from abroad. The Chief, Aerial Reconnaissance Coordination, All Hurricanes (CARCAH) unit tasks planes, for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turks And Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and northern West Indies. They are known primarily for tourism and as an offshore financial centre. The resident population in July 2021 was put at 57,196, making it the third-largest of the British overseas territories by population. The islands are southeast of Mayaguana in the Bahamas island chain and north of the island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Grand Turk (Cockburn Town), the capital since 1766, is situated on Grand Turk Island about east-southeast of Miami, United States. They have a total land area of . The islands were inhabited for centuries by indigenous peoples. The first recorded European sighting of them was in 1512. In subsequent centuries, they were claimed by several European powers, with the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnal Cycle
A diurnal cycle (or diel cycle) is any pattern that recurs every 24 hours as a result of one full rotation of the planet Earth around its axis. Earth's rotation causes surface temperature fluctuations throughout the day and night, as well as weather changes throughout the year. The diurnal cycle depends mainly on incoming solar radiation. Climate and atmosphere In climatology, the diurnal cycle is one of the most basic forms of climate patterns, including variations in diurnal temperature and rainfall. Diurnal cycles may be approximately sinusoidal or include components of a truncated sinusoid (due to the Sun's rising and setting) and thermal relaxation ( Newton cooling) at night. The diurnal cycle also has a great impact on carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, due to processes such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Biological effects Diurnal cycles of light and temperature can result in similar cycles in biological processes, such as photosynthesis i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure. Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclones, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge. The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent , image_name = , image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada. , image_alt = , locator_map = , location = Caribbean SeaNorth Atlantic Ocean , coordinates = , area_km2 = 3232.5 , total_islands = 90+ , major_islands = CarriacouDominicaGrenadaMartiniquePetite MartiniqueSaint Lucia Saint Vincent , highest_mount = Morne Diablotins, Dominica , elevation_m = 1,447 , country = Dominica , country_largest_city = Roseau , country1 = Grenada , country1_largest_city = St. George's , country2 = Martinique , country2_largest_city = Fort-de-France , country3 = Saint Lucia , country3_largest_city = Castries , country4 = Saint Vincent and the Grenadines , country4_largest_city = Kingstown , density_km2 = 227 , population = 854,000 , ethnic_groups = The Windward Islands are the southern, generally larger islands of the Lesser Antilles. Part of the West Indies, they lie south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda Weather Service
The Bermuda Weather Service is Bermuda's national meteorological service. It provides public, marine, tropical and aviation weather forecasts as well as warnings and climatolological services. The service began operations under contract from the Department of Airport Operations, Ministry of Transport and Tourism, in 1995. Prior to that, the island's meteorological services were provided by a US Navy The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of ... base on the island. References External links Organisations based in Bermuda Organizations established in 1995 1995 establishments in Bermuda Governmental meteorological agencies in North America {{Bermuda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)