 |
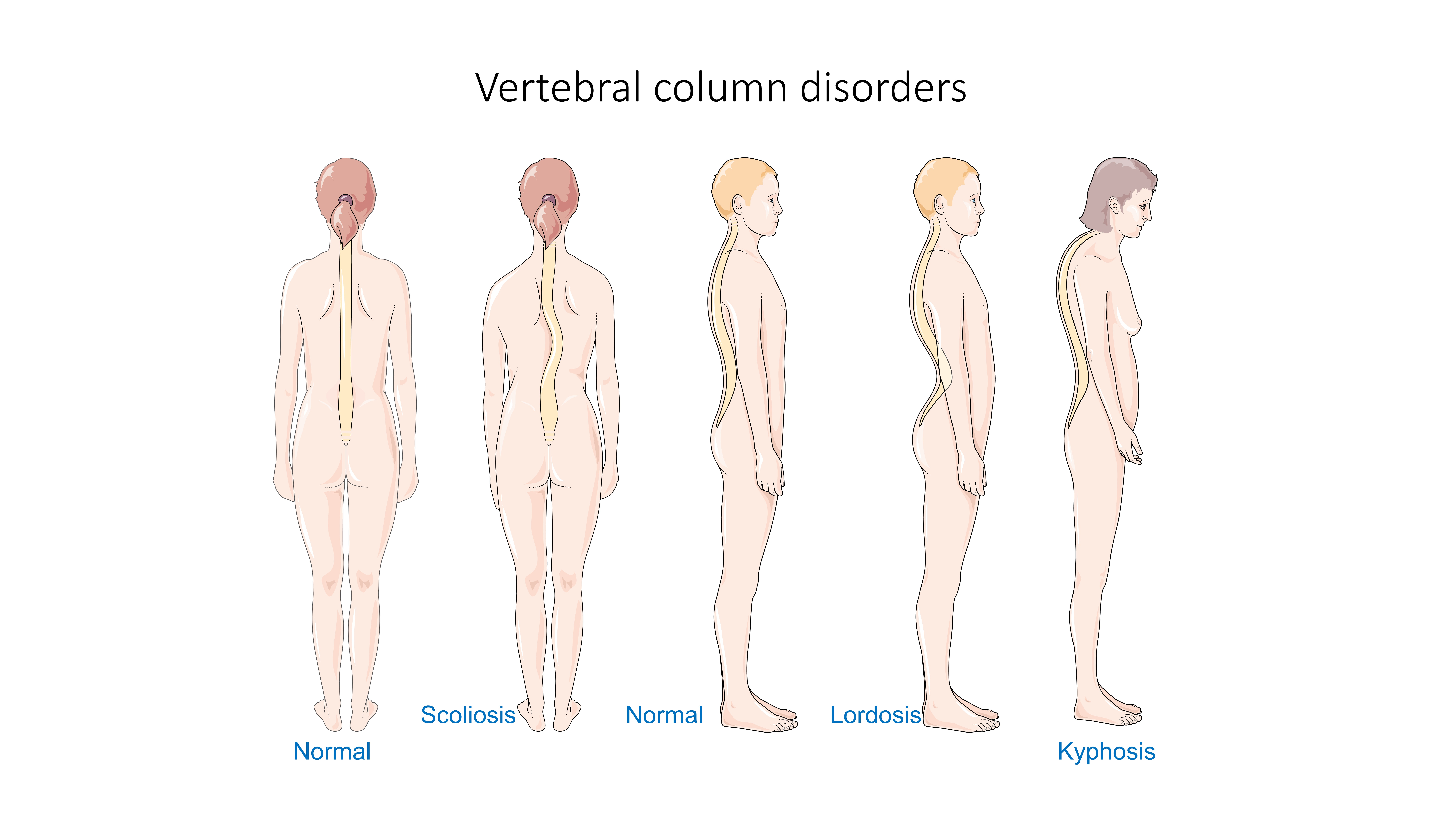
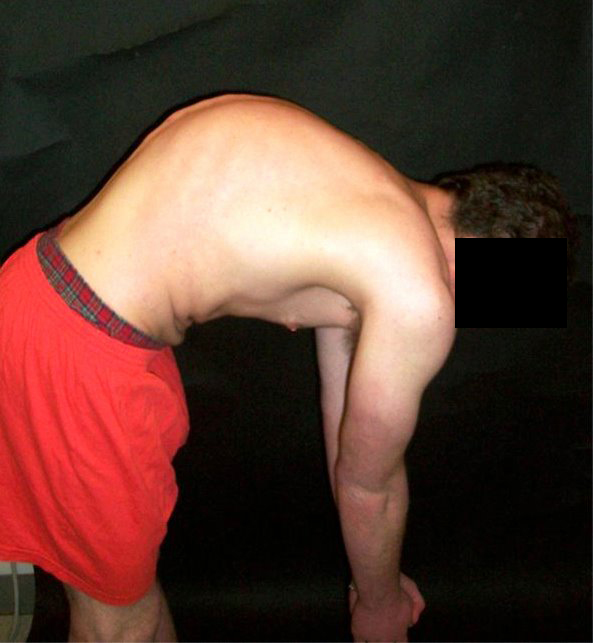
Hunchback
Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females. In the sense of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the Old age, elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the Vertebral column, spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal peak bone mass, maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases postmenopause, after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after 'andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Scheuermann's Disease
Scheuermann's disease is a self-limiting skeletal disorder of childhood. Scheuermann's disease describes a condition where the vertebrae grow unevenly with respect to the sagittal plane; that is, the posterior angle is often greater than the anterior. This uneven growth results in the signature "wedging" shape of the vertebrae, causing kyphosis. It is named after Danish surgeon Holger Scheuermann. Signs and symptoms Scheuermann's disease is considered to be a form of juvenile osteochondrosis of the spine. It is found mostly in teenagers and presents a significantly worse deformity than postural kyphosis. Patients suffering with Scheuermann’s kyphosis cannot consciously correct their posture. The apex of their curve, located in the thoracic vertebrae, is quite rigid. Scheuermann's disease is notorious for causing lower and mid-level back and neck pain, which can be severe and disabling. The sufferer may feel pain at the apex of the curve, which is aggravated by physical activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Fatigue (medical)
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Thoracic Vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of a bone, in particular to the epiphysis, followed by localized bony necrosis, and later, regrowth of the bone. This disorder is defined as a focal disturbance of endochondral ossification and is regarded as having a multifactorial cause, so no one thing accounts for all aspects of this disease. Osteochondrosis is a developmental disease. It usually occurs in an early stage of life. It has personified features as focal chondronecrosis and confinement of growth cartilage due to a failing of endochondral ossification. Fissures can develop from lesions over the top articular cartilage and form a cartilage flap and an osteochondral fragment. It is diagnosed as osteochondritis dissecans. In animals In dogs osteochondrosis is seen in elbow, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Spine (journal)
''Spine'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed medical journal covering research in the field of orthopaedics, especially concerning the spine. It was established in 1976 and is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. The current editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Andrew J. Schoenfeld, M.D.. Spine is considered the leading orthopaedic journal covering cutting-edge spine research. Spine is available in print and online. Spine is considered the most cited journal in orthopaedics. Affiliated societies The following societies are affiliated with ''Spine'': References External links * {{Official website, http://www.spinejournal.com Biweekly journals Lippincott Williams & Wilkins academic journals Publications established in 1976 English-la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Annals Of Internal Medicine
''Annals of Internal Medicine'' is an academic medical journal published by the American College of Physicians (ACP). It is one of the most widely cited and influential specialty medical journals in the world. ''Annals'' publishes content relevant to the field of internal medicine and related sub-specialties. ''Annals'' publishes a wide variety of original research, review articles, practice guidelines, and commentary relevant to clinical practice, health care delivery, public health, health care policy, medical education, ethics, and research methodology. In addition, the journal publishes personal narratives that convey the feeling and the art of medicine. Selected articles in the journal are open access; these include patient oriented content and Clinical Guidelines (and related reviews). Impact factor The most recent (2021) Impact Factor for ''Annals of Internal Medicine'' is 51.598 (Clarivate Analytics). According to the new 2021 Journal Citations Reports from Clarivate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Annals Of Human Biology
''Annals of Human Biology'' is a bimonthly academic journal that publishes review articles on human population biology, nature, development and causes of human variation. It is published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Society for the Study of Human Biology, of which it is the official journal. Coverage Includes * Global health * Ageing * Epidemiology * Ecology * Environmental physiology * Human genetics * Auxology * Population biology Society ''Annals of Human Biology'' is the official journal of the Society for the Study of Human Biology Editors-in-Chief Noël Cameron, Olga Rickards, and Babette Zemel are the Editors-in-Chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... of ''Annals of Human Biology''. Publication Format ''Annals of Human Biology'' publishes s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Slouching
The complications of prolonged standing are conditions that may arise after standing, walking, or running for prolonged periods. Many of the complications come from prolonged standing (more than 60% of a work day) that is repeated several times a week. Many jobs require prolonged standing, such as "retail staff, baristas, bartenders, assembly line workers, security staff, engineers, catering staff, library assistants, hair stylists and laboratory technicians". The basic physiological change that occurs in the body during prolonged standing or sudden stand from supine position is that there will be increased pooling of blood in leg, which decreases the venous return and so there will be decreased cardiac output, which ultimately causes systolic Blood pressure to fall (hypotension). This hypotension may lead the subject to faint or to have other symptoms of hypotension. Standing requires about 10% more energy than sitting. Prevalence There are no exact measures of how prevalent the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Disability And Rehabilitation
''Disability and Rehabilitation'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of disability and rehabilitation medicine, including practice and policy aspects of the rehabilitation process. The journal is published by Taylor and Francis Group and the editor-in-chief is Dave Müller (Suffolk New College). It was established in 1978 and has a 2018 impact factor of 2.054.''Journal Citation Reports'', 2018. Thomson Reuters Thomson Reuters Corporation ( ) is a Canadian multinational media conglomerate. The company was founded in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, where it is headquartered at the Bay Adelaide Centre. Thomson Reuters was created by the Thomson Corp ... The journal is published 26 times a year. References External links * {{Official website, http://www.tandfonline.com/idre English-language journals Taylor & Francis academic journals Publications established in 1978 Rehabilitation medicine journals Biweekly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which a person's spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually "S"- or "C"-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to another condition such as muscle spasms, cerebral palsy, Marfan syndrome, and tumors such as neurofibromatosis. Diagnosis is confirmed with X-rays. Scoliosis is typically classified as either structural in which the curve is fixed, or functional in which the underlying spine is normal. Treatment depends on the degree of curve, location, and cause. Minor curves may simply be watched periodically. Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |