|
Humaydah Al-Bariqi
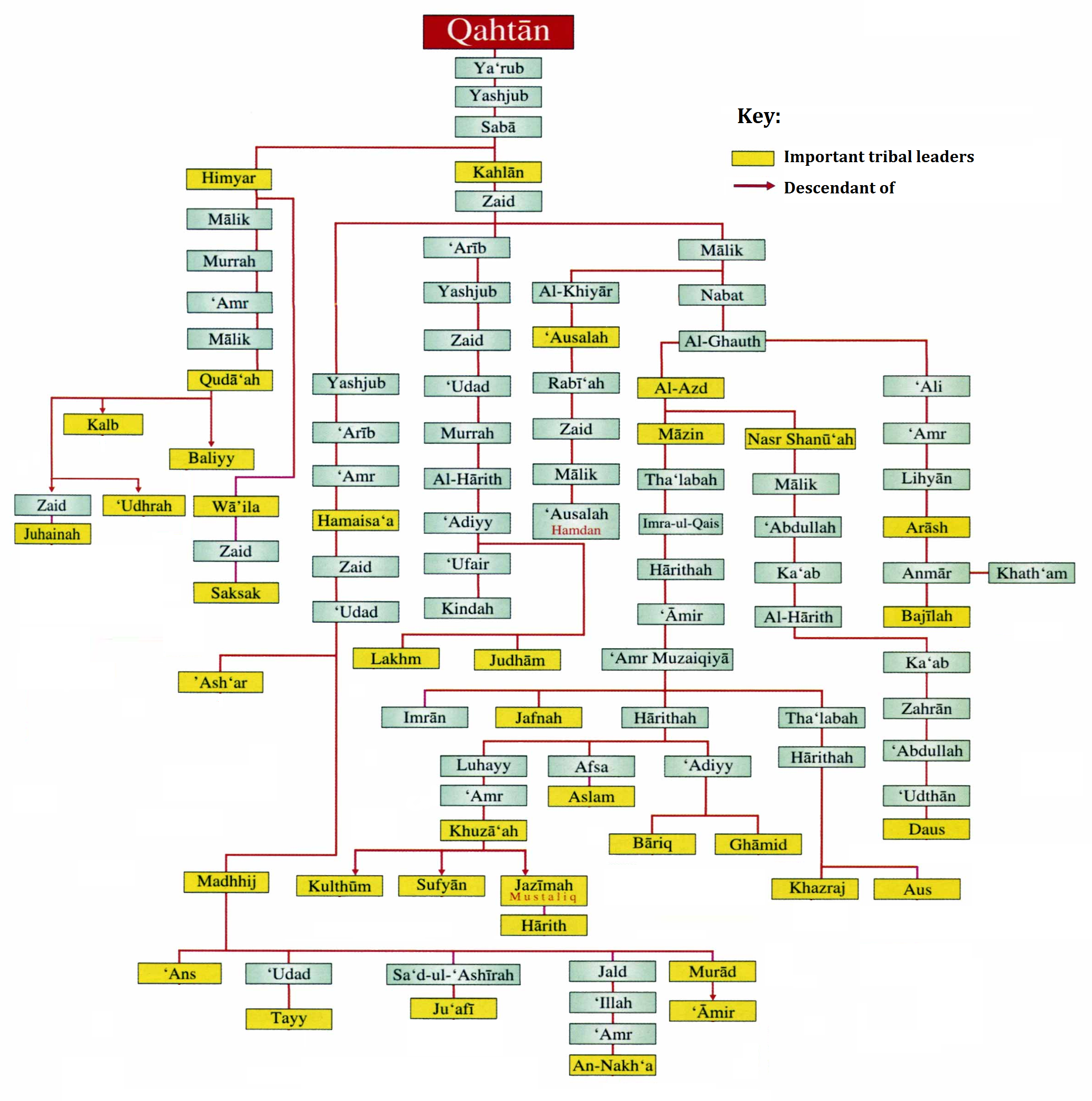
Humaydah ibn an-Nu'man al-Bariqi ( ar, žŁ┘ģ┘ŖžČž® ž©┘å ž¦┘ä┘åž╣┘ģž¦┘å ž¦┘äž©ž¦ž▒┘é┘Ŗ), was a companion of Muhammad. He was the leader of the tribe of Bariq and an extremely successful military general during the reign of Rashidun Caliph Umar. Humaydah also fought under Sa`d's command against the Sassanid army at the Battle of al-Q─üdisiyyah. Lineage His full name was Humaydah b. al-Nu'man b. Humaydah b. al-Harith b. Awf b. Amr b. Sa`d b. Thailbh b. Kinanah al-Bariqi Ibn Bariq Ibn Uday Ibn Haritha Ibn Amr Mazikiee Ibn Aamr bin Haritha Algtarif bin Imru al-Qais Thailb bin Mazen Ibn Al-Azd Ibn Al-Ghoth Ibn Nabit Ibn Malik bin Zaid Ibn Kahlan Ibn Saba'a (Sheba) Ibn Yashjub Ibn Yarab Ibn Qahtan Ibn Hud (Eber). Nu'man b. Humaydah al-Bariqi ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘åž╣┘ģž¦┘å ž©┘å žŁ┘ģ┘ŖžČž® ž¦┘äž©ž¦ž▒┘é┘Ŗ) was his father. References {{Reflist Further reading * History of the Prophets and Kings (1/2218 2258, 2259 and 2334) *The Complete History ''The Complete History'' (, ''al-K─ümil fit-T─ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bareq
Bareq ( ar, ž©ž¦ž▒┘é; also transliterated as '), is one of the governorates of Asir in the north-west of the region, north of Abha. It occupies a distinct location midway between Tihama and Asir, above sea level. With an estimated population of 75,351, it is well off economically; the city has grown rapidly and has many government services and public utilities available. It is one of Asir's winter resorts because of its natural environment and mild winter weather. Bareq has valleys. History Bareq was founded in 220 AD. (citation?) Bareq is part of the territory which is historically known as the "Yemen", which dates back to the second millennium BC and was inhabited by an immigrant tribe from Marib in Yemen called Bariq belonging to the ancient tribe of Al-Azd that has many clans linked to it. Known before the advent of Islam as ''Diy─ür B─üriq'', it was traversed by the ancient trade route from Yemen to Mecca and the Levant, known as the winter and summer journeys. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kahlan
Kahlan ( ar, ┘ā┘ć┘䞦┘å) was one of the main tribal confederations of Sabaeans, Saba' in Ancient history of Yemen, Ancient Yemen. They are descended from Kahlan bin Saba bin Yishjab bin Yarub bin Qahtan. Conflict with Himyar By the 2nd century BC Saba' was declining gradually and its southern neighbor Himyar was able to settle many nomadic tribes that were allied to Himyar and create a stronger Himyarite nation in the lowlands. Eventually Saba' was incorporated into Himyar and resistance was reduced to the Kahlan tribes who were overpowered by Himyar and forced out of Highlands in Yemen. Most Of Kahlan remained in the Yemeni desert region around Marib until the destruction of the Marib Dam, Dam in the 3rd century AD. this forced the Kahlani tribes to emigrate northwards through Arabia. They reaching as far as Mesopotamia and Syria prior to the 7th century Arab conquests under Islam. After the Arab conquests, the Kahlani Arabs, among other Qahtani and Adnani tribes, reached all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Generals
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘ī┘æ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, ž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Musl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generals Of The Medieval Islamic World
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine g├®n├®ral''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Complete History
''The Complete History'' (, ''al-K─ümil fit-T─ür─½kh)'', is a classic Islamic history book written by Ali ibn al-Athir. Composed in ca. 1231AD/628AH, it is one of the most important Islamic historical works. Ibn al-Athir was a contemporary and member of the retinue of Saladin, the Kurdish general who captured Jerusalem from the Crusaders and massively reduced European holdings in the Levant, leaving the Principality of Antioch and County of Tripoli much reduced and only a few cities on the coast to the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Format of ''The Complete History'' ''The Complete History'' is organised into several volumes, years, and subsections. Each volume is divided in chronological order into years. For instance, the year 491 AH starts "then the year one and ninety and four hundred began." Each year has several sections committed to major events, which are not necessarily in chronological order. These subsections may include the deaths, births, and dynastic succession of major stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Prophets And Kings
The ''History of the Prophets and Kings'' ( ar, ž¬ž¦ž▒┘Ŗž« ž¦┘äž▒ž│┘ä ┘łž¦┘ä┘ģ┘ä┘ł┘ā ''T─ür─½kh al-Rusul wa al-Mul┼½k''), more commonly known as ''Tarikh al-Tabari'' () or ''Tarikh-i Tabari'' or ''The History of al-Tabari '' ( fa, ž¬ž¦ž▒█īž« žĘž©ž▒█ī) is an Arabic-language historical chronicle completed by the Muslim historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari (225ŌĆō310 AH, 838ŌĆō923 AD) in 915 AD. It begins with creation, and charts Muslim and Middle Eastern history from the myths and legends associated with the Old Testament through to the history of the Abbasid era, down to the year 915. An appendix or continuation, was written by Abu Abdullah b. Ahmad b. Ja'far al-Farghani, a student of al-Tabari. Editions Various editions of the Annals include: * An edition published under the editorship of M.J. de Goeje in three series comprising 13 volumes, with two extra volumes containing indices, introduction and glossary (Leiden, 1879ŌĆō1901). * An edition published under the editorship o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eber
Eber ( he, , ╩┐─ÆßĖćer; grc-x-biblical, ß╝£╬▓╬ĄŽü, ├ēber; ar, ž╣┘░ž¦ž©┘Éž▒, ╩┐─Ćbir) is an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites according to the "Table of Nations" in the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles (). Lineage Eber was a great-grandson of Noah's son Shem and the father of Peleg, born when Eber was 34 years old, and of Joktan. He was the son of Shelah, a distant ancestor of Abraham. According to the Hebrew Bible, Eber died at the age of 464. In the Septuagint, the name is written as Heber/Eber (), and his father is called Sala (). His son is called Phaleg/Phalek (), born when Heber was 134 years old, and he had other sons and daughters. Heber lived to an age of 464 years. Name The Aramaic/Hebrew root () is connected with crossing over and the beyond. Considering that other names for descendants of Shem also stand for places, Eber can also be considered the name of an area, perhaps near Assyria. A number of mediaeval scholars such as Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hud (prophet)
), but this is disputed , image = Prophet Hud Name.svg , image_size = 150px , alt = , caption = The name ''Hud'' written in Islamic calligraphy, followed by "Peace be upon him". , birth_name = , birth_date = , birth_place = , death_date = , death_place = , resting_place = Possibly Qabr An-Nabi Hud in Hadhramaut, South Arabia , title = Prophet , predecessor = Nuh , successor = Salih , children = , parents = , relatives = Hud (; ar, ┘ć┘Å┘ł┘Æž», H┼½d) was a prophet of ancient Arabia mentioned in the Quran. The eleventh chapter of the Quran, ''Hud'', is named after him, though the narrative of Hud comprises only a small portion of the chapter. Historical context Hud has sometimes been identified with Eber, an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites who is mentioned in the Old Testament. He is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qahtan
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, ┘é┘ÄžŁ┘ÆžĘ┘Äž¦┘å┘É┘Ŗ; transliterated: QaßĖźß╣Ł─ün─½) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs. Traditional Arab genealogy According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarab
Ya'rub ( ar, ┘Ŗž╣ž▒ž©, also spelled ''Yarob'',''Ya'rob'', ''Yarrob'', ''Yarab'' or ''Yaarub'') is an ancient Arabic personal name. He is the grandson of Abir being the son of Qahtan and the ancestor of the Himyarite and Sabaean kings of Yemen.van Donzel, 1994, p. 483. A similar account places Ya'rub as Qahtan's grandson (Ya'rub bin Yashjub bin Qahtan) and holds that he is the forefather of ''al-'Arab al-'Ariba'' ("the arab arabs" or "pure arabs"), who are generally identified with the Qahtanites and its two main tribes, the Himyar and the Kahlan.Prentiss, 2003, p. 172. Some legendary accounts relate that Ya'rub was the first to speak Arabic and that the language was named for him.Crosby, 2007, pp. 74-75.Sperl, 1989, p. 209. Shams-i Qais Razi, writing in the 12-13th century CE, traced the origins of Arabic poetry to Ya'rub and he is also credited with having invented the Kufic script.Sperl et al., 1996, p. 138.Thackston, 2001, p. 7. Ancestor of kings Ya'rub was said to be one of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheba
Sheba (; he, ''┼Ā╔ÖßĖć─ü╩Š''; ar, ž│ž©žŻ ''Saba╩Š''; Ge'ez: ßł│ßēŻ ''Saba'') is a kingdom mentioned in the Hebrew Bible ( Old Testament) and the Quran. Sheba features in Jewish, Muslim, and Christian traditions, particularly the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo tradition. It was the home of the biblical "Queen of Sheba", who is left unnamed in the Bible, but receives the names ''Makeda'' in Ethiopian and ''Bilq─½s'' in Arabic tradition. According to Josephus it was also the home of the biblical " Princess Tharbis" said to have been the first wife of Moses when he was still a prince of Egypt. There are competing theories of where this kingdom was, with some placing it in either South Arabia or the Horn of Africa. Encyclopedia Britannica posits that the biblical narrative about the kingdom of Sheba was based on the ancient civilization of Saba (Old South Arabian: É®¬É®©É®▒ ''S-b-╩Š'') in South Arabia. This view is echoed by Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman who w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saba'a
The Sabaeans or Sabeans (Sabaean:, ; ar, ┘▒┘äž│┘Ä┘æž©┘Äž”┘É┘Ŗ┘Å┘æ┘ł┘Æ┘å, ''as-Saba╩Šiyy┼½n''; he, ūĪų░ūæųĖūÉų┤ūÖūØ, S╔ÖßĖć─ü╩Š─½m) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian languages.Stuart Munro-Hay, ''Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity'', 1991. They founded the kingdom of Saba╩Š ( ar, ž│┘Äž©┘ÄžŻ, links=no) in modern-day Yemen, Quran 27:6-93 Quran 34:15-18 which was believed to be the biblical land of Sheba and "the oldest and most important of the South Arabian kingdoms". The exact date of the foundation of Saba╩Š is a point of disagreement among scholars. Kenneth Kitchen dates the kingdom to between 1200 BCE and 275 CE, with its capital at Ma╩Šrib, in what is now Yemen.Kenneth A. Kitchen ''The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series''. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 On the other hand, Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |