|
Huijian Xinmo
''Huijian Xinmo'' is a ''wuxia'' novel by Liang Yusheng first published as a serial between 23 May 1966 and 14 March 1968 in the Hong Kong newspaper '' Ta Kung Pao''. The final part of a trilogy, the novel is preceded by ''Datang Youxia Zhuan'' and '' Longfeng Baochai Yuan''. The title of the novel comes from a Buddhist saying, ''huī huìjiàn, zhǎn xīnmó'' (), which means "brandish the sword of wisdom and slay your inner demons". Plot The novel is set in China during the Tang dynasty towards the end of the An Lushan Rebellion (755–763), and serves as a continuation of '' Longfeng Baochai Yuan'', the second part of the trilogy. Decades have passed since Wang Yanyu killed Dou Lingkan and the Wangs massacred the Dous in the first novel ''Datang Youxia Zhuan''. Unknown to everyone, Dou Yuan, a member of the Dou family, had survived the massacre and spent the past several years training in martial arts with the aim of avenging his family. Upon revealing himself to the '' wu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Yusheng
Chen Wentong (5 April 1924 – 22 January 2009), better known by his pen name Liang Yusheng, was a Chinese writer. Credited as the pioneer of the "New School" (新派) of the ''wuxia'' genre in the 20th century, Chen was one of the best known ''wuxia'' writers in the later half of the century, alongside Jin Yong and Gu Long. Life Chen was born in a family of scholars in Mengshan County, Guangxi Province, China. He was well-versed in ancient Chinese classics and '' duilian'' and could recite the ''Three Hundred Tang Poems'' by the age of seven. He started writing poems when he was attending Guilin High School in Guangxi. He was tutored by Jian Youwen, who specialised in the history of the Taiping Rebellion, and Rao Zongyi, who was well read in poetry, humanities, art and the history of Dunhuang. Chen learnt history and literature from both of them. Later, he was accepted into Guangzhou's Lingnan University, and he graduated in 1948 with a degree in economics. In 1949, he settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuxia
( ), which literally means "martial heroes", is a genre of Chinese fiction concerning the adventures of martial artists in ancient China. Although is traditionally a form of historical fiction, its popularity has caused it to be adapted for such diverse art forms as Chinese opera, manhua, television dramas, films, and video games. It forms part of popular culture in many Chinese-speaking communities around the world. The word "" is a compound composed of the elements (, literally "martial", "military", or "armed") and (, literally "chivalrous", "vigilante" or "hero"). A martial artist who follows the code of is often referred to as a (, literally "follower of ") or (, literally "wandering "). In some translations, the martial artist is referred to as a "swordsman" or "swordswoman" even though they may not necessarily wield a sword. The heroes in wuxia fiction typically do not serve a lord, wield military power, or belong to the aristocratic class. They often originat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ta Kung Pao
''Ta Kung Pao'' (; formerly ''L'Impartial'') is the oldest active Chinese language newspaper in China. Founded in Tianjin in 1902, the paper is state-owned, controlled by the Liaison Office of the Central Government after the Chinese Civil War. It is widely regarded as a veteran pro-Beijing newspaper. In 2016, it merged with Hong Kong newspaper Wen Wei Po. History In the final years of the Qing dynasty, Ying Lianzhi, a Catholic Manchu aristocrat, founded the newspaper in Tianjin on 17 June 1902, in order to, "help China become a modern and democratic nation". The paper put forward the slogan ''Four-No-ism" (四不主義)'' in its early years, pledging to say "No" to all political parties, governments, commercial companies, and persons. It stood up to the repression at the time, openly criticising the Empress Dowager Cixi and reactionary leaders, and promoted democratic reforms, pioneering the use of written vernacular Chinese (''baihua''). Readership fell after the Xinhai Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longfeng Baochai Yuan
''Longfeng Baochai Yuan'' is a ''wuxia'' novel by Liang Yusheng first published as a serial between 25 June 1964 and 15 May 1966 in the Hong Kong newspaper '' Ta Kung Pao''. The second part of a trilogy, the novel is preceded by ''Datang Youxia Zhuan'' and followed by ''Huijian Xinmo''. Plot The novel is set in China during the Tang dynasty against the backdrop of the rebellion against the Tang government (755–763) by An Lushan, and serves as a continuation of the previous novel ''Datang Youxia Zhuan''. Duan Guizhang and Shi Yiru had arranged for their respective children to be married if they were of opposite sexes. A pair of ornamental hairpins, the titular Dragon and Phoenix Hairpins, were exchanged by both sides as a token of their agreement; the Duans kept the Dragon Hairpin while the Shis had the Phoenix Hairpin. Earlier in ''Datang Youxia Zhuan'', Shi Yiru had committed suicide while he was held captive by An Lushan, and Duan Guizhang had been killed in battle durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuxia
( ), which literally means "martial heroes", is a genre of Chinese fiction concerning the adventures of martial artists in ancient China. Although is traditionally a form of historical fiction, its popularity has caused it to be adapted for such diverse art forms as Chinese opera, manhua, television dramas, films, and video games. It forms part of popular culture in many Chinese-speaking communities around the world. The word "" is a compound composed of the elements (, literally "martial", "military", or "armed") and (, literally "chivalrous", "vigilante" or "hero"). A martial artist who follows the code of is often referred to as a (, literally "follower of ") or (, literally "wandering "). In some translations, the martial artist is referred to as a "swordsman" or "swordswoman" even though they may not necessarily wield a sword. The heroes in wuxia fiction typically do not serve a lord, wield military power, or belong to the aristocratic class. They often originat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial (literature)
In literature, a serial is a printing or publishing format by which a single larger work Work may refer to: * Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community ** Manual labour, physical work done by humans ** House work, housework, or homemaking ** Working animal, an animal t ..., often a work of narrative fiction, is published in smaller, sequential instalments. The instalments are also known as ''numbers'', ''parts'' or ''fascicles'', and may be released either as separate publications or within sequential issues of a periodical publication, such as a magazine or newspaper. Serialisation can also begin with a single short story that is subsequently turned into a series. Historically, such series have been published in periodicals. Popular short-story series are often published together in book form as collections. Early history The growth of moveable type in the 17th century prompted episodic and often disconnec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datang Youxia Zhuan
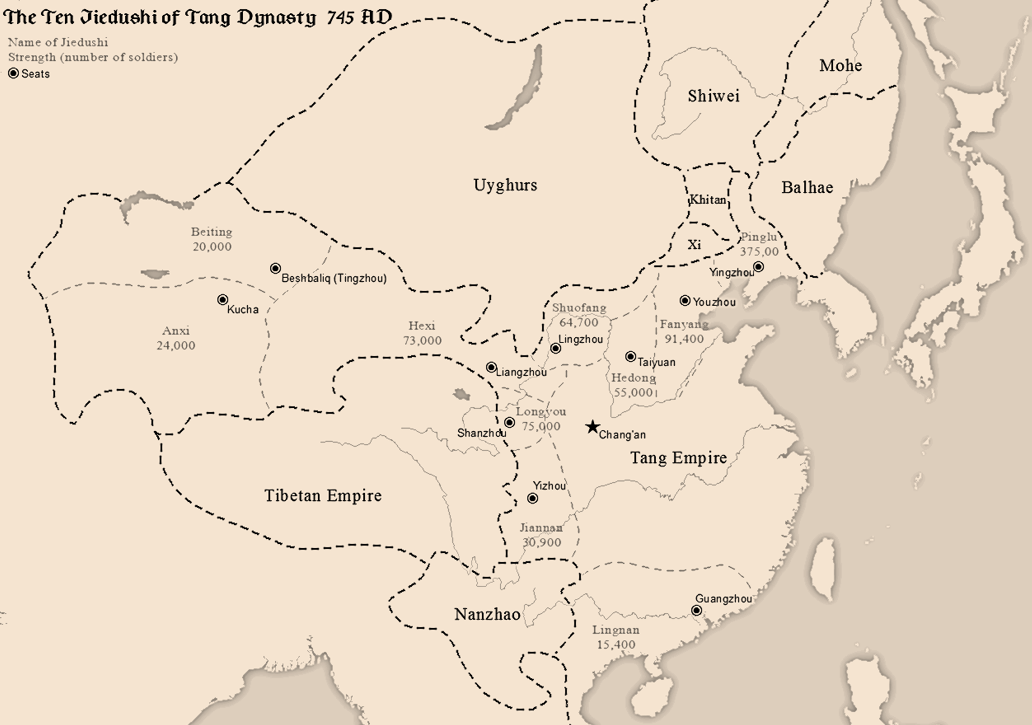
''Datang Youxia Zhuan'' is a ''wuxia'' novel by Liang Yusheng. It was first serialised between 1 January 1963 and 14 June 1964 in the Hong Kong newspaper ''Ta Kung Pao''. The novel is the first part of a trilogy, and is followed by '' Longfeng Baochai Yuan'' and '' Huijian Xinmo''. Plot The novel is set in the Tianbao era (742–756) of the Tang dynasty during the reign of Emperor Xuanzong. The emperor appoints the incompetent Yang Guozhong as chancellor because his cousin, Yang Yuhuan, is the emperor's favourite concubine. Nepotism and cronyism prevail as Yang Guozhong places his relatives and supporters in high-ranking posts in the Tang government, which becomes increasingly corrupt over time. The power-hungry barbarian An Lushan wins the emperor's trust through flattery and gets promoted to the position of ''jiedushi'' (military governor) of Fanyang. An Lushan wields great power in his hands and secretly builds up his military forces in preparation for a rebellion. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prajñā (Buddhism)
Prajñā (Sanskrit: प्रज्ञा) or paññā (Pāli: पञ्ञा), is a Buddhist term often translated as "wisdom", "intelligence", or "understanding". It is described in Buddhist texts as the understanding of the true nature of phenomena. In the context of Buddhist meditation, it is the ability to understand the three characteristics of all things: ''anicca'' ("impermanence"), '' dukkha'' ("dissatisfaction" or "suffering"), and '' anattā'' ("non-self"). Mahāyāna texts describe it as the understanding of ''śūnyatā'' ("emptiness"). It is part of the Threefold Training in Buddhism, and is one of the ten '' pāramīs'' of Theravāda Buddhism and one of the six Mahāyāna ''pāramitās''. Etymology ''Prajñā'' () is often translated as "wisdom", but according to Buddhist bioethics scholar Damien Keown, it is closer in meaning to "insight", "non-discriminating knowledge", or "intuitive apprehension". * ''jñā'' () can be translated as "consciousness", "knowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jianghu
''Jianghu'' () is a term that generally refers to the milieu, environment, or sub-community in which many Chinese wuxia stories are set. The term is used flexibly, and can be used to describe a fictionalized version of Historical China (usually using loose influences from across the ~1000 BCE–280 AD period); a setting of feuding martial arts clans and the people of that community; a secret and possibly criminal underworld; a general sense of the "mythic world" where fantastical stories happen; or some combination thereof. Background In modern Chinese culture, ''jianghu'' is commonly accepted as an alternative universe coexisting with the actual historical one in which the context of the wuxia genre was set. Unlike the normal world, in the ''jianghu'' ''xia'' (wanderers, knight-errants) are free to act on their own initiative, including with violence, to punish evil and foes, and to reward goodness and allies. While the term literally means "rivers and lakes", it is broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur People
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central Asia, Central and East Asia. The Uyghurs are recognized as native to the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwest China. They are one of Ethnic minorities in China, China's 55 officially recognized ethnic minorities. The Uyghurs are recognized by the Government of China, Chinese government as a Regional language, regional minority and the Titular nation, titular people of Xinjiang. The Uyghurs have traditionally inhabited a series of Oasis, oases scattered across the Taklamakan Desert within the Tarim Basin. These oases have historically existed as independent states or were controlled by many civilizations including History of China, China, the Mongol Empire, Mongols, the Tibetan Empire, Tibetans and various List of Turkic dynasties and countries, Turkic po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |