|
Huayna PotosĂ
Huayna PotosĂ is a mountain in Bolivia, located near El Alto and about 25 km north of La Paz in the Cordillera Real. Huayna PotosĂ is the closest high mountain to La Paz. Surrounded by high mountains, it is roughly 15 miles due north of the city, which makes this mountain the most popular climb in Bolivia. The normal ascent route is a fairly straightforward glacier climb, with some crevasses and a steep climb to the summit. However, the other side of the mountainâHuayna PotosĂ West Faceâis the biggest face in Bolivia. Several difficult snow and ice routes ascend this 1000 meter high face. The first ascent of the normal route was undertaken in 1919 by Germans Rudolf Dienst and Adolf Schulze. Some climbing books report this mountain as the "easiest 6000er in the world", but this claim is debatable. The easiest route entails an exposed ridge and sections of moderately steep ice, with a UIAA rating of PD. There are many 6000m mountains that are easier to cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancohuma
Ancohuma or Janq'u Uma (Aymara ''janq'u'' white, ''uma'' water, "white water", also spelled Janq'uma, other spellings, ''Jankho Uma'', ''Jankhouma'') is the third highest mountain in Bolivia (after Sajama and Illimani). It is located in the northern section of the Cordillera Real, part of the Andes, east of Lake Titicaca. It lies just south of the slightly lower Illampu, near the town of Sorata Sorata ( Aymara: ''Surat'a'') is a small town in the La Paz Department in the Bolivian Andes, northwest of the city of La Paz and east of Lake Titicaca. It is the seat of the Larecaja Province and the Sorata Municipality. At the time of census .... Despite being higher than Illampu, Ancohuma is a gentler peak, with less local relief, and it is a somewhat easier climb. The peak was first climbed in 1919, by Rudolf Dienst and Adolf Schulze. Their route, still the easiest, climbs the southwest face, and is rated PD (not very difficult). Other routes exist on the northwest ridge and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acclimatization
Acclimatization or acclimatisation ( also called acclimation or acclimatation) is the process in which an individual organism adjusts to a change in its environment (such as a change in altitude, temperature, humidity, photoperiod, or pH), allowing it to maintain fitness across a range of environmental conditions. Acclimatization occurs in a short period of time (hours to weeks), and within the organism's lifetime (compared to adaptation, which is evolution, taking place over many generations). This may be a discrete occurrence (for example, when mountaineers acclimate to high altitude over hours or days) or may instead represent part of a periodic cycle, such as a mammal shedding heavy winter fur in favor of a lighter summer coat. Organisms can adjust their morphological, behavioral, physical, and/or biochemical traits in response to changes in their environment. While the capacity to acclimate to novel environments has been well documented in thousands of species, research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PotosĂ Mountain Range
The PotosĂ mountain range in Bolivia is situated east and southeast of the city of PotosĂ. It is at least 25 km long stretching from north to south. Its highest mountain is Khunurana (Anaruyu) rising up to 5,071 m (16,637 ft). The features of the range are considered the product of volcanic activity known as the Khari Khari caldera (19Âș43'S; 65Âș38'W). The caldera is about 40 km long and 25 km at its widest point. The range was named ''Cordillera de PotosĂ'' by the German alpinist Henry Hoek in 1903. He collected information about the range like the local names and published several papers about it. The inhabitants of the area, however, use the names Khari Khari for the northern part and Anta Q'awa for the southern one. The two sections are separated by a depression, the Jach'a Molino Pampa. Mountains Khari Khari range The Khari Khari range contains a number of mountains which are more than 4,900 m high, the highest elevation being Khari K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Kunturiri, Los Andes
Kunturiri (Aymara language, Aymara ''kunturi'' condor, ''-(i)ri'' a suffix, Hispanicized spelling ''Condoriri'') is a mountain in the Cordillera Real (Bolivia), Cordillera Real of Bolivia, about high. It is also the name of the whole massif. Kunturiri is located in the La Paz Department (Bolivia), La Paz Department, Los Andes Province, Bolivia, Los Andes Province, Pucarani Municipality, Pukarani Municipality, southeast of Chachakumani and northwest of Huayna PotosĂ. The central part of the Kunturiri group is formed by three peaks which resemble a condor with wings spread: * the Kunturiri itself, also called ''Cabeza de(l) Condor'' (Spanish language, Spanish for "head of the condor") (), * ''Ala Izquierda'' ("left wing"), ''Ala Norte'' ("north wing") (), the Kunturiri west peak and * ''Ala Derecha'' ("right wing") or ''Ala Sur'' ("south wing") (). Kuchillu Khunu (Aymara ''kuchillu'' knife (from Spanish ''cuchillo''), ''khunu'' snow, "knife snow") is the name of the peak south o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milluni Peak
Milluni Peak, also known as or Pico Milluni (composed of Spanish ''pico'' peak and Aymara ''milluni'', ''millu'' light brown, reddish, fair-haired, dark chestnut, ''-ni'' suffix to indicate ownership, "the brown one"), is a mountain in the Andes, about 5,483 m (17,989 ft) high, located in the Cordillera Real of Bolivia in the La Paz Department, Pedro Domingo Murillo Province, El Alto Municipality. Map of the area (north is upper left) showing "Cerro Pico Milluni" It is situated south of Wayna PotosĂ and northeast of and |
Guest Book
A guestbook (also guest book, visitor log, visitors' book, visitors' album) is a paper or electronic means for a visitor to acknowledge a visit to a site, physical or web-based, and leave details such as their name, postal or electronic address and any comments. Such paper-based ledgers or books are traditional in church (building), churches, at weddings, funerals, Bed and breakfast, B&Bs, museums, schools, institutions and other private facilities open to the public. Some private homes keep visitors' books. Specialised forms of guestbooks include hotel registers, wherein guests are required to provide their contact information, and Books of Condolence, which are used at funeral homes and more generally after notable public deaths, such as the death of a monarch or president, or after a public disaster, such as an airplane crash. On the web, a guestbook is a logging system that allows visitors of a website to leave a public comment. It is possible in some guestbooks for vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
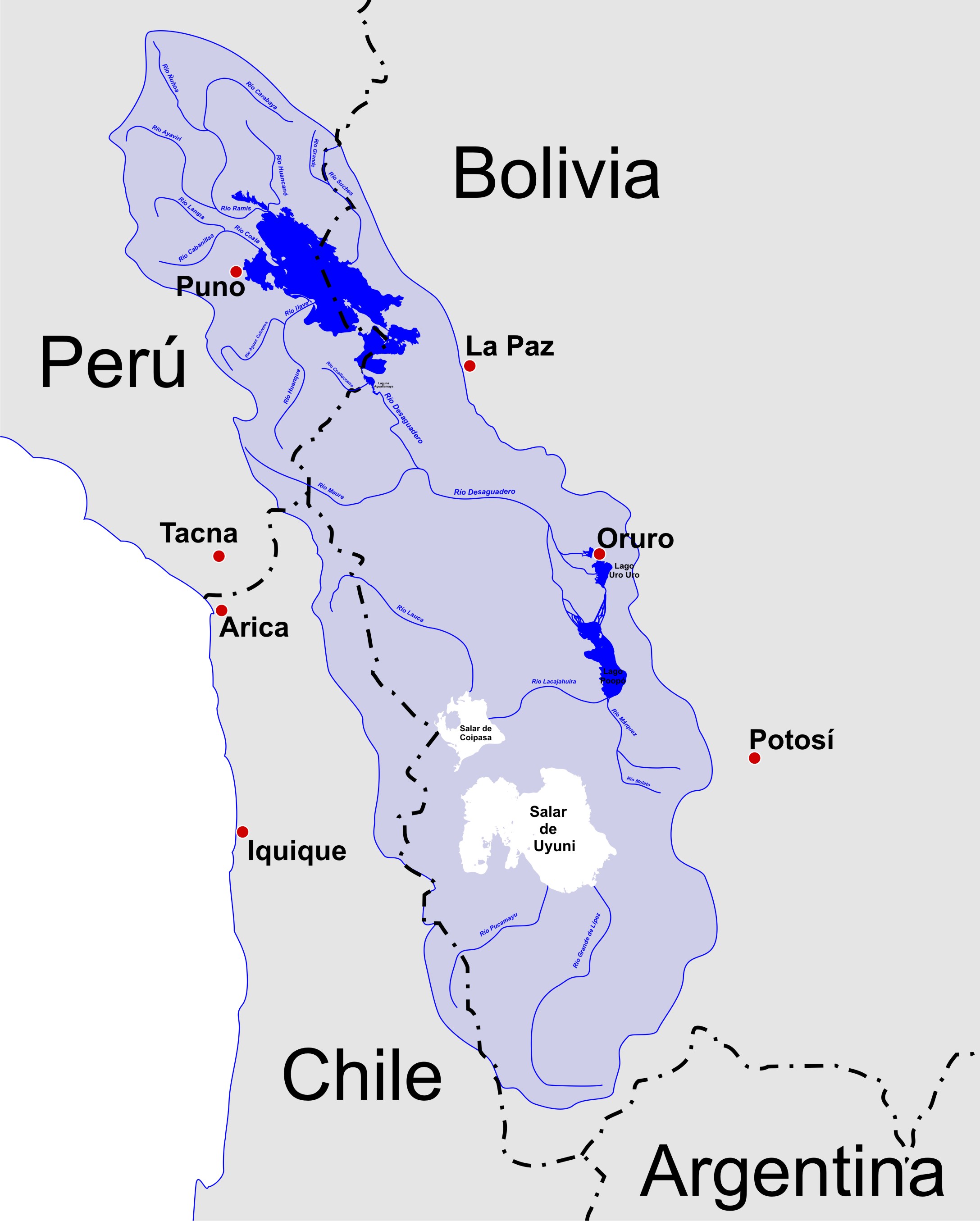
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the BoliviaâPeru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake PoopĂł, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Titicaca
Lake Titicaca (; es, Lago Titicaca ; qu, Titiqaqa Qucha) is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. By volume of water and by surface area, it is also the largest lake in South America.Grove, M. J., P. A. Baker, S. L. Cross, C. A. Rigsby and G. O. Seltzer 2003 Application of Strontium Isotopes to Understanding the Hydrology and Paleohydrology of the Altiplano, Bolivia-Peru. ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' 194:281-297. Lake Titicaca has a surface elevation of . The "highest lake" claim is generally considered to refer to commercial craft. Numerous smaller bodies of water (that are not considered lakes) around the world are at higher elevations. For many years, the largest vessel afloat on the lake was the 2,200-ton (2,425 U.S. tons), SS ''Ollanta''. Today, the largest vessel is most likely the similarly sized train barge/float ''Manco Capac'', operated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain. Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and earthquakes. Primarily composed of flowing snow and air, large avalanches have the capability to capture and move ice, rocks, and trees. Avalanches occur in two general forms, or combinations thereof: slab avalanches made of tightly packed snow, triggered by a collapse of an underlying weak snow layer, and loose snow avalanches made of looser snow. After being set off, avalanches usually accelerate rapidly and grow in mass and volume as they capture more snow. If an avalanche moves fast enough, some of the snow may mix with the air, forming a powder snow avalanche. Though they appear to share similarities, avalanches are distinct from slush flows, mudslides, rock slides, and serac collapses. They are also different from large scale movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
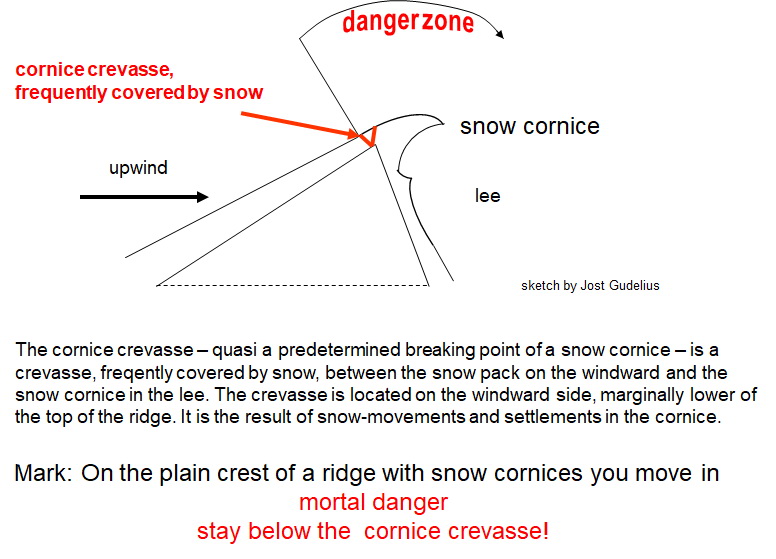
Cornice (climbing)
A snow cornice or simply cornice (from the Italian cornice meaning "ledge") is an overhanging edge of snow on a ridge or the crest of a mountain and along the sides of gullies. Formation A snow cornice forms by wind blowing snow over sharp terrain breaks (e.g. the crest of the mountain) where it attaches and builds out horizontally. This build-up is most common on the steeper and leeward sides of mountains. Cornices are extremely dangerous and travelling above or below them should be avoided. When a cornice ''collapses'', it breaks in from the cornice to the top of the peak; even being on the snow on top of rock exposes the alpinist to hazard in this situation. The best practice in mountaineering is to stay far enough back from the edge so as not to be able to see the drop, as an approximate metric of exposure. Interview und Bilder zum UnglĂŒck In avalanche safety, cornices are a high avalanche danger as they often break and trigger larger avalanches that permeate several snow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArĂȘte
An arĂȘte ( ) is a narrow ridge of rock which separates two valleys. It is typically formed when two glaciers erode parallel U-shaped valleys. ArĂȘtes can also form when two glacial cirques erode headwards towards one another, although frequently this results in a saddle-shaped pass, called a col. The edge is then sharpened by freeze-thaw weathering, and the slope on either side of the arĂȘte steepened through mass wasting Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ... events and the erosion of exposed, unstable rock. The word ''arĂȘte'' () is actually French for "edge" or "ridge"; similar features in the Alps are often described with the German language, German equivalent term ''Grat''. Where three or more cirques meet, a pyramidal peak is created. Cleaver A ''cleaver' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergschrund
A bergschrund (from the German for ''mountain cleft'') or rimaye (from French; ) is a crevasse that forms where moving glacier ice separates from the stagnant ice or firn above. It is often a serious obstacle for mountaineers, who sometimes abbreviate "bergschrund" to "schrund". Bergschrunds extend to the bedrock and can have a depth of well over . The bergschrund is distinct from the randkluft (also called ''rimaye''), which is the crevasse of which one face is the rock, back wall of the corrie. The randkluft arises in part from the melting of the ice due to the presence of the warmer rock face. However, the randkluft is sometimes called a bergschrund. The French word ''rimaye'' covers both notions of randkluft and bergschrund. In a corrie or cirque, the bergschrund is positioned at the rear, parallel to the back wall of the corrie. It is caused by the rotational movement of the glacier. In a longitudinal glacier, the bergschrund is at the top end of the glacier at a right angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |