|
Huantajaya
Huantajaya or San Agustín de Huantajaya was a silver mine in Chile in the Tarapacá area of Atacama Desert east of Iquique. The silver riches of Tarapacá were known to the Spanish since the time of the conquest of the Inca Empire. Pedro Pizarro mentions Tarapacá as region with silver in his 1571 book ''Relación del descubrimiento y conquista de los reinos del Perú''. The main period of activity was in the 18th century. During this time the nearby oasis town of Pica prospered as a supply center. In the 18th century the richest area of Huantajaya was known as ''Criadero'' and tuberous aggregates of silver dug there were known as ''papas'' (lit. potatoes). One of the largest such ''papas'', weighing 800 pounds, was unearthed in 1729 and sent as gift to the King of Spain. The geology of the silver deposit at Huatajaya was recognised by contemporary mining businessman Bartolomé Loayza y Valdés as "not of the same caste as the other minerals epositsof the Kingdom". This geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pica, Chile
Pica is a Chilean town and commune in Tamarugal Province, Tarapacá Region. Situated in the inland of the Atacama Desert on an oasis, Pica is famous for its small and unusually acidic limes known as Limón de Pica. The town has a communal hot spring with a surface temperature of 40 °C, which makes it a popular bath place in the middle of the desert. It has hotels and all basic services. The town lies four kilometers to the northeast of the oasis village of Matilla. Pica has a mild microclimate that does not display the typical high temperature oscillations seen in many of the worlds deserts. The settlement has pre-Hispanic origins and served as an important stopover for transit between the coast and the Altiplano during the time of the Inca Empire. Bird mummies of pre-Hispanic origin have been found next to Pica. Pica gained prominence over the course of the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries when it grew in association with important mining cycles of nearby areas. The first min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarapacá Region
The Tarapacá Region ( es, Región de Tarapacá, ) is one of Chile's 16 first-order administrative divisions. It comprises two provinces, Iquique and Tamarugal. It borders the Chilean Arica and Parinacota Region to the north, Bolivia's Oruro Department and Potosí Department on the east, Chile's Antofagasta Region to the south and the Pacific Ocean to the west. The port city of Iquique is the region's capital. Much of the region was once the Tarapacá Province of Peru, which was annexed by Chile under the 1883 Treaty of Ancón at the close of the War of the Pacific. The region was important economically as a site of intense saltpeter mining, before synthetic nitrate manufacturing became possible. A number of abandoned mining towns can still be found in the region. The present day Tarapacá Region was created in 2007 by subdividing the former Tarapacá Region under Law No. 20,175, which was signed by President Michelle Bachelet in Arica. Administration The government of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ... element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Mines In Chile
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mines In Tarapacá Region
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines * Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacna
Tacna was known for its mining industry; it had significant deposits of sodium nitrate and other resources. Its economic prosperity attracted a wave of immigrants from Italy. Today, their Italian Peruvian descendants live in the city and many of them still have Italian surnames. This era of successful commerce and agriculture ended drastically with the start of the War of the Pacific. Hosting a large Peru-Bolivian army under poor sanitary conditions the city lost a substantial part of its population to infectious diseases before its capture by Chile in May 1880 following a Battle of Tacna, defeat of the allied army in the outskirts of the city by a Chilean force under General Manuel Baquedano. Occupation by Chile During the war, the cities of Tacna and Arica, Chile, Arica were occupied by the Chilean Army, with Tacna being incorporated as a Communes of Chile, commune with a Tacna Province (Chile), province of the same name. A peace agreement, the Treaty of Ancón, was signed in 188 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potosí
Potosí, known as Villa Imperial de Potosí in the colonial period, is the capital city and a municipality of the Department of Potosí in Bolivia. It is one of the highest cities in the world at a nominal . For centuries, it was the location of the Spanish colonial silver mint. A considerable amount of the city's colonial architecture has been preserved in the historic center of the city, which - along with the globally important Cerro Rico de Potosí - are part of a designated UNESCO World Heritage Site. Potosí lies at the foot of the ''Cerro de Potosí'' —sometimes referred to as the ''Cerro Rico'' ("rich mountain")— a mountain popularly conceived of as being "made of" silver ore that dominates the city. The Cerro Rico is the reason for Potosí's historical importance since it was the major supply of silver for the Spanish Empire until Guanajuato in Mexico surpassed it in the 18th century. The silver was taken by llama and mule train to the Pacific coast, shipped north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lima
Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of the central coastal part of the country, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaside city of Callao, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area. With a population of more than 9.7 million in its urban area and more than 10.7 million in its metropolitan area, Lima is one of the largest cities in the Americas. Lima was named by natives in the agricultural region known by native Peruvians as ''Limaq''. It became the capital and most important city in the Viceroyalty of Peru. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru (República del Perú). Around one-third of the national population now lives in its Lima Metropolitan Area, metropolitan area. The city of Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chungara (journal)
''Chungara Revista de Antropología Chilena'' (English: ''The Journal of Chilean Anthropology'') is a peer-reviewed academic journal on anthropology and archaeology with particular, but not exclusive, focus on the Andean region. The journal is published by the Departamento de Antropología (Universidad de Tarapacá) and the editor-in-chief is Vivien G. Standen (Universidad de Tarapacá). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index, Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 0.694. References External links * Anthropology journals Multilingual journals Academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
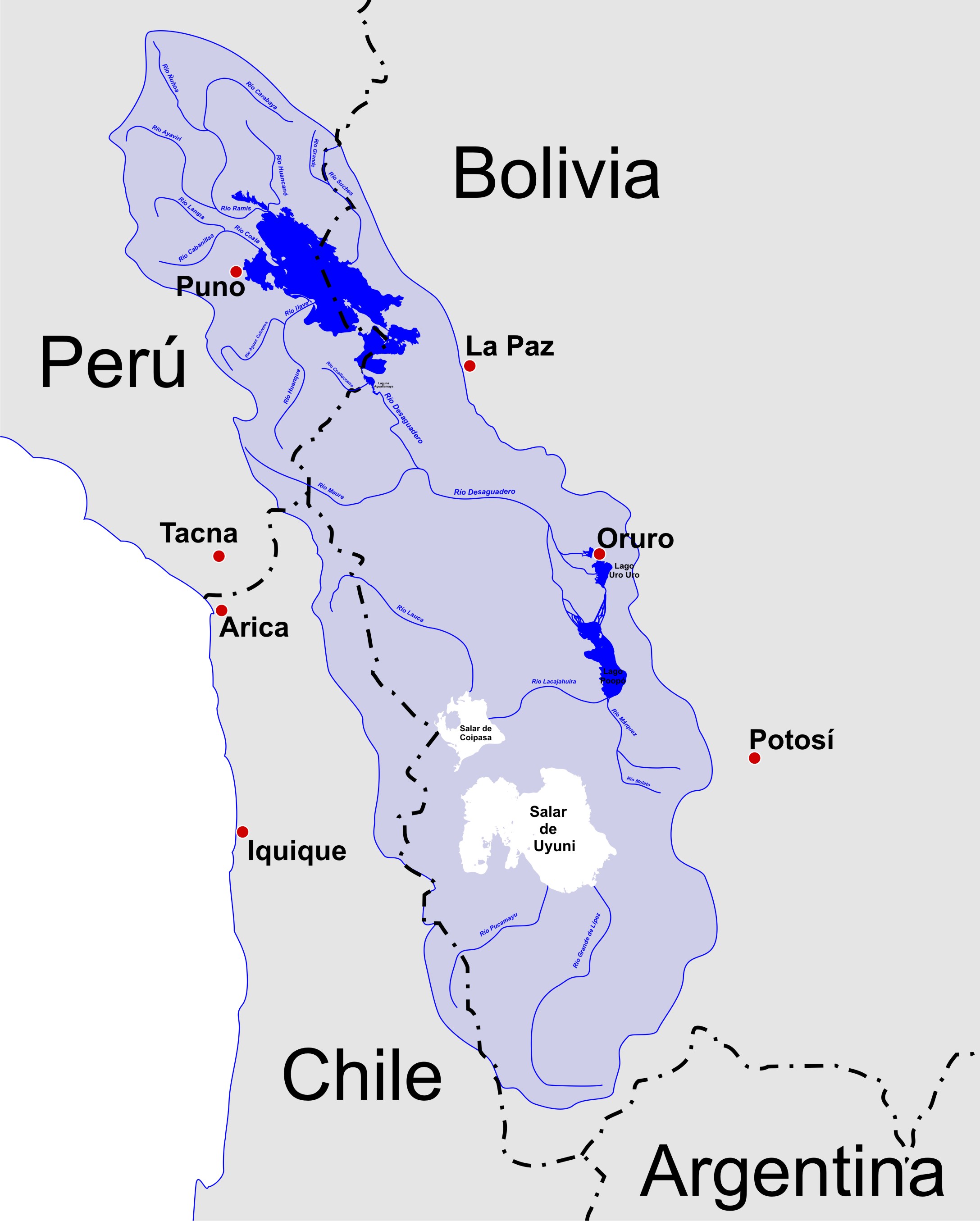
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carangas Province
Carangas is a province in the northern parts of the Bolivian department of Oruro. Location ''Carangas'' province is one of sixteen provinces in the Oruro Department. It is located between 17° 59' and 18° 54' South and between 67° 09' and 67° 45' West. It borders San Pedro de Totora Province in the northwest, Sajama Province in the west, Litoral Province in the southwest, Sud Carangas Province in the southeast, Saucarí Province in the east, and Nor Carangas Province in the northeast. The province extends over 105 km from North to South, and 75 km from east to west. Population The main language of the province is Aymara, spoken by 94%, while 84% of the population speak Spanish and 13% Quechua. The population increased from 7,930 inhabitants (1992 census) to 10,505 (2001 census), an increase of 32.5%. - 43.1% of the population is younger than 15 years old. 92.5% of the population have no access to electricity, 98.1% have no sanitary facilities. 79.8% of the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_Guamán_Poma%2C_1616.jpg)