|
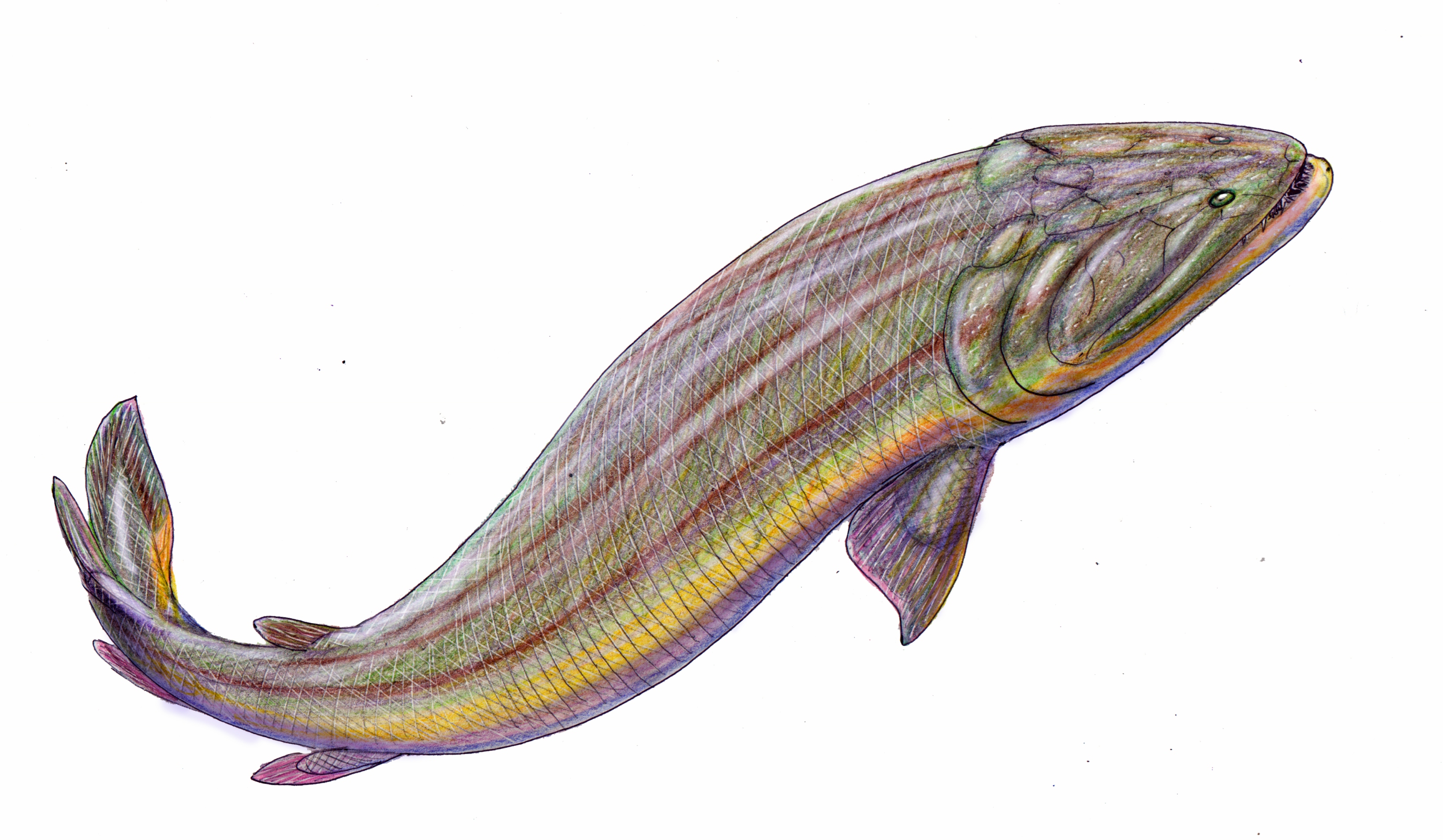
Hongyu Chen
''Hongyu'', represented by its type species ''Hongyu chowi'', is an extinct Devonian lobe-finned fish. About 1.5 m in length, it resembles both Elpistostegalia and Rhizodontida, making its phylogenetic placement uncertain. The type specimen was discovered in the Zhongning Formation near Ningxia in China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...’s North China Block. References Tetrapodomorphs Prehistoric lobe-finned fish genera Devonian bony fish Prehistoric animals of China {{Paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famennian
The Famennian is the latter of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Epoch. The most recent estimate for its duration estimates that it lasted from around 371.1 million years ago to 359.3 million years ago. An earlier 2012 estimate, still used by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, estimated that it lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Frasnian stage and followed by the Tournaisian stage. Major events In the seas, a novel major group of ammonoid cephalopods called clymeniids appeared, underwent tremendous diversification and spread worldwide, then just as suddenly went extinct. The beginning of the Famennian is marked by the final stages of a major extinction event, the Kellwasser Event, which is the largest component of the Late Devonian Mass extinction. The end of the Famennian experiences a smaller but still quite severe extinction event, the Hangenberg Event. A brief episode of glaciation, possibly linked to the Hangenber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elpistostegalia
Elpistostegalia or Panderichthyida is an order of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which lived during the Middle Devonian to Late Devonian period (about 385 to 374 million years ago). They represent the advanced tetrapodomorph stock, the fishes more closely related to tetrapods than the osteolepiform fishes. The earliest elpistostegalians, combining fishlike and tetrapod-like characters, are sometimes called fishapods, a phrase coined for the advanced elpistostegalian ''Tiktaalik''. Through a strict cladistic view, the order includes the terrestrial tetrapods. Palaeobiology of the elpistostegalians A rise in global oxygen content allowed for the evolution of large, predatory fish that were able to exploit the shallow tidal areas and swamplands as top predators. Several groups evolved to fill these niches, the most successful were the elpistiostegalians. In such environments, they would have been challenged by periodic oxygen deficiency. In comparable modern aquatic environments l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizodontida
Rhizodontida is an extinct group of predatory tetrapodomorphs known from many areas of the world from the Givetian through to the Pennsylvanian - the earliest known species is about 377 million years ago (Mya), the latest around 310 Mya. Rhizodonts lived in tropical rivers and freshwater lakes and were the dominant predators of their age. They reached huge sizes - the largest known species, '' Rhizodus hibberti'' from Europe and North America, was an estimated 7 m in length, making it the largest freshwater fish known. Description The upper jaw had a marginal row of small teeth on the maxilla and premaxilla, medium-sized fangs on the ectopterygoid and dermopalatine bones, and large tusks on the vomers and premaxillae. On the lower jaw were marginal teeth on the dentary, with fangs on the three coronoids and a huge tusk at the symphysial tip of the dentary. Apparently, the left and right mandibles rotated inwards towards each other on biting. This may have been a kinetic mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongning Formation
Zhongning County is a county under the administration of Zhongwei city in west-central Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, bordering Inner Mongolia to the northwest. It is the point at which the northern twist of the Yellow River begins, creating the Ordos Loop. It has a total area of , and a population of approximately 410,000 people. Zhongning County is an agricultural county. In addition to traditional agricultural products, Wolfberries have begun to be cultivated in recent years. However, due to a drought, the growing range for the berries has not significantly increased. The county government is located in the town of Ningan and the county's postal code is 755100. Administrative divisions Zhongning County has 6 towns and 6 townships. ;6 towns * Ning′an (, ) * Enhe Enhe Russian Ethnic Township () is an ethnic township in Northeast Inner Mongolia under the administration of Ergun City. The township along the banks of the Argun River. Enhe i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1954 but was later separated from Gansu in 1958 and reconstituted as an autonomous region for the Hui people, one of the 56 officially recognised nationalities of China. Twenty percent of China's Hui population lives in Ningxia. Ningxia is bounded by Shaanxi to the east, Gansu to the south and west and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north and has an area of around . This sparsely settled, mostly desert region lies partially on the Loess Plateau and in the vast plain of the Yellow River and features the Great Wall of China along its northeastern boundary. Over about 2000 years an extensive system of canals (The total length about 1397 kilometers) has been built from Qin dynasty. Extensive land reclamation and irrigation projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North China Craton
The North China Craton is a continental crustal block with one of Earth's most complete and complex records of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic processes. It is located in northeast China, Inner Mongolia, the Yellow Sea, and North Korea. The term craton designates this as a piece of continent that is stable, buoyant and rigid. Basic properties of the cratonic crust include being thick (around 200 km), relatively cold when compared to other regions, and low density. The North China Craton is an ancient craton, which experienced a long period of stability and fitted the definition of a craton well. However, the North China Craton later experienced destruction of some of its deeper parts (decratonization), which means that this piece of continent is no longer as stable. The North China Craton was at first some discrete, separate blocks of continents with independent tectonic activities. In the Paleoproterozoic (2.5-1.8 billion years ago) the continents collided and amalg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorphs
The Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) are a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as ''Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodamorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the Stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a humerus with convex he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Lobe-finned Fish Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Bony Fish
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |