|
Hominid Dispersals In Europe
Hominid dispersals in Europe refers to the colonisation of the European continent by various species of hominid, including hominins and archaic and modern humans. Short and repetitive migrations of archaic humans before 1 million years ago suggest that their residence in Europe was not permanent at the time. Colonisation of Europe in prehistory was not achieved in one immigrating wave, but instead through multiple dispersal events. Most of these instances in Eurasia were limited to 40th parallel north. Besides the findings from East Anglia, the first constant presence of humans in Europe begins 500,000–600,000 years ago. However, this presence was limited to western Europe, not reaching places like the Russian plains, until 200,000–300,000 years ago. The exception to this was discovered in East Anglia, England, where hominids briefly inhabited 700,000 years ago. Prior to arriving in Europe, the source of hominids appeared to be East Africa, where stone tools and hominid fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonisation (biology)
Colonisation or colonization is the process in biology by which a species spreads to new areas. Colonisation often refers to ''successful'' immigration where a population becomes integrated into an ecological community, having resisted initial local extinction. In ecology, it is represented by the symbol ''λ'' (lowercase lambda) to denote the long-term intrinsic growth rate of a population. One classic scientific model in biogeography posits that species must continue to colonize new areas through its life cycle (called a ''taxon cycle'') in order to achieve longevity. Accordingly, colonisation and extinction are key components of island biogeography, a theory that has many applications in ecology, such as metapopulations. Scale Colonisation occurs on several scales. In the most basic form, as biofilm in the formation of communities of microorganisms on surfaces. In small scales such as colonising new sites, perhaps as a result of environmental change. And on larger scales w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenyapithecus
''Kenyapithecus wickeri'' is a fossil ape discovered by Louis Leakey in 1961 at a site called Fort Ternan in Kenya. The upper jaw and teeth were dated to 14 million years ago. One theory states that ''Kenyapithecus'' may be the common ancestor of all the great apes. More recent investigations suggest ''Kenyapithecus'' is more primitive than that and is only slightly more modern than ''Proconsul'', which is considered to be an ape. Evidence suggests that ''Kenyapithecus wickeri'' was one of the species that started a radiation of apes out of Africa. Morphology Impressed by ''Kenyapithecus''s modern-looking teeth, Leakey declared ''Kenyapithecus'' to be "a very early ancestor of man himself." ''Kenyapithecus'' possessed craniodental adaptations for hard object feeding including thicker molar enamel, and a large mandible, large premolars and upper incisors that are similar to those seen in living pitheciine monkeys. ''Kenyapithecus'' also possessed macaque-like limbs ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas). The term was originally introduced by Camille Arambourg (1948). Arambourg combined the categories of ''Hominina'' and ''Simiina'' due to Gray (1825) into his new subtribe. Traditionally, chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans were grouped together as pongids. Since Gray's classification, evidence has accumulated from genetic phylogeny confirming that humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas are more closely related to each other than to the orangutan. The former pongids were reassigned to the subfamily Hominidae ("great apes"), which already included humans, but the details of this reassignment remain contested; within Hominini, not every source excludes gorillas, and not every source includes chimpanzees. Humans are the only extant species in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
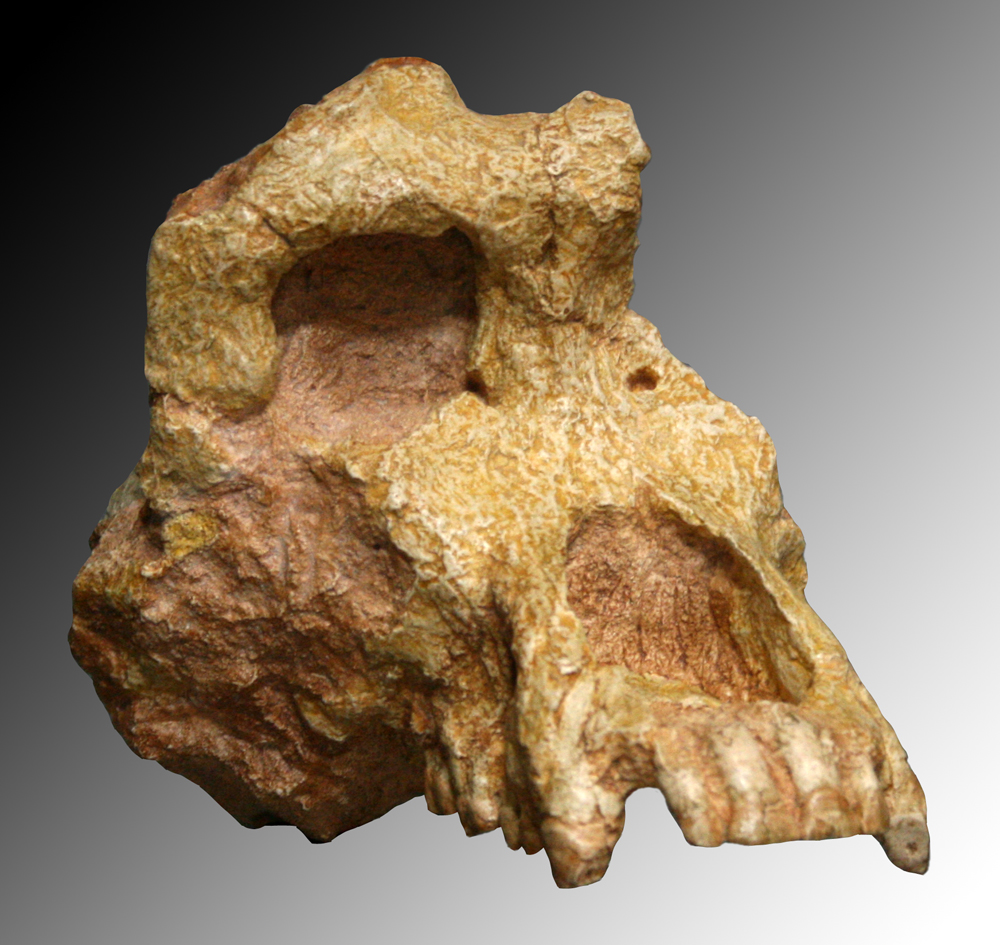
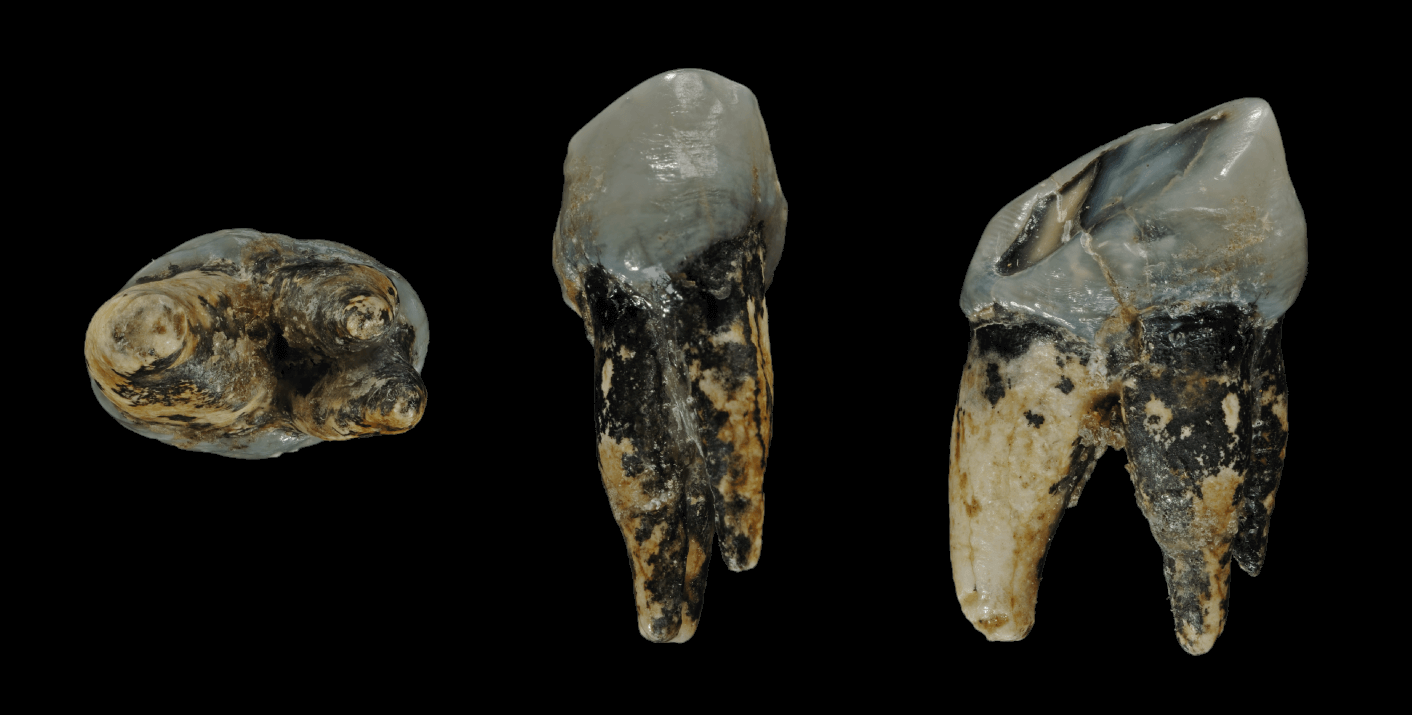
Graecopithecus Freybergi
''Graecopithecus'' is an extinct species of hominid that lived in southeast Europe during the late Miocene around 7.2 million years ago. Originally identified by a single lower jaw bone bearing a molar tooth found in Pyrgos Vasilissis, Athens, Greece, in 1944, other tooth specimens were discovered from Azmaka quarry in Bulgaria in 2012. With only little and badly preserved materials to reveal its nature, it is considered as "the most poorly known European Miocene hominoids." The creature was popularly nicknamed 'El Graeco' (word play on the Spanish painter El Greco) by scientists. In 2017, an international team of palaeontologists led by Madelaine Böhme of the Eberhard-Karls-University Tübingen, Germany, published a detailed analysis of the teeth and age of the specimens, and came to the conclusion that it could be the oldest hominin, meaning that it could be the oldest direct ancestors of humans after splitting from that of the chimpanzees. Their simultaneous study also cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus
''Ouranopithecus'' ("celestial ape" from Ancient Greek οὐρανός (ouranós), "sky, heaven" + πίθηκος (píthēkos),"ape") is a genus of extinct Eurasian great ape represented by two species, ''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'', a late Miocene (9.6–8.7 mya) hominoid from Greece and ''Ouranopithecus turkae'', also from the late Miocene (8.7–7.4 mya) of Turkey. The first specimen ''O. macedoniensis'' was discovered by French palaeontologists Louis de Bonis and Jean Melentis in 1977, and ''O. turkae'' by Turkish team led by Erksin Savaş Güleç in 2007. For a long time it was considered as similar (synonymous) to ''Graecopithecus'' and member of the genus ''Sivapithecus,'' which more discoveries proved otherwise. Description and systematics Based on ''O. macedoniensis dental and facial anatomy, it has been suggested that ''Ouranopithecus'' was actually a dryopithecine. However, it is probably more closely related to the Ponginae. Some researchers consider ''O. macedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugium (population Biology)
Refugium, plural refugia, the Latin for "refuge" or "hideaway", may refer to: * Refugium (fishkeeping), an appendage to a marine, brackish, or freshwater fish tank that shares the same water supply * Refugium (population biology), a location of an isolated or relict population of a once widespread animal or plant species ** Last Glacial Maximum refugia specifically, in anthropology * Refugium Range The Refugium Range is a low, small mountain range comprising the mountains/hills of the Brooks Peninsula on northern Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It has an area of and is a subrange of the Vancouver Island Ranges which in turn for ..., a mountain range on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada See also * Refuge (Buddhism) * Refugium Peccatorum {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oreopithecus
''Oreopithecus'' (from the Greek , and , , meaning "hill-ape") is an extinct genus of hominoid primate from the Miocene epoch whose fossils have been found in today's Tuscany and Sardinia in Italy. It existed nine to seven million years ago in the Tusco-Sardinian area when this region was an isolated island in a chain of islands stretching from central Europe to northern Africa in what was becoming the Mediterranean Sea. ''Oreopithecus'' was one of many European immigrants that settled this area in the Vallesian–Turolian transition and one of few hominoids, together with ''Sivapithecus'' in Asia, to survive the so-called Vallesian Crisis. To date, dozens of individuals have been discovered at the Tuscan localities of Montebamboli, Montemassi, Casteani, Ribolla, and, most notably, in the fossil-rich lignite mine in the Baccinello Basin, making it one of the best-represented fossil apes. Evolutionary history ''Oreopithecus bambolii'' was first described by French paleontol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction Event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vallesian Crisis
The Vallesian age is a period of geologic time (11.6–9.0 Ma) within the Miocene used more specifically with European Land Mammal Ages. It precedes the Turolian age and follows the Astaracian age. The so-called Vallesian Crisis resulted in the extinction of several mammalian taxa characteristic of the Middle Miocene. The term "Vallesian" was introduced by Catalan palaeontologist Miquel Crusafont in 1950 to mark the arrival of the equid ''Hipparion'' in Europe. The remaining European palaeofaunas, however, had been around since the Middle Miocene, including the moschid ''Micromeryx'' (a musk deer), the cervid ''Euprox'', the suid '' Listriodon'', and the felids ''Sansanosmilus'' and ''Pseudaelurus'', and the Aragonian-Vallesian"Aragonian" is a Spanish term for a continental stage, roughly equivalent to the Middle Miocene or Astaracian (16–11 Ma). boundary does not represent a major shift in the European mammalian record. In contrast, the transition between Lower and Upper Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudapithecus
''Rudapithecus'' is a chimpanzee-likeLászló Kordos: 50 years of Rudapithecus (in Hungarian) genus of ape which inhabited during the Late Miocene, approximately 10 million years ago. One species is known, ''Rudapithecus hungaricus''. The genus name "''Rudapithecus''" comes from where it was discovered, in Rudabánya'','' in 1965 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispanopithecus
''Hispanopithecus'' is a genus of apes that inhabited Europe during the Miocene epoch. It was first identified in a 1944 paper by J. F. Villalta and M. Crusafont in . Anthropologists disagree as to whether ''Hispanopithecus'' belongs to the subfamily Ponginae (most closely related to modern orangutans) or Homininae (most closely related to gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans). The genus contains two known species: ''Hispanopithecus laietanus'' and ''Hispanopithecus crusafonti''. The fossils have been dated to between 11.1 and 9.5 million years ago. Morphology Postcranial features exhibit morphological features that suggest a mosaic of locomotive behaviors. The structure of the cortical bone at the proximal and distal ends of the femur, particularly the neck of the femoral head, indicate an orthograde body plan. Recovered vertebrae indicate a relatively short, wide, and deep thorax support the orthograde posture for climbing, clambering, and feeding in an arboreal environment. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryopithecus
''Dryopithecus'' is a genus of extinct great apes from the middle– late Miocene boundary of Europe 12.5 to 11.1 million years ago (mya). Since its discovery in 1856, the genus has been subject to taxonomic turmoil, with numerous new species being described from single remains based on minute differences amongst each other, and the fragmentary nature of the holotype specimen makes differentiating remains difficult. There is currently only one uncontested species, the type species ''D. fontani'', though there may be more. The genus is placed into the tribe Dryopithecini, which is either an offshoot of orangutans, African apes, or is its own separate branch. A male specimen was estimated to have weighed in life. ''Dryopithecus'' likely predominantly ate ripe fruit from trees, suggesting a degree of suspensory behaviour to reach them, though the anatomy of a humerus and femur suggest a greater reliance on walking on all fours (quadrupedalism). The face was similar to gorilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |