|
Homer E. Newell Jr.
Homer Edward Newell Jr. (March 11, 1915 – July 18, 1983) was a mathematics professor and author who became a powerful United States government science administrator—eventually rising to the number three position at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In the early 1960s, he either controlled or influenced virtually all non-military unmanned space missions for the free world. Early life and education Newell was born March 11, 1915 in Holyoke, Massachusetts. He was educated in the public schools, graduating at the top of his class from Holyoke High in 1932. In a 1980 interview, he recalled that his interest in science arose from his grandfather Arthur J. Newell, an engineer for a local electrical equipment manufacturer, who had an extensive private library where Newell found books on astronomy and chemistry. Arthur also provided the money for his grandson's university education at Harvard University, where he graduated with a 1936 Bachelor of Arts in Math, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holyoke, Massachusetts
Holyoke is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, that lies between the western bank of the Connecticut River and the Mount Tom Range. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 38,238. Located north of Springfield, Holyoke is part of the Springfield Metropolitan Area, one of the two distinct metropolitan areas in Massachusetts. Holyoke is among the early planned industrial cities in the United States. Built in tandem with the Holyoke Dam to utilize the water power of Hadley Falls, it is one of a handful of cities in New England built on the grid plan. During the late 19th century the city produced an estimated 80% of the writing paper used in the United States and was home to the largest paper mill architectural firm in the country, as well as the largest paper, silk, and alpaca wool mills in the world. Although a considerably smaller number of businesses in Holyoke work in the paper industry today, it is still commonly referred to as "The Paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer I
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union's Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2, beginning the Cold War Space Race between the two nations. Explorer 1 was launched on 1 February 1958 at 03:47:56 GMT (or 31 January 1958 at 22:47:56 Eastern Time) atop the first Juno booster from LC-26A at the Cape Canaveral Missile Test Center of the Atlantic Missile Range (AMR), in Florida. It was the first spacecraft to detect the Van Allen radiation belt, returning data until its batteries were exhausted after nearly four months. It remained in orbit until 1970. Explorer 1 was given Satellite Catalog Number 00004 and the Harvard designation 1958 Alpha 1, the forerunner to the modern International Designator. Background The U.S. Earth satellite program began in 1954 as a joint U.S. Army and U.S. Navy pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Vanguard
Project Vanguard was a program managed by the United States Navy Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), which intended to launch the first artificial satellite into low Earth orbit using a Vanguard rocket. as the launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Missile Annex, Florida. In response to the launch of Sputnik 1 on 4 October 1957, the U.S. restarted the Explorer program, which had been proposed earlier by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA). Privately, however, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and President Dwight D. Eisenhower were aware of progress being made by the Soviets on Sputnik from secret spy plane imagery. Together with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), ABMA built Explorer 1 and launched it on 1 February 1958 ( UTC). Before work was completed, however, the Soviet Union launched a second satellite, Sputnik 2, on 3 November 1957. Meanwhile, the spectacular televised failure of Vanguard TV3 on 6 December 1957, deepened American dismay over the country's position in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China (Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it covered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwight D
Dwight may refer to: People * Dwight (given name) * Dwight D. Eisenhower (1890–1969), 34th president of the United States and former military officer *New England Dwight family of American educators, military and political leaders, and authors * Ed Dwight (born 1933), American test pilot, participated in astronaut training program * Mabel Dwight (1875–1955), American artist * Elton John (born Reginald Dwight in 1947), English singer, songwriter and musician Places Canada * Dwight, Ontario, village in the township of Lake of Bays, Ontario United States * Dwight (neighborhood), part of an historic district in New Haven, Connecticut * Dwight, Illinois, village in Livingston and Grundy counties * Dwight, Kansas, city in Morris County * Dwight, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Dwight, Nebraska, village in Butler County * Dwight, North Dakota, city in Richland County * Dwight Township, Livingston County, Illinois * Dwight Township, Michigan Institutions * Dwight Correctional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces. The power of the presidency has grown substantially since the first president, George Washington, took office in 1789. While presidential power has ebbed and flowed over time, the presidency has played an increasingly strong role in American political life since the beginning of the 20th century, with a notable expansion during the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. In contemporary times, the president is also looked upon as one of the world's most powerful political figures as the leader of the only remaining global superpower. As the leader of the nation with the largest economy by nominal GDP, the president possesses significant domestic and international hard and soft power. Article II of the Constitution establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range. Significant events *The first atomic bomb (code named Trinity) was test detonated at Trinity Site near the northern boundary of the range on 16 July 1945, seven days after the White Sands Proving Ground was established. *After the conclusion of World War II, 100 long-range German V-2 rockets that were captured by U.S. military troops were brought to WSMR. Of these, 67 were test-fired between 1946 and 1951 from the White Sands V-2 Launching Site. (This was followed by the testing of American rockets, which continues to this day, along with testing other technologies.) *NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia landed on the Northrop Strip at WSMR on 30 March 1982 as the conclusion to mission STS-3. This was the only ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
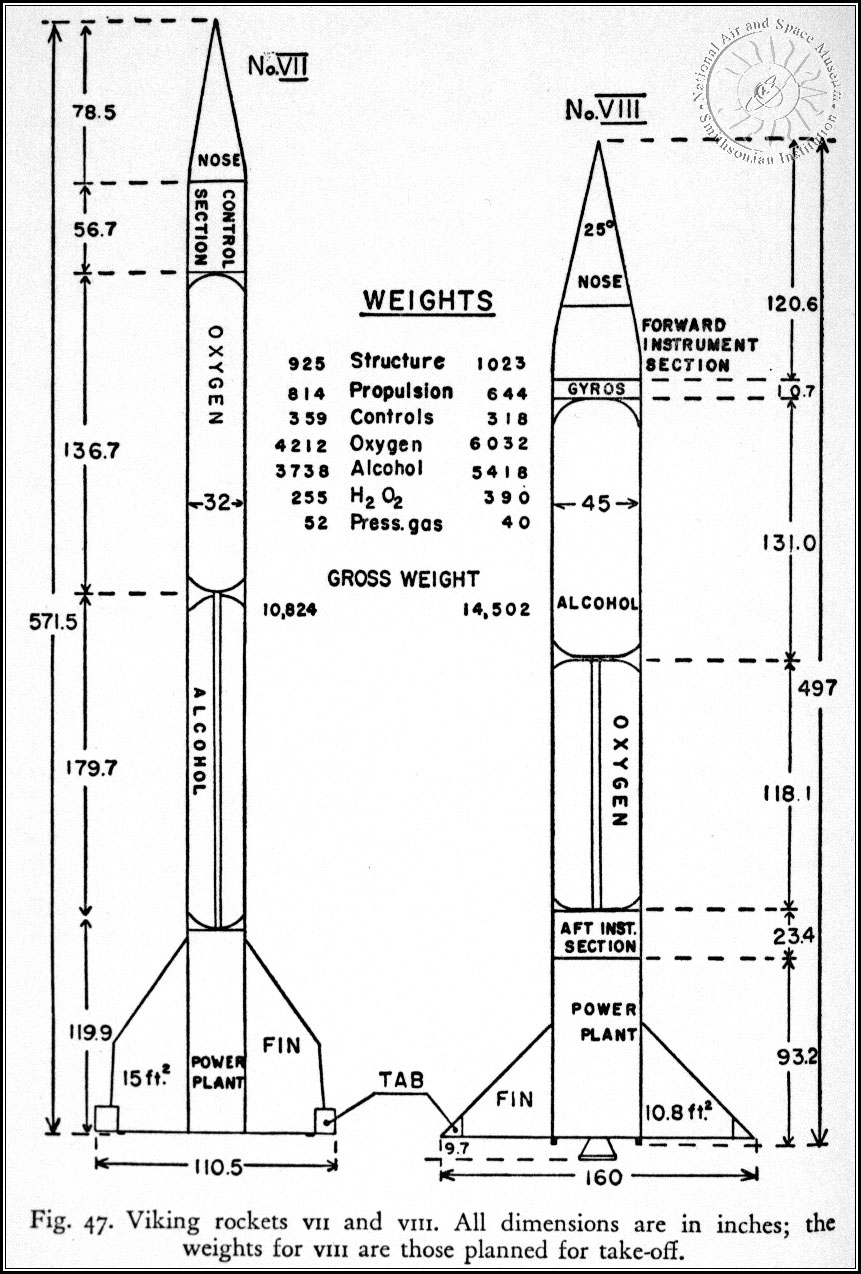
Viking Rocket
Viking was series of twelve sounding rockets designed and built by the Glenn L. Martin Company under the direction of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). Designed to supersede the German V-2, the Viking was the most advanced large, liquid-fueled rocket developed in the United States in the late 1940s, returning valuable scientific data from the edge of space between 1949 and 1955. Viking 4, launched in 1950, was the first sounding rocket to be launched from the deck of a ship. After twelve flights, the Viking was adapted into the first stage for the Vanguard rocket, which launched America's second satellite into orbit in 1958. Origins After World War II, the United States experimented with captured German V-2 rockets as part of the Hermes program. Based on these experiments the U.S. issued a contract 21 August 1946 to the Glenn L. Martin Company for a series of ten large liquid-fueled rockets. The intent was to provide an independent U.S. capability in rocketry, to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobee
The Aerobee rocket was one of the United States' most produced and productive sounding rockets. Developed by the Aerojet Corporation, the Aerobee was designed to combine the altitude and launching capability of the V-2 with the cost effectiveness and mass production of the WAC Corporal. More than 1000 Aerobees were launched between 1947 and 1985, returning vast amounts of astronomical, physical, aeronomical, and biomedical data. Development Research using V-2 rockets after World War II produced valuable results concerning the nature of cosmic rays, the solar spectrum, and the distribution of atmospheric ozone. However, the limited supply and the expense of assembling and firing the V-2 rockets, as well as the small payload capacity of the first purpose-built sounding rocket, the WAC Corporal, created demand for a low cost sounding rocket to be used for scientific research. An Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) effort led by James Van Allen led to a contract presented 17 May 1946 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |