|
Homaloceras
''Homaloceras'' is an extinct nautiloid cephalopod from the Middle Devonian with a strongly curved shell, included in the nautilid family Centroceratidae. ''Homaloceras'' is characterized by a smooth, exogastrically curved and laterally compressed, cyrtoconic to gyroconic, shell with the ventral margin the outer rim. The venter is narrow and concave with a groove running down the middle; the dorsum on the inner rim, rounded; the sides broadly convex and convergent. The suture is only slightly sinuous, the siphuncle tubular and near the venter. ( 1964) ''Homaloceras'', named by Whiteavus in 1891, and found in North America, in Canada, is the most primitive and one of the earliest genera assigned to the Centroceratidae. ( 1964) The Nautiloidea, in which ''Homaloceras'' is included, is a subclass of once diverse and numerous shelled cephalopods characterized by a retrochoantic siphuncle in which the septal necks point back toward the apex. See also *List of nautiloids R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centroceratidae
The Centroceratidae is the ancestral family of the Trigonoceratoidea and of the equivalent Centroceratina; extinct shelled cephalopods belonging to the order Nautilida Diagnosis The Centroceratidae, which range from the Middle Devonian to the Lower Permian, are characterized by gyroconic, evolute tarphyceraconic, and involute nautiliconic shells with compressed whorls, typically with a quadrangular whorl section in which the flanks converge on venter that is much narrower than the dorsum and ventral and umbilical shoulders are sharply angular, or rarely rounded. In some, e.g. ''Centroceras'', the flanks are divided by a ridge that runs along the middle. Sutures have ventral and lateral lobes but are transverse dorsally. The siphuncle is tubular and close to but not on in contact with the venter (Kummel 1964). Phylogeny and genera Evolutionary sequence The Centroceratidae are thought probably to be derived from the rutoceratid stock (Flower 1950, 1988, Kummel 1964) Earliest are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nautiloids
This list of nautiloids is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the subclass Nautiloidea, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered nautiloids. Most of the listed genera are found in Part K of the ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology''. Some, added since the year of publication (1964) are found simply in various scientific journals and special publications. The named genera are based on type specimens which are housed in various museums and other academic institutions worldwide, available to interested researchers. Note that ''Allonautilus'' and ''Nautilus'' are the only extant genera. A *†'' Acanthonautilus'' *†'' Acaroceras'' *†'' Acleistoceras'' *†'' Acrosphaerorthoceras' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautiloidea
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms ( orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day. In a broad sense, "nautiloid" refers to a major cephalopod subclass or collection of subclasses (Nautiloidea ''sensu lato''). Nautiloids are typically considered one of three main groups of cephalopods, along with the extinct ammonoids (ammonites) and living coleoids (such as squid, octopus, and kin). While ammonoids and coleoids are monophyletic clades with exclusive ancestor-descendant rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilida
The Nautilida constitute a large and diverse order of generally coiled nautiloid cephalopods that began in the mid Paleozoic and continues to the present with a single family, the Nautilidae which includes two genera, ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus'', with six species. All told, between 22 and 34 families and 165 to 184 genera have been recognised, making this the largest order of the subclass Nautiloidea. Classification and phylogeny Current classification The current classification of the Nautilida, in prevalent use, is that of Bernhard Kummel (Kummel 1964) in the Treatise which divides the Nautilida into five superfamilies, the Aipocerataceae, Clydonautilaceae, Tainocerataceae, and Trigonocerataceae, mostly of the Paleozoic, and the later Nautilaceae. These include 22 families and some 165 or so genera (Teichert and Moore 1964) Other concepts Shimansky 1962 (in Kummel 1964) divided the Nautilida into five suborders, the mostly Paleozoic Centroceratina, Liroceratina, Rutoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogastrically
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrtoconic
Endocerida is an extinct nautiloid order, a group of cephalopods from the Lower Paleozoic with cone-like deposits in their siphuncle. Endocerida was a diverse group of cephalopods that lived from the Early Ordovician possibly to the Late Silurian. Their shells were variable in form. Some were straight (orthoconic), others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like ''Endoceras'' attained shell lengths close to . The related ''Cameroceras'' is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching , but these claims are problematic. The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long when fully grown. Morphology Endocerids had a relatively small body chamber as well as a proportionally large siphuncle, which in some genera reached nearly half the shell diameter. This suggests that much of the visceral mass may have been housed within the siphuncle itse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphuncle
The siphuncle is a strand of tissue passing longitudinally through the shell of a cephalopod mollusk. Only cephalopods with chambered shells have siphuncles, such as the extinct ammonites and belemnites, and the living nautiluses, cuttlefish, and ''Spirula''. In the case of the cuttlefish, the siphuncle is indistinct and connects all the small chambers of that animal's highly modified shell; in the other cephalopods it is thread-like and passes through small openings in the septa (walls) dividing the camerae (chambers). Some older studies have used the term siphon for the siphuncle, though this naming convention is uncommon in modern studies to prevent confusion with a mollusc organ of the same name. Function The siphuncle is used primarily in emptying water from new chambers as the shell grows. To perform this task, the cephalopod increases the saltiness of the blood in the siphuncle, and the water moves from the more dilute chamber into the blood through osmosis. At the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
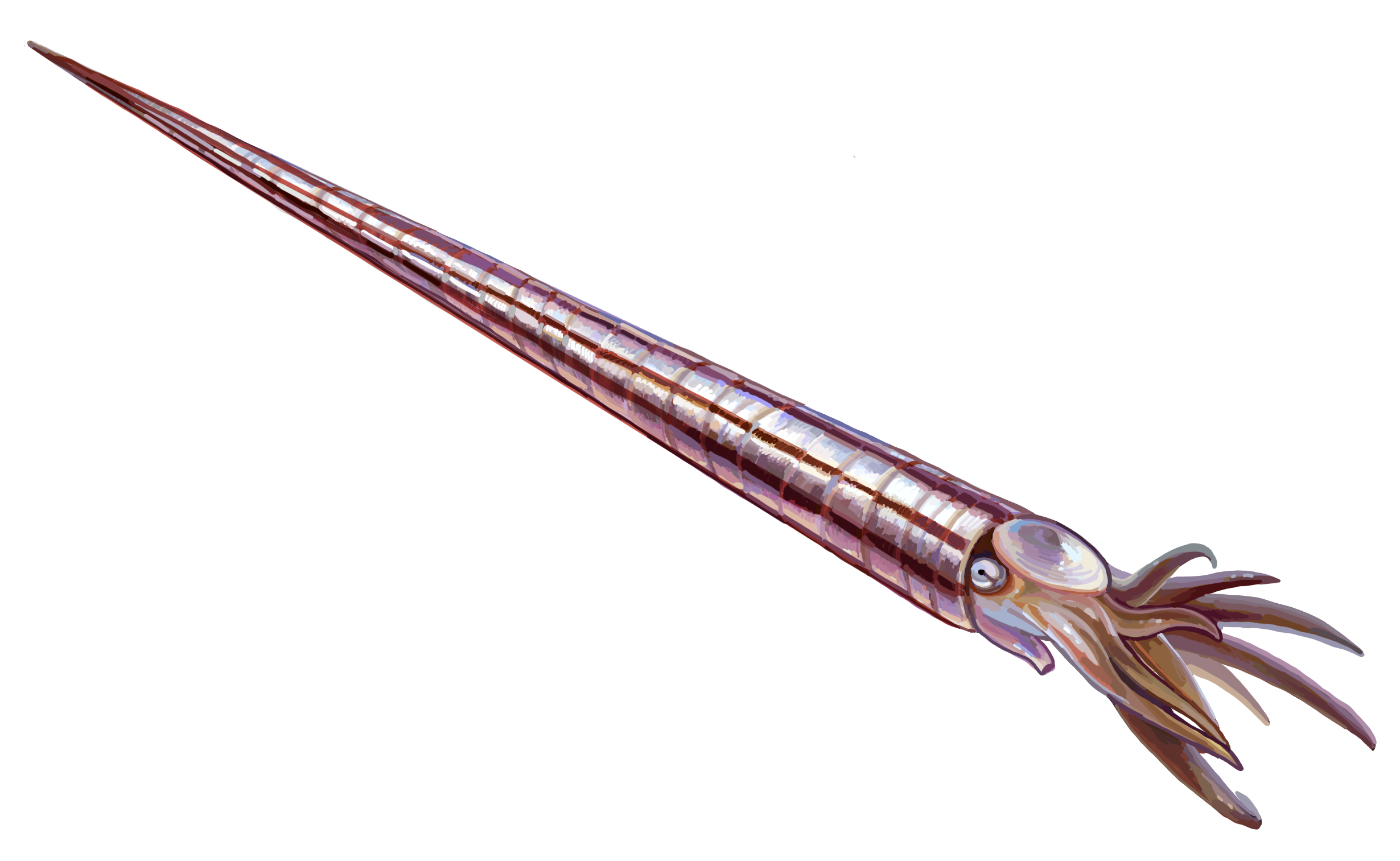
Cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been identified. Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)