|
Holonematidae
Holonematidae is an extinct family of relatively large arthrodire placoderms from the Early to Late Devonian. Almost all fossil specimens are of armor fragments, though, all have distinctive ornamentation, often of unique arrangements and patterns of tubercles, that are diagnostic of the family. The trunkshield is very elongated, giving the armor an overall "barrel" like appearance. Due to pebbles found inside articulated specimens of the Frasnian species, ''Holonema westolli'', holonematids are thought to have been specialized herbivores that grazed on a form of horn-shaped, stony algae called "onycholite," snipping off the tips with their odd snouts. Genera ''Artesonema'' A poorly known genus from the Givetian-aged Blacourt Formation of Boulonnais, France.LELIEVRE, n.; GOUJET, D., BLIECK, A. & JANVIER, P. 1986. ''Poissons du DEvonien du Boutonnais (France)''. - n:BRICE, D. d.Le DEvonien de Ferques, Bas -Boulonnais (N. France) - Biostratigraphie du PalEozoique 7: 503-522, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropidosteus
''Tropidosteus curvatus'' is a large, extinct holonematid arthrodire placoderm from the Givetian-aged Crinoidenmergel stratum of Middle Devonian Rheinland, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... ''T. curvatus'' is known from primarily from a slender, 42 centimeter long, arched median dorsal plate, where the two sides meet at a sixty to ninety degree angle, which would have given the live animal a humped appearance. The median dorsal plate is very similar to the median dorsal plates of '' Rhenonema'' and '' Belemnacanthus'', and is the primary reason for ''T. curvatus''' placement within Holonematidae. After stating this reason, Denison, 1978, then questions ''Tropidosteus placement within the family, noting that the dorsal plate lacks ridged ornamentation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnacanthus
''Belemnacanthus giganteus'' ("Gigantic arrow-spine") is a large, extinct, barrel-shaped holonematid arthrodire placoderm from Givetian-aged strata of Middle Devonian Eifel, Germany. ''B. giganteus'' is known only from the holotype, a portion of a median dorsal plate with a long, somewhat high, arching crest running down the median line of the exterior/dorsal side of the plate. The plate has an ornamentation of ridges that originate from a point posterior to the preserved portion of the median dorsal plate. Before the plate was identified as that of a holonematid, the plate of ''B. giganteus'' had been successively described as a tremendous spine of an elasmobranch, an agnathan, and lastly, the plate of an antiarch Antiarchi ("opposite anus") is an order of heavily armored placoderms. The antiarchs form the second-most successful group of placoderms after the arthrodires in terms of numbers of species and range of environments. The order's name was coi .... Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenonema
''Rhenonema eifeliense'' ("Rheinland thread of Eifel") is a large, extinct, high-crested holonematid arthrodire placoderm from Givetian-aged strata of Middle Devonian Gerolstein, Germany. It is known from some fragments of armor, including an anterior-lateral plate estimated to be around long, and a portion of a median dorsal plate with a very tall crest running along the median line of the dorsal surface. The ornamentation is very similar to that of ''Holonema'', but the concentrically arranged ridges are much coarser in ''Rhenonema''. The holotype was originally described by Kayser, in 1880, as a species of ''Dinichthys ''Dinichthys'' (from el, δεινός , 'terrible' and el, ἰχθύς 'fish') is an extinct monospecific genus of giant, marine arthrodire placoderm from the Late Devonian (Famennian stage), comparable in size, shape, and ecological role ...'', but was then redescribed in 1964 by Obruchev as a holonematid. References Holonematidae Placo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspidichthys
''Aspidichthys'' ("shield fish") is a genus of large, distinctively tuberculated arthrodire placoderm of uncertain affinities from Upper Devonian marine strata in the Eastern United States and Europe. Anatomy The dermal surfaces of the thick bones are decorated with an irregular arrangement of large, rounded tubercles. Some specimens may display patterns of "imperfectly concentric rows." The long median dorsal plate is subrectangular in shape, and is gently bent along the midline, which tends to have a corresponding low ridge, and a posteriorly placed carinal process on the dorsal surface. In 1938, Schmidt made a restoration of ''A. ingens'' as a large-bodied, small-headed arthrodire with tremendous orbits after the now-lost holotype of that species. Taxonomy The taxonomic relationships of the genus remain uncertain. Miles, 1973, suggested the genus was related to the Euleptaspidae, though, this is disproved through noting the drastically different proportions of the nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holonema
''Holonema'' is an extinct genus of relatively large, barrel-shaped arthrodire placoderms that were found in oceans throughout the world from the Mid to Late Devonian, when the last species perished in the Frasnian-Fammian extinction event. Most species of the genus are known from fragments of their armor, but the Gogo Reef species, ''H. westolli'', is known from whole, articulated specimens. Holonema is thought to have been a Demersal fish, benthic-dwelling fish, based on its cambered body shape, which performs better Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamically when closer to the sea bed.https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/sites/default/files/articles/pdf/g1999n1a4.pdf According to these specimens, species of ''Holonema'' lived by grazing on stony, horn-shaped, stromatolite-like algae called oncholite, apparently by snipping off the points with a specialized snout. Species ''H. rugosum'' ''H. rugosum'' is the type species. It was originally described as a species of the antiarch genus, ''Pteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulonnais (land Area)
The Boulonnais () is a coastal area of northern France, around Calais and Boulogne-sur-Mer. It has a curved belt of chalk downs which run into the sea at both ends, and geologically is the east end of the Weald-Artois Anticline. Administration The Pays Boulonnais is subdivided into 3 intercommunalities: the Communauté d'agglomération du Boulonnais, the Communauté de communes de la Terre des Deux Caps & the Communauté de communes de Desvres - Samer. Towns and villages of the Boulonnais See also *Côte d'Opale *Nausicaä Centre National de la Mer Nausicaa (; grc, Ναυσικάα, Nausikáa, or , ) also spelled Nausicaä or Nausikaa, is a character in Homer's ''Odyssey''. She is the daughter of King Alcinous and Queen Arete of Phaeacia. Her name means "burner of ships" ( 'ship'; 'to b ... External links Tourism in Boulogne and in the Boulonnais region [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifel
The Eifel (; lb, Äifel, ) is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Community of Belgium. The Eifel is part of the Rhenish Massif; within its northern portions lies the Eifel National Park. Geography Location The Eifel lies between the cities of Aachen to the north, Trier to the south and Koblenz to the east. It descends in the northeast along a line from Aachen via Düren to Bonn into the Lower Rhine Bay. In the east and south it is bounded by the valleys of the Rhine and the Moselle. To the west it transitions in Belgium and Luxembourg into the geologically related Ardennes and the Luxembourg Ösling. In the north it is limited by the Jülich-Zülpicher Börde. Within Germany it lies within the states of Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia; in the Benelux the area of Eupen, St. Vith and Luxemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emsian
The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 407.6 ± 2.6 million years ago to 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian Stage and followed by the Eifelian Stage. It is named after the Ems river in Germany. The GSSP is located in the Zinzil'ban Gorge in the Kitab State Geological Reserve of Uzbekistan, above the contact with the Madmon Formation. In North America the Emsian Stage is represented by Sawkill or Sawkillian time. Biological events During this period, earliest known agoniatitid ammonoid fossils began appearing within this stage after first appearing in previous stage and began to evolutionarily radiate within this stage, in which a new ammonoid order Goniatitida rises in the end of Zlichovian stage (Siberian representation; corresponds to early Eifelian and after the end of Early Devonian, before 391.9 mya). Later agoniatitid ammonoids would die out in the Taghanic event in the upper middle Givetian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are jawed vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, scales, and a heart with its chambers in series. Extant chondrichthyes range in size from the 10 cm (3.9 in) finless sleeper ray to the 10 m (32 ft) whale shark. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, except in Holocephali, where the notochord stays intact. In some deepwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate-skinned') is a Class (biology), class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their Fish jaw, jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyly, paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct Outgroup (cladistics), outgroups or sister taxon, sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
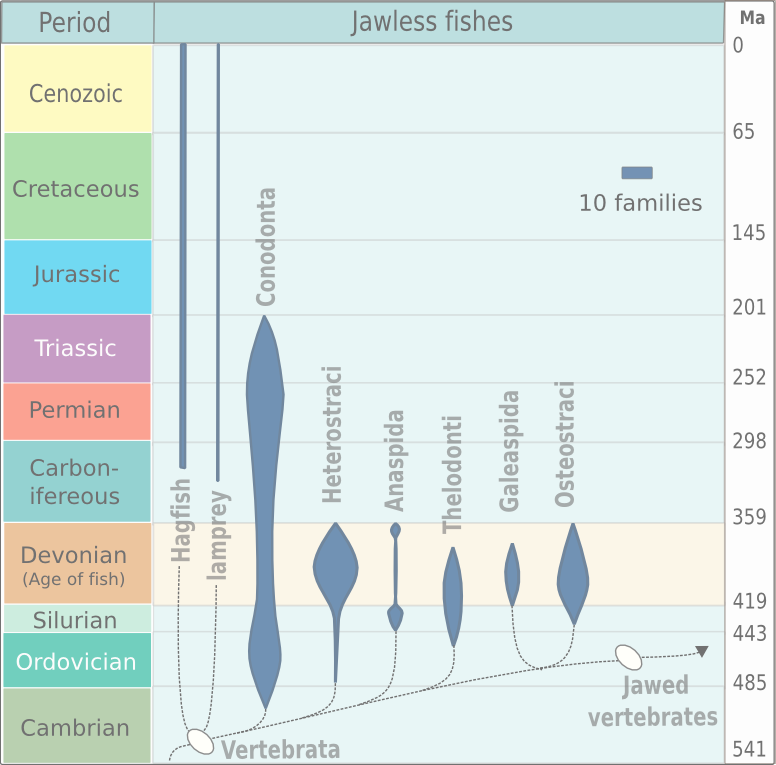
Agnatha
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct ( conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |