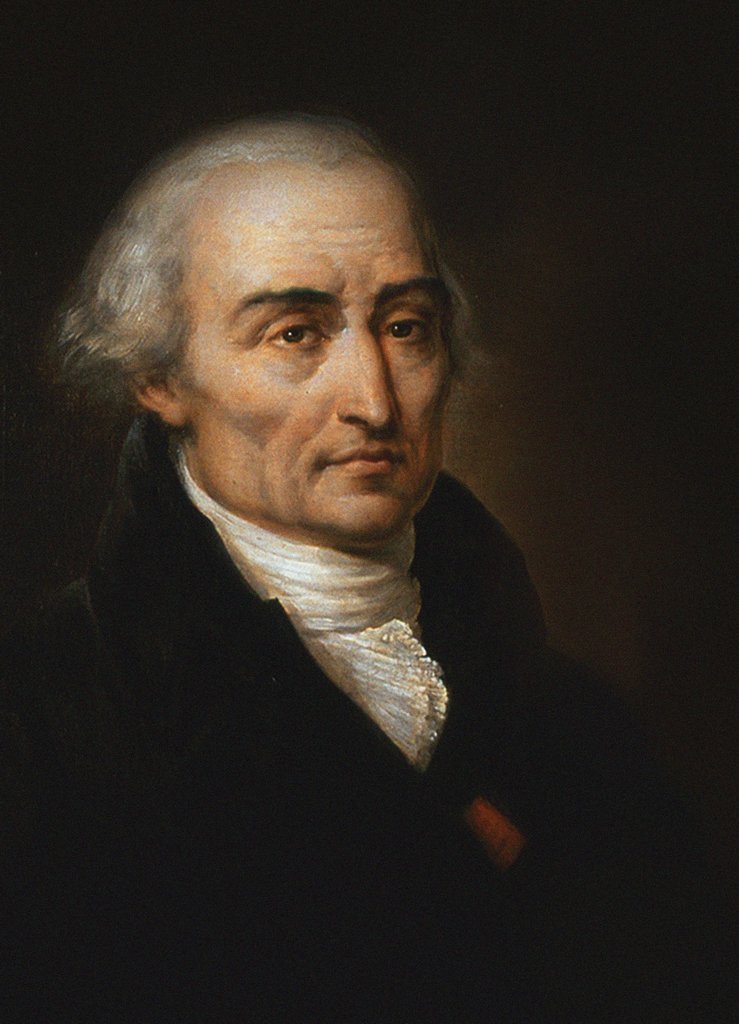|
History Of Variational Principles In Physics
A variational principle in physics is an alternative method for determining the state or dynamics of a physical system, by identifying it as an extremum (minimum, maximum or saddle point) of a function or functional. This article describes the historical development of such principles. Before modern times Variational principles are found among earlier ideas in surveying and optics. The rope stretchers of ancient Egypt stretched corded ropes between two points to measure the path which minimized the distance of separation, and Claudius Ptolemy, in his Geographia (Ptolemy), Geographia (Bk 1, Ch 2), emphasized that one must correct for "deviations from a straight course"; in ancient Greece Euclid states in his ''Catoptrica'' that, for the path of light reflecting from a mirror, the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection; and Hero of Alexandria later showed that this path was the shortest length and least time. This was generalized to refractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is called a land surveyor. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designed positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales. Surveyors work with elements of geodesy, geometry, trigonometry, regression analysis, physics, engineering, metrology, programming languages, and the law. They use equipment, such as total stations, robotic total stations, theodolites, GNSS receivers, retroreflectors, 3D scanners, LiDAR sensors, radios, inclinometer, handheld tablets, optical and digital levels, subsurface locators, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, and nothing else can replace it." Euler is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marston Morse
Harold Calvin Marston Morse (March 24, 1892 – June 22, 1977) was an American mathematician best known for his work on the ''calculus of variations in the large'', a subject where he introduced the technique of differential topology now known as Morse theory. The Morse–Palais lemma, one of the key results in Morse theory, is named after him, as is the Thue–Morse sequence, an infinite binary sequence with many applications. In 1933 he was awarded the Bôcher Memorial Prize for his work in mathematical analysis. Biography He was born in Waterville, Maine to Ella Phoebe Marston and Howard Calvin Morse in 1892. He received his bachelor's degree from Colby College (also in Waterville) in 1914. At Harvard University, he received both his master's degree in 1915 and his PhD in 1917. He wrote his PhD thesis, ''Certain Types of Geodesic Motion of a Surface of Negative Curvature'', under the direction of George David Birkhoff. Morse was a Benjamin Peirce Instructor at Harvard in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddle Point
In mathematics, a saddle point or minimax point is a point on the surface of the graph of a function where the slopes (derivatives) in orthogonal directions are all zero (a critical point), but which is not a local extremum of the function. An example of a saddle point is when there is a critical point with a relative minimum along one axial direction (between peaks) and at a relative maximum along the crossing axis. However, a saddle point need not be in this form. For example, the function f(x,y) = x^2 + y^3 has a critical point at (0, 0) that is a saddle point since it is neither a relative maximum nor relative minimum, but it does not have a relative maximum or relative minimum in the y-direction. The name derives from the fact that the prototypical example in two dimensions is a surface that ''curves up'' in one direction, and ''curves down'' in a different direction, resembling a riding saddle or a mountain pass between two peaks forming a landform saddle. In te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Gustav Jacobi
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (; ; 10 December 1804 – 18 February 1851) was a German mathematician who made fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, Dynamics (mechanics), dynamics, differential equations, determinants, and number theory. His name is occasionally written as Carolus Gustavus Iacobus Iacobi in his Latin books, and his first name is sometimes given as Karl. Jacobi was the first Jews, Jewish mathematician to be appointed professor at a German university. Biography Jacobi was born of Ashkenazi Jewish parentage in Potsdam on 10 December 1804. He was the second of four children of banker Simon Jacobi. His elder brother Moritz von Jacobi would also become known later as an engineer and physicist. He was initially home schooled by his uncle Lehman, who instructed him in the classical languages and elements of mathematics. In 1816, the twelve-year-old Jacobi went to the Potsdam Gymnasium (Germany), Gymnasium, where students were taught all the standard subjects: cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Equations Of Motion
In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the stationary-action principle (also known as the principle of least action). It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his 1788 work, '' Mécanique analytique''. Lagrangian mechanics describes a mechanical system as a pair (M,L) consisting of a configuration space M and a smooth function L within that space called a ''Lagrangian''. By convention, L = T - V, where T and V are the kinetic and potential energy of the system, respectively. The stationary action principle requires that the action functional of the system derived from L must remain at a stationary point (a maximum, minimum, or saddle) throughout the time evolution of the system. This constraint allows the calculation of the equations of motion of the system using Lagrange's equations. Introduction Suppose there exists a bead sliding around on a wire, or a swinging simple p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Rowan Hamilton
Sir William Rowan Hamilton Doctor of Law, LL.D, Doctor of Civil Law, DCL, Royal Irish Academy, MRIA, Royal Astronomical Society#Fellow, FRAS (3/4 August 1805 – 2 September 1865) was an Irish mathematician, astronomer, and physicist. He was the Andrews Professor of Astronomy at Trinity College Dublin, and Royal Astronomer of Ireland, living at Dunsink Observatory. Hamilton's scientific career included the study of geometrical optics, ideas from Fourier analysis, and his work on quaternions which made him one of the founders of modern linear algebra. He made major contributions in optics, classical mechanics and abstract algebra. His work was fundamental to modern theoretical physics, particularly his reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, now called Hamiltonian mechanics. It is now central both to electromagnetism and to quantum mechanics. Early life Hamilton was the fourth of nine children born to Sarah Hutton (1780–1817) and Archibald Hamilton (1778–1819),Bruno (2003) who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an and , later naturalized [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors. Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potential energy of an object, the elastic potential energy of an extended spring, and the electric potential energy of an electric charge in an electric field. The unit for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule, which has the symbol J. The term ''potential energy'' was introduced by the 19th-century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine, although it has links to Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of potentiality. Potential energy is associated with forces that act on a body in a way that the total work done by these forces on the body depends only on the initial and final positions of the body in space. These forces, that are called ''conservative forces'', can be represented at every point in space by vec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Family
The Bernoulli family () of Basel was a patrician family, notable for having produced eight mathematically gifted academics who, among them, contributed substantially to the development of mathematics and physics during the early modern period. History Originally from Antwerp, a branch of the family relocated to Basel in 1620. While their origin in Antwerp is certain, proposed earlier connections with the Dutch family ''Bornouilla'' (''Bernoullie''), or with the Castilian family ''de Bernuy'' (''Bernoille'', ''Bernouille''), are uncertain. The first known member of the family was Leon Bernoulli (d. 1561), a doctor in Antwerp, at that time part of the Spanish Netherlands. His son, Jacob, emigrated to Frankfurt am Main in 1570 to escape from the Spanish persecution of the Protestants. Jacob's grandson, a spice trader, also named Jacob, moved to Basel, Switzerland in 1620, and was granted citizenship in 1622. His son, (Nicolaus, 1623–1708), Leon's great-great-grandson, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—especially Criticism of the Catholic Church, of the Roman Catholic Church—and of slavery. Voltaire was an advocate of freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and separation of church and state. Voltaire was a versatile and prolific writer, producing works in almost every literary form, including stageplay, plays, poems, novels, essays, histories, and scientific Exposition (narrative), expositions. He wrote more than 20,000 letters and 2,000 books and pamphlets. Voltaire was one of the first authors to become renowned and commercially successful internationally. He was an outspoken advocate of civil liberties and was at constant risk from the strict censorship laws of the Catholic French monarchy. His polemics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Hermann (mathematician)
Jakob Hermann (16 July 1678 – 11 July 1733) was a mathematician who worked on problems in classical mechanics. He is the author of ''Phoronomia'', an early treatise on Mechanics in Latin, which has been translated by Ian Bruce in 2015-16. In 1729, he proclaimed that it was as easy to graph a locus on the polar coordinate system as it was to graph it on the Cartesian coordinate system. He appears to have been the first to show that the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector is a constant of motion for particles acted upon by an inverse-square central force. Hermann was born and died in Basel. He received his mathematical training from Jacob Bernoulli at the University of Basel and graduated with a degree in 1695. In 1696, he obtained a Master's Degree by defending a dissertation on infinite series. Jacob Bernoulli considered Hermann to be the best of his many students at the university and when Jacob Bernoulli died in 1705, Gottfried Leibniz asked Hermann to write an obituary for Bernoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_crop.jpg)