|
History Of Sylhet
The Greater Sylhet region predominantly includes the Sylhet Division in Bangladesh, and Karimganj district in Assam, India. The history of the Sylhet region begins with the existence of expanded commercial centres in the area that is now Sylhet City. Historically known as ''Srihatta'' and ''Shilhatta'', it was ruled by the Buddhist and Hindu kingdoms of Harikela and Kamarupa before passing to the control of the Sena and Deva dynasties in the early medieval period. After the fall of these two Hindu principalities, the region became home to many more independent petty kingdoms such as Jaintia, Gour, Laur, and later Taraf, Pratapgarh, Jagannathpur, Chandrapur and Ita. After the Conquest of Sylhet in the 14th century, the region was absorbed into Shamsuddin Firoz Shah's independent principality based in Lakhnauti, Western Bengal. It was then successively ruled by the Muslim sultanates of Delhi and the Bengal Sultanate before collapsing into Muslim petty kingdoms, mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
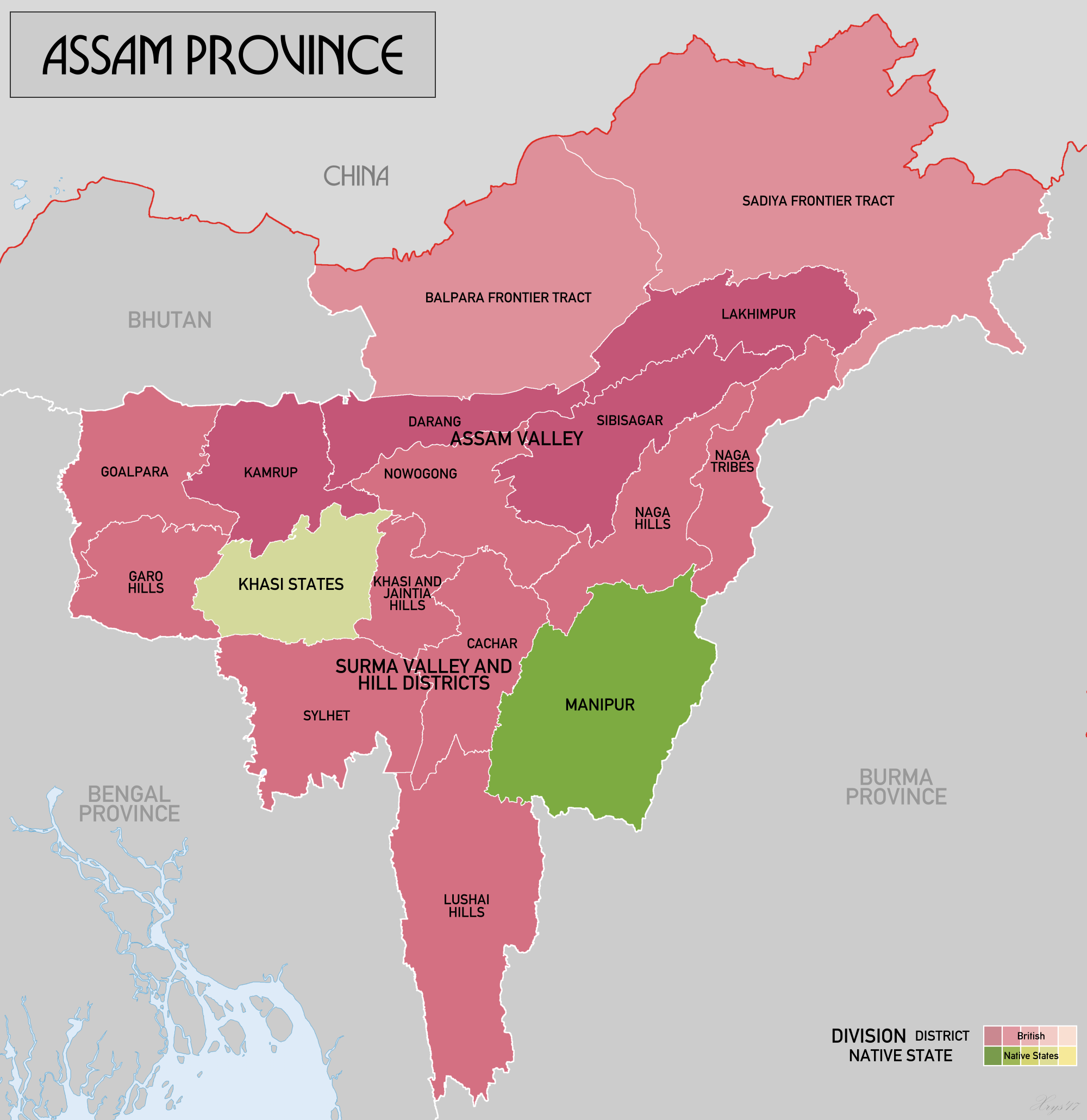
Greater Sylhet
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gour Kingdom
The Kingdom of Gour was one of the greater of the many petty kingdoms of the medieval Sylhet region. According to legend, it was founded by Gurak, off-shooting from Kamarupa's Jaintia Kingdom in 630. Much of its early history is considered legendary or mythological up until Navagirvana who is mentioned in the Bhatera copper-plate inscriptions. The Kings of Gour are described as patrons of Hindu revivalism in what was previously a predominantly Buddhist and animist populated land. The 11th century king Govinda-Rana Kesava Deva is recognised for introducing the ''navadinga'' (nine war boats) and heavily improving the kingdom's infantry, cavalry, and elephant power. Due to familial tensions, the kingdom split into two separate kingdoms in 1170; Gour (Northern Sylhet) and Brahmachal (Southern Sylhet), before being reunited by Raja Govardhan in the early years of his reign. However, this would be short-lasted as during Govardhan's reign, the kingdom would suffer attacks from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karrani Dynasty
The Karrani dynasty ( ps, کرلاڼي, Karlāṇī, bn, কররাণী, Korrāṇī) was founded in 1564 by Taj Khan Karrani, an ethnic Pashtun from the Karlani tribe, hailing from Bangash district. It was the last dynasty to rule the Sultanate of Bengal. Founding Taj Khan was formerly an employee of the Sur Emperor Sher Shah Suri. From 1562 to 1564, Taj Khan captured south-eastern Bihar and west Bengal, and with his assassination of the last Muhammed Shahi ruler, he seized all of Bengal. The capital was at Gaur. Taj Khan was followed by Sulaiman Khan Karrani, who shifted the seat of government from Gaur to Tanda (also in Malda) in 1565. In 1568, Sulaiman Khan annexed Orissa to the Karrani sultanate permanently. Nominally he accepted sovereignty of the Mughal Emperor Akbar, and his prime minister Lodi Khan placated the Mughals with gifts and banqueting. Sulaiman Khan's authority extended from Koch Bihar to Puri, and from Son River to Brahmaputra River. Mughal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry from there. Afghanistan is made up of various ethnicities, of which the Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras and Uzbeks are the largest; the pre-nation state, historical ethnonym Afghan was used to refer to a member of the Pashtun ethnic group. Due to the changing political nature of the state, such as the British-drawn border with Pakistan (then British India) the meaning has changed, and term has shifted to be the national identity of people from Afghanistan from all ethnicities. The two main languages spoken by Afghans are Pashto and Dari (the Afghan dialect of Persian language), and many are bilingual. Background The earliest mention of the name ''Afghan'' (''Abgân'') is by Shapur I of the Sassanid Empire during the 3rd century CE, In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. Its raids and conquests reached Nepal in the north, Assam in the east, and Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the north, east and northeast Indian subcontinent during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Hussain Shahi dynasty. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms. The Ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica Following the invasion of South Asia by the Ghurid dynasty, five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk dynasty (1206–1290), the (1290–1320), the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate
This article includes a list of successive Islamic state, Islamic states and History of Islam, Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that Spread of Islam, spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continuing through to the present day. The first-ever establishment of an Islamic polity goes back to the Muhammad in Medina, Islamic State of Medina, which was established by Muhammad in the city of Medina in 622 CE. Following Death of Muhammad, his death in 632 CE, Rashidun, his immediate successors established the Rashidun Caliphate, which was further succeeded by the Umayyad Caliphate and later the Abbasid Caliphate. While the primary Caliphate, caliphates gradually fractured and fell, other Muslim dynasties rose; some of these dynasties established notable and prominent Islamic empires, such as the Ottoman Empire centered around Anatolia, the Safavid Iran, Safavid Empire of Greater Iran, Persi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts ('' hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourth-most populous and thirteenth-largest state by area in India, as well as the eighth-most populous country subdivision of the world. As a part of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, it borders Bangladesh in the east, and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim and Assam. The state capital is Kolkata, the third-largest metropolis, and seventh largest city by population in India. West Bengal includes the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region, the Ganges delta, the Rarh region, the coastal Sundarbans and the Bay of Bengal. The state's main ethnic group are the Bengalis, with the Bengali Hindus forming the demographic majority. The area's early history featured a succession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauḍa (city)
Gauḍa (also known as Gaur, Gour, Lakhnauti, and Jannatabad) is a historic city of Bengal in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, and one of the most prominent capitals of classical and medieval India, being the capital city of Bengal under several kingdoms. The Gauḍa region was also a province of several pan-Indian empires. During the seventh century, the Gauda Kingdom was founded by King Shashanka, whose reign corresponds with the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Gauda gradually became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis. It was conquered by Bakhtiyar Khalji, a lieutenant of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor in 1203. For a period of 112 years, between 1453 and 1565, Gauda was the capital of the Bengal Sultanate. In 1500, Gauda was the fifth-most populous city in the world, with a population of 200,000, as well as one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent. The Portuguese left detailed accounts of the city. The Sultans built a citadel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamsuddin Firoz Shah
Shamsuddin Firuz Shah ( fa, شمس الدين فيروز شاه, bn, শামসুদ্দীন ফিরুজ শাহ, ''Shams Ad-Dīn Firūz Shāh'') (reigned: 1301–1322) was the independent ruler of the Lakhnauti Kingdom. He ascended the throne with the title of ''Al-Sultan Al-Azam Shams Al-Duniya wa Al-Din Abu Al-Muzaffar Firuz Shah Al-Sultan'' and invoked the name of the ''Abbaside Caliph Mustasim Billah'' in his coins. Origin His origin and identity is uncertain. He was once thought, based on the writings of Ibn Battuta, to be the son of Bughra Khan and the grandson of Sultan Ghiyasuddin Balban. This belief was challenged in the 1940s by scholars who showed Ibn Batuta to be unreliable regarding this part of the history of Bengal. They furthermore observed, on a close examination of his coins, that Firuz called himself only "Sultan", not "Sultan bin Sultan" or "Sultan bin Sultan bin Sultan" as would have been customary if he were a descendant of Balbani. KR Qanu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Sylhet
The Conquest of Sylhet ( bn, শ্রীহট্টের বিজয়, Srīhôtter Bijôy, Conquest of Srihatta) predominantly refers to an Islamic conquest of Srihatta (present-day Sylhet, Bangladesh) led by Sikandar Khan Ghazi, the military general of Sultan Shamsuddin Firoz Shah of the Lakhnauti Sultanate, against the Hindu king Gour Govinda. The conquest was aided by a Muslim saint known as Shah Jalal, who later ordered his disciples to scatter throughout eastern Bengal and propagate the religion of Islam. The Conquest of Sylhet may also include other minor incidents taking place after Govinda's defeat, such as the capture of nearby Taraf. Background The Greater Sylhet region historically consisted of many Hindu petty kingdoms such as Srihatta (Gour), Laur and Jaintia. Govinda was a conservative Hindu ruler of the Gour Kingdom, intolerant and harsh towards other faiths such as Islam, Buddhism and even certain denominations of Hinduism. It was known by his peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |