|
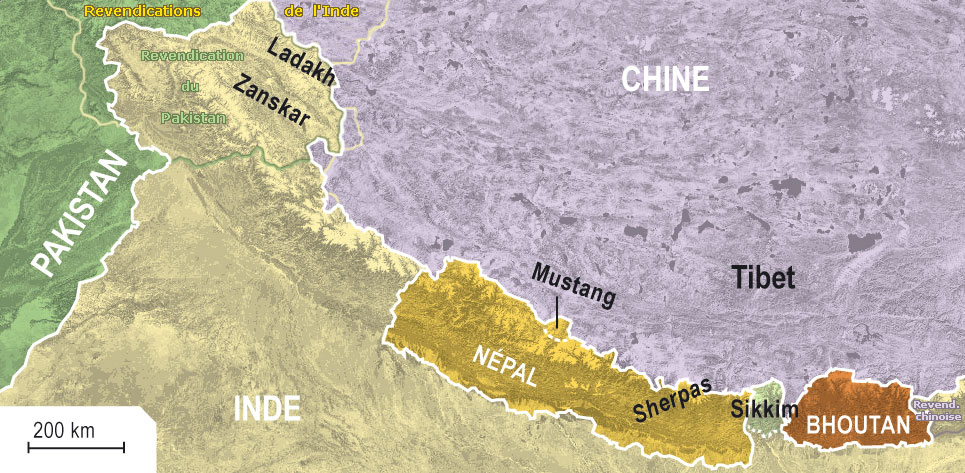
History Of Tibet (1950–present)
The history of Tibet from 1950 to the present includes the Chinese invasion of Tibet in 1950, and the Battle of Chamdo. Before then, Tibet had been a ''de facto'' independent nation. In 1951, Tibetan representatives in Beijing signed the Seventeen-point Agreement under duress, which affirmed China's sovereignty over Tibet while it simultaneously provided for an autonomous administration led by Tibet's spiritual leader, and then-political leader, the 14th Dalai Lama. During the 1959 Tibetan uprising, when Tibetans arose to prevent his possible assassination, the Dalai Lama escaped from Tibet to northern India where he established the Central Tibetan Administration, which rescinded the Seventeen-point Agreement. The majority of Tibet's land mass, including all of U-Tsang and areas of Kham and Amdo, was officially established in 1965 as Tibet Autonomous Region, within China. 1950–1955: Traditional systems In 1949, seeing that the Communists were gaining control of China, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Tibet (1950–1951)
The Battle of Chamdo (or Qamdo; ) occurred from 6 to 24 October 1950. It was a military campaign by the People's Republic of China (PRC) to take the Chamdo Region from a ''de facto'' independent Tibetan state.Shakya 1999 pp.28–32. The campaign resulted in the capture of Chamdo and the annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China. Background Kham was a border region of Tibet. Prior to the establishment of the PRC, it roughly coincided with the Sikang Province under Kuomintang-led Republic of China. Its western half is known as Chamdo. The Khampa Tibetans and Lhasa Tibetans held each other in mutual contempt and dislike, with the Khampas in some cases hating Lhasa rule even more than Chinese rule, which was why the Khampas did little to resist Chinese forces as they entered eastern Kham and subsequently took over the whole of Tibet. Likewise, the Qinghai (Amdo) Tibetans view the Tibetans of Central Tibet (Tibet proper, ruled by the Dalai Lamas from Lhasa) as diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, Rocket Force, and Strategic Support Force. It is under the leadership of the Central Military Commission (CMC) with its chairman as commander-in-chief. The PLA can trace its origins during the Republican Era to the left-wing units of the National Revolutionary Army (NRA) of the Kuomintang (KMT) when they broke away on 1 August 1927 in an uprising against the nationalist government as the Chinese Red Army before being reintegrated into the NRA as units of New Fourth Army and Eighth Route Army during the Second Sino-Japanese War. The two NRA communist units were reconstituted into the PLA on 10 October 1947. Today, the majority of military units around the country are assigned to one of five theater commands by geographical location. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
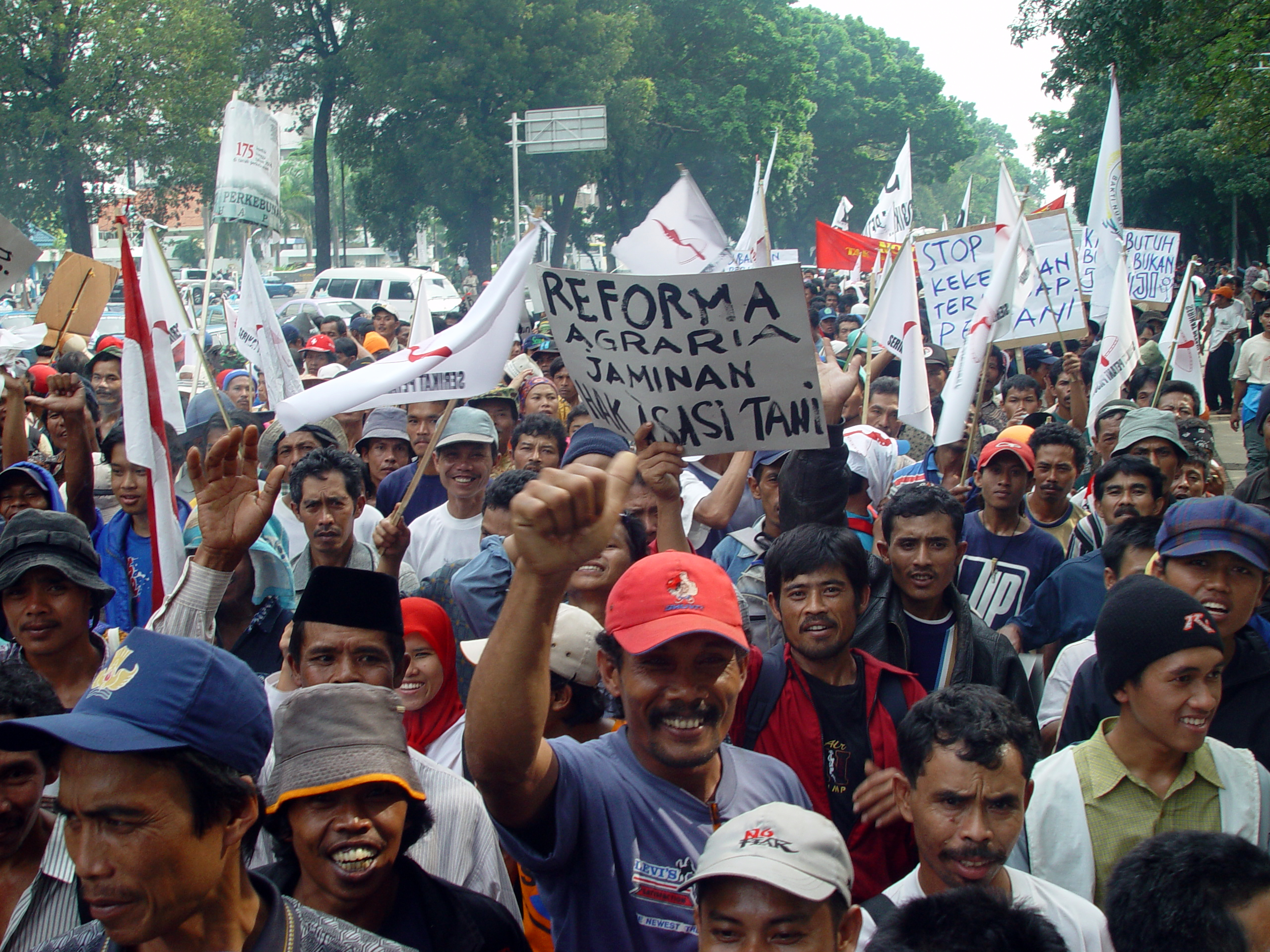
Land Reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural land. Land reform can, therefore, refer to transfer of ownership from the more powerful to the less powerful, such as from a relatively small number of wealthy or noble owners with extensive land holdings (e.g., plantations, large ranches, or agribusiness plots) to individual ownership by those who work the land. Such transfers of ownership may be with or without compensation; compensation may vary from token amounts to the full value of the land. Land reform may also entail the transfer of land from individual ownership—even peasant ownership in smallholdings—to government-owned collective farms; it has also, in other times and places, referred to the exact opposite: division of government-owned collective farms into smallholdings. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xikang
Xikang (also Sikang or Hsikang) was a nominal province formed by the Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and continued by the early People's Republic of China. Thei idea was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then independent Tibet controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River. The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement. The eastern part of the province was inhabited by a number of different ethnic groups, such as Han Chinese, Yi, Qiang people and Tibetan, then known as ''Chuanbian'' (), a special administrative region of the Republic of China. In 1939, it becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highways
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access highway, or a translation for ''autobahn'', '' autoroute'', etc. According to Merriam Webster, the use of the term predates the 12th century. According to Etymonline, "high" is in the sense of "main". In North American and Australian English, major roads such as controlled-access highways or arterial roads are often state highways (Canada: provincial highways). Other roads may be designated "county highways" in the US and Ontario. These classifications refer to the level of government (state, provincial, county) that maintains the roadway. In British English, "highway" is primarily a legal term. Everyday use normally implies roads, while the legal use covers any route or path with a public right of access, including footpaths etc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom In Exile
''Freedom in Exile: The Autobiography of the Dalai Lama'' is the second autobiography of the 14th Dalai Lama, released in 1991. The Dalai Lama's first autobiography, '' My Land and My People'', was published in 1962, a few years after he reestablished himself in India and before he became an international celebrity. He regards both of the autobiographies as authentic and re-issued ''My Land and My People'' in 1997 to coincide with the release of the film ''Kundun''. Background In the introduction, the Dalai Lama explains that he wrote the book "to counter Chinese claims and misinformation" about the history of Tibet. The title "Freedom in exile" refers to the freedoms he says that India offers to him. The idea for a second autobiography came from a British journalist, Alexander Norman, in the 1980s, who sat and taped the Dalai Lama for "several hours at a time" and wrote the book out of the manuscripts. Synopsis The autobiography starts with the Dalai Lama's "birth to a fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenzin Gyatso
The 14th Dalai Lama (spiritual name Jetsun Jamphel Ngawang Lobsang Yeshe Tenzin Gyatso, known as Tenzin Gyatso (Tibetan: བསྟན་འཛིན་རྒྱ་མཚོ་, Wylie: ''bsTan-'dzin rgya-mtsho''); né Lhamo Thondup), known as Gyalwa Rinpoche to the Tibetan people, is the current Dalai Lama. He is the highest spiritual leader and former head of the country of Tibet. He was born on 6 July 1935, or in the Tibetan calendar, in the Wood-Pig Year, 5th month, 5th day. He is considered a living Bodhisattva, specifically, an emanation of Avalokiteśvara in Sanskrit and Chenrezig in Tibetan. He is also the leader and a monk of the Gelug school, the newest school of Tibetan Buddhism, formally headed by the Ganden Tripa. The central government of Tibet, the Ganden Phodrang, invested the Dalai Lama with temporal duties until his exile in 1959. The 14th Dalai Lama was born to a farming family in Taktser (Hongya Village), in the traditional Tibetan region of Amdo (administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Peissel
Michel Georges Francois Peissel (February 11, 1937 – October 7, 2011) was a French ethnologist, explorer and author. He wrote twenty books mostly on his Himalayan and Tibetan expeditions. Peissel was an emeritus member of the Explorers Club and a Fellow of the Royal Geographical Society. Biography Peissel was the son of a French diplomat, raised in England after his father was posted to London, and able to speak English from early childhood. He later became fluent in several languages, including Tibetan. He studied for a year at Oxford University and the Harvard Business School and obtained a doctorate in Tibetan Ethnology from the Sorbonne, Paris. First journey In 1958, at the age of 21 — stranded on the coast of Quintana Roo, Mexico,— he walked down the coast to Belize discovering, on the way, 14 unrecorded Mayan archeological sites. This journey changed his life, and is an account of Quintana Roo State that unveils a world where 'chicleros', 'cocaleros' and Mayan fishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)