|
Hisingerfjellet
Hisingerfjellet is a mountain in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has two peaks with heights of 1,078 and 1.044 m.a.s.l., respectively. The mountain is located between Krylbreen, Krylen, Breskarvet and Bromelldalen, at the southern side of Van Mijenfjorden. It is named after Swedish geologist Wilhelm Hisinger Wilhelm Hisinger (23 December 1766 – 28 June 1852) was a Swedish physicist and chemist who in 1807, working in coordination with Jöns Jakob Berzelius, noted that in electrolysis any given substance always went to the same pole, and that substanc .... References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Hisinger
Wilhelm Hisinger (23 December 1766 – 28 June 1852) was a Swedish physicist and chemist who in 1807, working in coordination with Jöns Jakob Berzelius, noted that in electrolysis any given substance always went to the same pole, and that substances attracted to the same pole had other properties in common. This showed that there was at least a qualitative correlation between the chemical and electrical natures of bodies. Career In 1803, in separate laboratories, Martin Heinrich Klaproth in one, and Berzelius and Hisinger in another, the element Cerium was discovered, which was named after the newly discovered asteroid, Ceres. It was discovered nearly simultaneously by both laboratories, though it was later shown that Berzelius and Hisinger's cerium was actually a mixture of cerium, lanthanum and so-called didymium. The element was first isolated by Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1838. Hisinger was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1804. Death and legacy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromelldalen
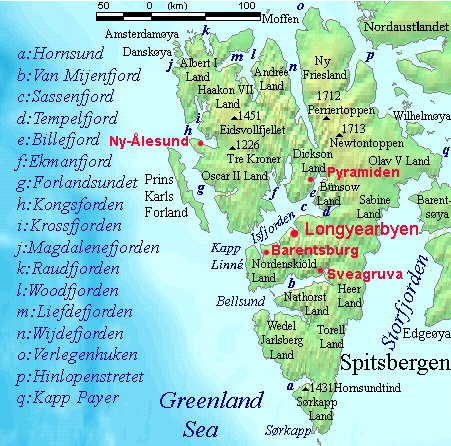
Bromelldalen is a valley in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about eight kilometers, and is located between the mountains of Sven Nilssonfjellet and Bassøefjellet on the eastern side, and Hisingerfjellet to the west, at the southern side of Van Mijenfjorden Van Mijenfjorden is the third-longest fjord in Norway's Svalbard archipelago. It lies in the southern portion of Spitsbergen island, south of Nordenskiöld Land and north of Nathorst Land. The fjord is long, being separated from Bellsund further .... The valley is named after Swedish botanist Olof Bromelius. References Valleys of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krylbreen
Krylbreen is a glacier in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about four kilometers, and extends northwards from the mountain of Krylen, between the mountains of Hisingerfjellet and Wahlenbergfjellet Wahlenbergfjellet is a mountain in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has two peaks, with heights of 949 and 915 m.a.s.l., respectively. The mountain is located between Krylbreen, Krylen and Frysjadalen, at the southern side of Van Mije .... References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathorst Land
Nathorst Land is the land area between Van Keulenfjorden and Van Mijenfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after Alfred Gabriel Nathorst Alfred Gabriel Nathorst (7 November 1850 – 20 January 1921) was a Swedish Arctic explorer, geologist, and palaeobotanist. Life He was born in Väderbrunn in Sweden. Nathorst's interest in geology was awoken by Charles Lyell’s ‘’Pr .... The Aspelintoppen mountain is the highest peak in Nathorst Land. References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breskarvet
Breskarvet is a mountain ridge in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about six kilometres. It is situated north of the mountain range of Törnbohmfjella, and south of Krylen. Surrounding glaciers are Martinbreen, Richterbreen, Frysjabreen Frysjabreen is a glacier in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about six kilometers, and extends from the ridges of Breskarvet and Kjellmanberget down to the valley of Frysjadalen. The glacier is named after the river Frys ..., Skarvisen and Greenbreen. References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Mijenfjorden
Van Mijenfjorden is the third-longest fjord in Norway's Svalbard archipelago. It lies in the southern portion of Spitsbergen island, south of Nordenskiöld Land and north of Nathorst Land. The fjord is long, being separated from Bellsund further out by Akseløya and Mariaholmen. The settlement of Sveagruva lies on the fjord's north bank. The fjord is named after the Dutch Dutch commonly refers to: * Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands * Dutch people () * Dutch language () Dutch may also refer to: Places * Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States * Pennsylvania Dutch Country People E ... whaler Willem Cornelisz. van Muyden, who was involved in the trade in 1612 and 1613. Van Mijenfjorden (an obvious corruption of Van Muyden's name) was originally called ''Lowe Sound'', while the small cove north of Axel Island (at the mouth of the fjord) was called ''Van Muyden's Haven''. This latter name was moved from its proper location by Giles and Rep (c. 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |