|
High Prussian Dialect
High Prussian (german: Hochpreußisch) is a group of East Central German dialects in former East Prussia, in present-day Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (Poland) and Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia). High Prussian developed in the 13th–15th centuries, brought in by German settlers mainly from Silesia and Thuringia, and was influenced by the Baltic Old Prussian language. Classification High Prussian is a Central German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, Low Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Low German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. It shares some features with Low Prussian, differentiating it from other Central German dialects east of the . Those Borussisms are: * Loss of ''/-n/'' in infinitives (''mache'' for Standard German , "to make"); * retention of the prefix ''//ge-//'' in the participe perfect passive (compare Meckel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectuals and leaders in the arts: Johann Sebastian Bach, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, and Fried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight And Expulsion Of Germans From Poland During And After World War II
The flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland was the largest of a series of flights and expulsions of Germans in Europe during and after World War II. The German population fled or was expelled from all regions which are currently within the territorial boundaries of Poland, including the former eastern territories of Germany annexed by Poland after the war and parts of pre-war Poland. West German government figures of those evacuated, migrated, or expelled by 1950 totaled 8,030,000 (6,981,000 from the former eastern territories of Germany; 290,800 from Danzig, 688,000 from pre-war Poland and 170,000 Baltic Germans resettled in Poland during the war). Research by the West German government put the figure of Germans emigrating from Poland from 1951 to 1982 at 894,000; they are also considered expellees under German Federal Expellee Law. The German population east of Oder-Neisse was estimated at over 11 million in early 1945. The first mass flight of Germans followed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evacuation Of East Prussia
The evacuation of East Prussia was the movement of German civilian population and military personnel from East Prussia between 20 January and March 1945, that was initially organized and carried out by state authorities but quickly turned into a chaotic flight from the Red Army. A part of the evacuation of German civilians towards the end of World War II, these events are not to be confused with the expulsion from East Prussia that followed after the war had ended. The area that was evacuated was not the Gau East Prussia, but the inter-war East Prussia where most people already held German citizenship. German citizens in Memel and other regions with proximity to East Prussia also took part in the evacuation, wishing to escape by sea, even though in their regions there was no official evacuation announced. The evacuation, which had been delayed for months, was initiated due to fear of the Red Army advances during the East Prussian Offensive. Some parts of the evacuation were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endonym And Exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, or linguistic community in question; it is their self-designated name for themselves, their homeland, or their language. An exonym (from Greek: , 'outer' + , 'name'; also known as xenonym) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used only outside that particular place, group, or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonym ''Germany'' in English, in Spanish and in French. Naming and etymology The terms ''autonym'', ''endonym'', ''exonym'' and ''xe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
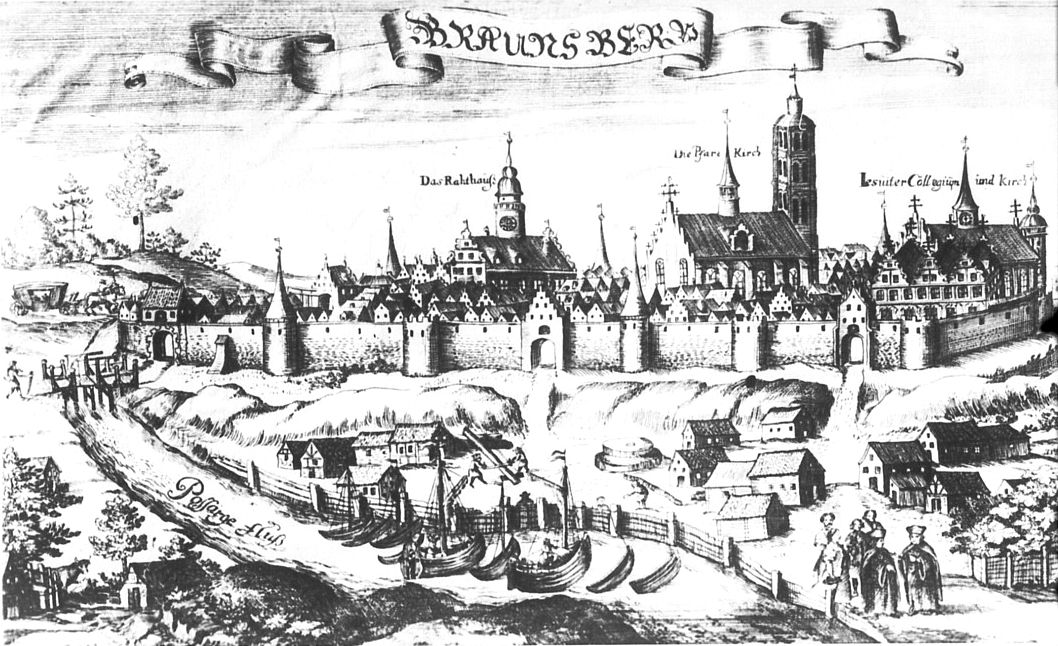
Braniewo
Braniewo () (german: Braunsberg in Ostpreußen, la, Brunsberga, Old Prussian: ''Brus'', lt, Prūsa), is a town in northern Poland, in Warmia, in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, with a population of 16,907 as of June 2021. It is the capital of Braniewo County. Braniewo is the second biggest city of Warmia after Olsztyn and one of the historical centers of the region. Location Braniewo lies on the Pasłęka River about 5 km from the Vistula Lagoon, about 35 km northeast of Elbląg and southwest of Kaliningrad ( pl, Królewiec). The Polish border with Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast lies 6 km north, and may be reached from Braniewo via National road 54. History Middle Ages According to the German geographer Johann Friedrich Goldbeck (1748-1812), the town originally was named Brunsberg after Bruno von Schauenburg (1205–1281), bishop of Olomouc in Moravia, who accompanied King Ottokar II of Bohemia in 1254 and 1267 when the latter participated in the crusade of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umlaut (diacritic)
The umlaut () is the diacritical mark used to indicate in writing (as part of the letters , , and ) the result of the historical sound shift due to which former back vowels are now pronounced as front vowels (for example , , and as , , and ). (The term ermanicumlaut is also used for the underlying historical sound shift process.) In its contemporary printed form, the mark consists of two dots placed over the letter to represent the changed vowel sound. It looks identical to the diaeresis mark used in other European languages and is represented by the same Unicode code point. The word '' trema'' (french: tréma), used in linguistics and also classical scholarship, describes the form of both the umlaut diacritic and the diaeresis rather than their function and can therefore be used to refer to both. German origin and current usage (literally "changed sound") is the German name of the sound shift phenomenon also known as ''i-mutation''. In German, this term is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant shift, and the dialect continuum that connects German to the neighboring varieties of Low Franconian (Dutch) and Frisian. The varieties of German are conventionally grouped into Upper German, Central German and Low German; Upper and Central German form the High German subgroup. Standard German is a standardized form of High German, developed in the early modern period based on a combination of Central German and Upper German varieties. Etymology and nomenclature Traditionally, all of the major dialect groupings of German dialects are typically named after so-called " stem duchies" or "tribal duchies" (German: ''Stammesherzogtümer'') by early German linguists, among whom the Brothers Grimm were especially influential. These triba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uerdingen Line
The Uerdingen Line (german: Ürdinger Linie, Uerdinger Linie, nl, Uerdinger linie; named after Uerdingen by Georg Wenker) is the isogloss within West Germanic languages that separates dialects which preserve the ''-k'' sound in the first person singular pronoun word "ik" (north of the line) from dialects in which the word-final ''-k'' has changed to word final ''-ch'' in the word "ich" (IPA ) (south of the line). This sound shift is the one that progressed the farthest north among the consonant shifts that characterize High German and Middle German dialects. The line passes through Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany. North of the line Low German and Dutch are spoken. South of the line Central German is spoken. In the area between the Uerdingen line and the Benrath line to its south, which includes parts of Belgium and the Netherlands, the Germanic dialect Limburgish is spoken. Especially in eastern Germany, the regional languages have been largely replaced by standard German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
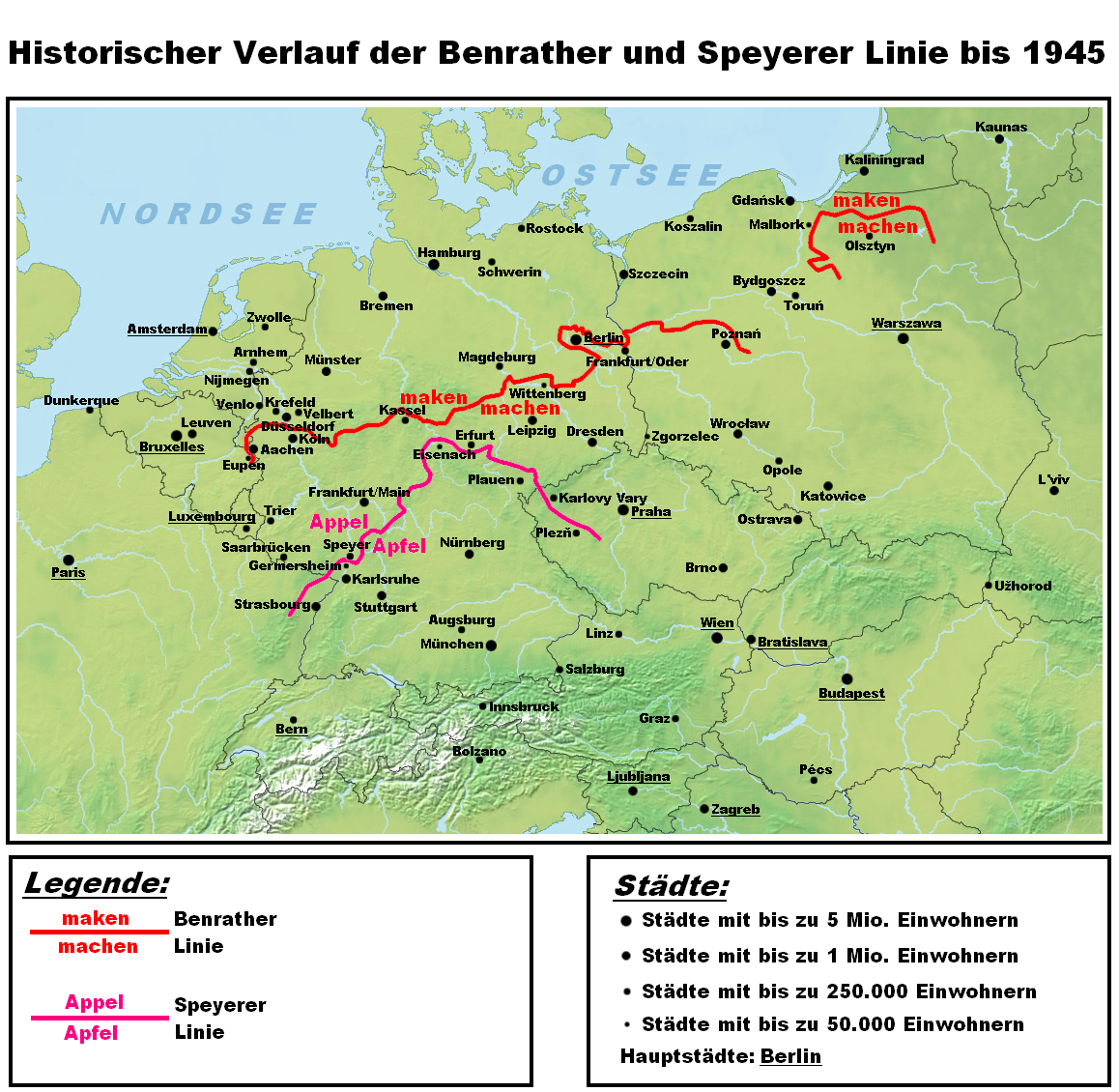
Benrath Line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs from Aachen in the west via Benrath (south of Düsseldorf) to eastern Germany near Frankfurt an der Oder in the area of Berlin and Dessau and through former East Prussia dividing Low Prussian dialect and High Prussian dialect. It is called Benrath line because Benrath is the place where it crosses the Rhine. The High German consonant shift (3rd to 9th centuries AD), in which the (northern) Low German dialects for the most part did not participate, affected the southern varieties of the West Germanic dialect continuum. This shift is traditionally seen to distinguish the High German varieties from the other West Germanic languages. The impact of the High German consonant shift increases gradually to the South. The Benrath line does not mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia (region)
Prussia (Old Prussian: ''Prūsa''; german: Preußen; lt, Prūsija; pl, Prusy; russian: Пруссия, tr=Prussiya, ''/Prussia/Borussia'') is a historical region in Europe on the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, that ranges from the Vistula delta in the west to the end of the Curonian Spit in the east and extends inland as far as Masuria. Tacitus's ''Germania'' (98 AD) is the oldest known record of an eyewitness account on the territory and its inhabitants. Pliny the Elder had already confirmed that the Romans had navigated into the waters beyond the ''Cimbric peninsula'' (Jutland). Suiones, Sitones, Goths and other Germanic people had temporarily settled to the east and west of the Vistula River during the Migration Period, adjacent to the Aesti, who lived further to the east. Overview The region's inhabitants of the Middle Ages have first been called ''Bruzi'' in the brief text of the Bavarian Geographer and since been referred to as Old Prussians, who, beginning in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |