|
Heywood Class Attack Transport
The ''Heywood''-class attack transport was a class of US Navy attack transport built in 1919 that saw service in World War II. Like all attack transports, the purpose of the ''Heywood'' class ships was to transport troops and their equipment to hostile shores in order to execute amphibious invasions. To fulfill their mission, attack transports were fitted with a substantial number of integral landing craft, and were well armed with antiaircraft weaponry to protect themselves and their vulnerable cargo of troops from air attack in the battle zone. Background The ''Heywood'' class is amongst the few classes of attack transport that were converted from pre-war tonnage rather than built from either Maritime Commission or Victory ship hull types during the war. The origins of the ''Heywood'' class go back to the U.S. entry into World War I. At that time, the US Shipping Board was set up to modernize America's merchant cargo fleet, and to provide ships suitable for service as naval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alameda Works Shipyard
The Alameda Works Shipyard, in Alameda, California, United States, was one of the largest and best equipped shipyards in the country. The only building remaining from the yard is the Union Iron Works Powerhouse, which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.1956. History Established in the early 1900s by United Engineering Works, the yard was purchased by Union Iron Works (Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation) in 1916 and came to be known as the Alameda Works. During the World War I period the yard built cargo ships, tankers and 2 small tugboats. For the UK Admiralty * '' War Knight'', '' War Monarch'', '' War Sword'' (1917, 7,700t cargo) * ''War Harbor'', ''War Haven'', ''War Ocean'', ''War Rock'', ''War Sea'' (1918, 7,600t cargo) * ''War Cape'' / '' Pan Massachusetts, ''War Surf'', ''War Wave'' (1919, 7,600t cargo) For other private contractors * ''Talabot'', ''Bessa'' (1917, 7,700t cargo) For Atlantic Refining * ''J. E. O'Neill'', ''Herbert L. Pratt'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Commission
The United States Maritime Commission (MARCOM) was an independent executive agency of the U.S. federal government that was created by the Merchant Marine Act of 1936, which was passed by Congress on June 29, 1936, and was abolished on May 24, 1950. The commission replaced the United States Shipping Board which had existed since World War I. It was intended to formulate a merchant shipbuilding program to design and build five hundred modern merchant cargo ships to replace the World War I vintage vessels that comprised the bulk of the United States Merchant Marine, and to administer a subsidy system authorized by the Act to offset the cost differential between building in the U.S. and operating ships under the American flag. It also formed the United States Maritime Service for the training of seagoing ship's officers to man the new fleet. As a symbol of the rebirth of the U.S. Merchant Marine and Merchant Shipbuilding under the Merchant Marine Act, the first vessel contracted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Guadalcanal
The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theater of World War II. It was the first major land offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan. On 7 August 1942, Allied forces, predominantly United States Marines, landed on Guadalcanal, Tulagi, and Florida in the southern Solomon Islands, with the objective of using Guadalcanal and Tulagi as bases in supporting a campaign to eventually capture or neutralize the major Japanese base at Rabaul on New Britain. The Japanese defenders, who had occupied those islands since May 1942, were outnumbered and overwhelmed by the Allies, who captured Tulagi and Florida, as well as the airfield – later named Henderson Field – that was under construction on Guadalcanal. Surprised by the Allied offensive, the Japanese made se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Invasion Of Sicily
The Allied invasion of Sicily, also known as Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II in which the Allied forces invaded the island of Sicily in July 1943 and took it from the Axis powers ( Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany). It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian campaign. To divert some of the Axis forces to other areas, the Allies engaged in several deception operations, the most famous and successful of which was Operation Mincemeat. Husky began on the night of 9–10 July 1943 and ended on 17 August. Strategically, Husky achieved the goals set out for it by Allied planners; the Allies drove Axis air, land and naval forces from the island and the Mediterranean sea lanes were opened for Allied merchant ships for the first time since 1941. These events led to the Italian leader, Benito Mussolini, being toppled from power in Italy on 25 July, and to the Allied invasion of Italy on 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
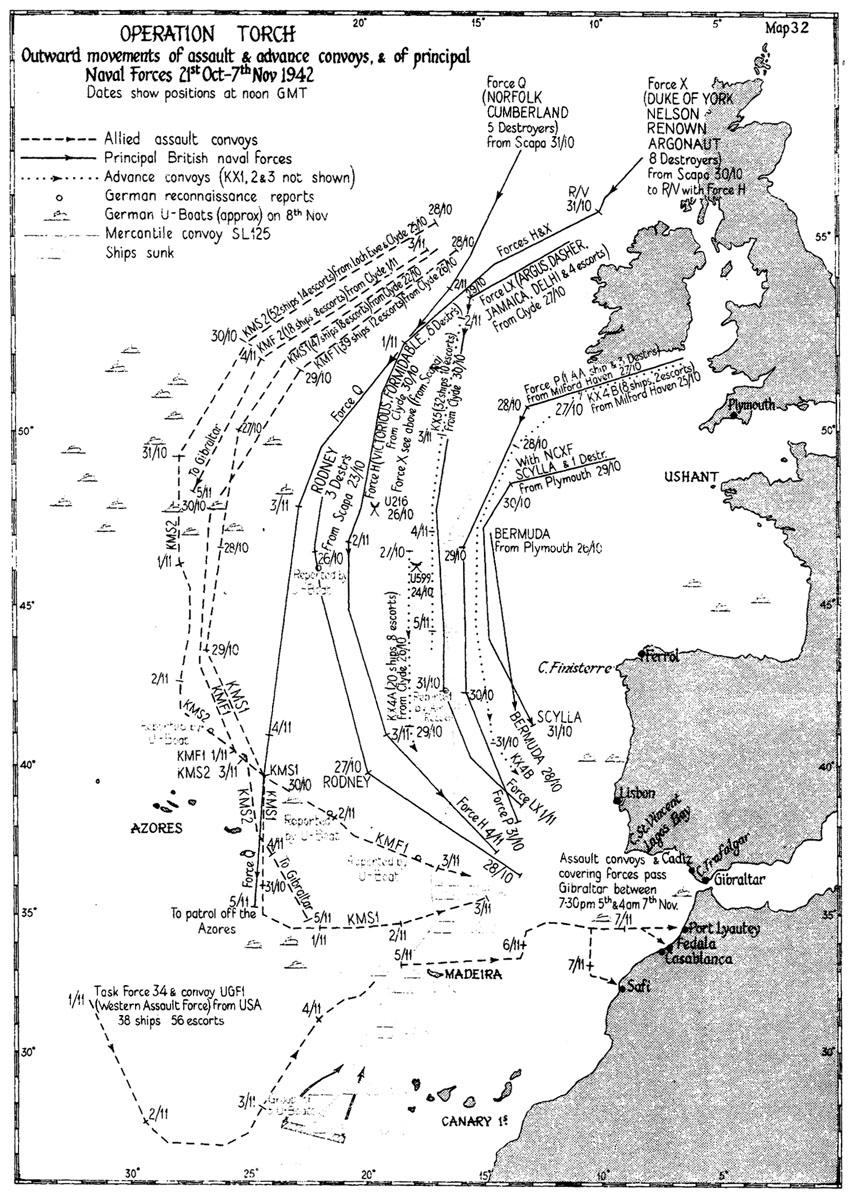
Operation Torch
Operation Torch (8 November 1942 – Run for Tunis, 16 November 1942) was an Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. Torch was a compromise operation that met the British objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to engage in the fight against Nazi Germany on a limited scale. It was the first mass involvement of US troops in the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II, European–North African Theatre, and saw the first major airborne assault carried out by the United States. While the French colonies were formally aligned with Germany via Vichy France, the loyalties of the population were mixed. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in Mediterranean Theater of Operations, planned a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Center) and Algiers (Easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs & Cox
Gibbs & Cox is an American naval architecture firm that specializes in designing surface warships. Founded in 1922 in New York City, Gibbs & Cox is now headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. The firm has offices in New York City; Washington, D.C.; Newport News, Virginia; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; and New Orleans, LA. In 2003, more than 150 warships built to the firm's designs, including 60 percent of the U.S. Navy's surface combatant fleet, were on active duty in nearly 20 navies. History The firm was founded as "Gibbs Brothers" by self-taught naval architect William Francis Gibbs and his brother Frederic H. Gibbs. The name was changed when architect Daniel H. Cox of Cox & Stevens joined the firm in 1929. In 1931, Gibbs & Cox designed the MV ''Savarona'', a large luxury yacht. According to company officials, more than 70 percent of U.S. tonnage launched during World War II was built to Gibbs & Cox designs. Ship types included destroyers, LST landing craft, minesweepers, tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore Steamship Company
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by population, the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an Independent city (United States), independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the List of metropolitan areas of the United States, 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area, Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest combined statistical area, CSA in the nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |