|
Hertford, Luton And Dunstable Railway
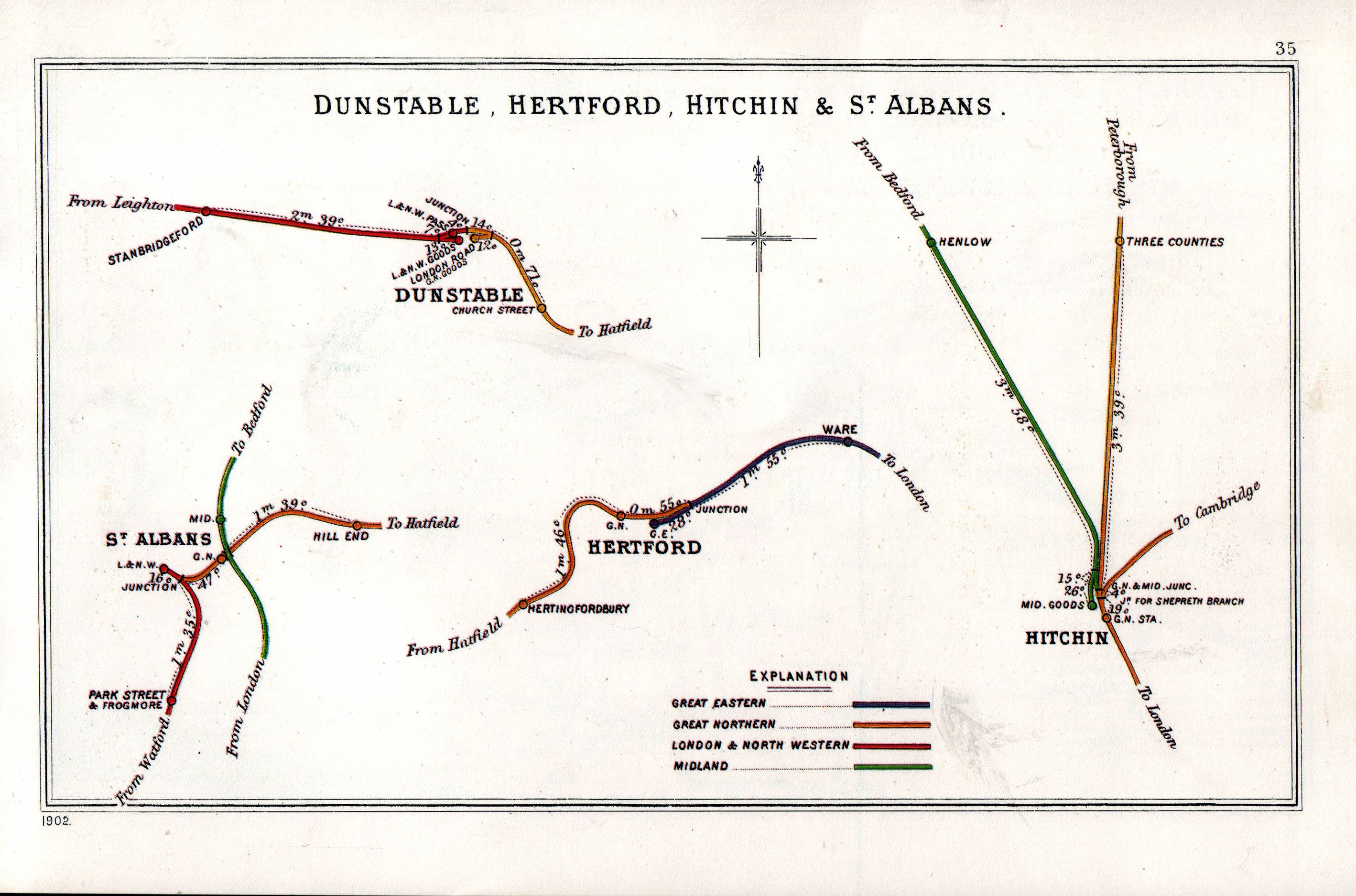
The Hertford, Luton and Dunstable Railway was a railway affiliated to the Great Northern Railway (Great Britain), Great Northern Railway. It was formed when the Hertford and Welwyn Junction Railway (opened 1858) merged with the Luton, Dunstable and Welwyn Junction Railway, partly opened in the same year. The merger and change of title took place in 1860. The line joined the Dunstable Branch Lines, Dunstable branch of the London and North Western Railway at Dunstable. For some time the HL&DR was the only railway at Luton, and the early industry took considerable benefit from it, and later industry was encouraged by it. Even when the competing direct line from Luton to London was opened, the route via Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield held its own for some time. The Hertford extremity did not fare so well, and remained rural and relatively undeveloped throughout its life. Passenger services on the Hatfield to Hertford line ended in 1951; those between Hatfield and Dunstable ended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway (Great Britain)
The Great Northern Railway (GNR) was a British railway company incorporated in 1846 with the object of building a line from London to York. It quickly saw that seizing control of territory was key to development, and it acquired, or took leases of, many local railways, whether actually built or not. In so doing, it overextended itself financially. Nevertheless, it succeeded in reaching into the coalfields of Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire, as well as establishing dominance in Lincolnshire and north London. Bringing coal south to London was dominant, but general agricultural business, and short- and long-distance passenger traffic, were important activities too. Its fast passenger express trains captured the public imagination, and its Chief Mechanical Engineer Nigel Gresley became a celebrity. Anglo-Scottish travel on the East Coast Main Line became commercially important; the GNR controlled the line from London to Doncaster and allied itself with the North Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major town on the old Roman Britain, Roman road of Watling Street for travellers heading north and became the city of Verulamium. It is within the London commuter belt and the Greater London Built-up Area. Name St Albans takes its name from the first British saint, Saint Alban, Alban. The most elaborate version of his story, Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', relates that he lived in Verulamium, sometime during the 3rd or 4th century, when Christians were suffering persecution. Alban met a Christian priest fleeing from his persecutors and sheltered him in his house, where he became so impressed with the priest's piety that he converted to Christianity. When the authorities searched Alban's house, he put on the priest's cloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertingfordbury Railway Station (1953)
Hertingfordbury railway station was a station at Hertingfordbury, Hertfordshire, England, on the Hertford and Welwyn Junction Railway. It was a passenger station from December 1858 until 18 June 1951. It had a single platform and a small goods yard to the east. The line was finally closed to all traffic in 1962. The station building has been converted to a private residence, with the old line open as a public right of way, named the Cole Green Way The Cole Green Way is a rail trail which runs east-west from the eastern edge of Welwyn Garden City to Hertford in Hertfordshire. Part of National Cycle Network Route 61, and the Lea Valley Walk, it runs for more than six miles along the for .... References Disused railway stations in Hertfordshire Former Great Northern Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1858 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1951 1858 establishments in England 1951 disestablishments in England {{EastEn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railmotor
Railmotor is a term used in the United Kingdom and elsewhere for a railway lightweight railcar, usually consisting of a railway carriage with a steam traction unit, or a diesel or petrol engine, integrated into it. Steam railcars Overview In the earliest days of railways, designers wished to produce a vehicle for passenger carrying that was economical to build and operate on routes where passenger numbers were light. A single coach with its own prime mover was a solution adopted in some cases; this may be thought of as the predecessor to the railcar, a term more associated with the use of internal combustion engines. William Bridges Adams started building railmotors in small numbers as early as 1848. The Bristol and Exeter Railway used a steam carriage. In most cases the early designs were unsuccessful technically, but in the early years of the twentieth century, street-running passenger tramways started to use small steam engines to draw tramcars, replacing the customary hors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertford Cowbridge Railway Station
Hertford Cowbridge railway station was a station on the Hertford and Welwyn Junction Railway, and was situated in Hertford, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b .... History The station was opened on 1 March 1858, originally being named ''Hertford Cowbridge''. It was situated on the branch from , between and a junction with the Great Eastern Railway just to the east of their Hertford station. On 1 July 1923, the station was renamed ''Hertford North'', but did not last long under that name. When the Hertford Loop Line opened on 2 June 1924, a new ' station was opened on that line, the old one being closed the same day. Route Notes References * * External linksSite of Hertford Cowbridge on a navigable 1946 O.S. map Disused railway stations in H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia (Roman-governed Great Britain during the Roman Empire). The route linked Dover and London in the southeast, and continued northwest via St Albans to Wroxeter. The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England. First used by the ancient Britons, mainly between the areas of modern Canterbury and using a natural ford near Westminster, the road was later paved by the Romans. It connected the ports of Dubris (Dover), Rutupiae (Richborough Castle), Lemanis (Lympne), and Regulbium (Reculver) in Kent to the Roman bridge over the Thames at Londinium (London). The route continued northwest through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for International Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of all matters relating to Trade and Foreign Plantations, but is commonly known as the Board of Trade, and formerly known as the Lords of Trade and Plantations or Lords of Trade, and it has been a committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. The board has gone through several evolutions, beginning with extensive involvement in colonial matters in the 17th century, to powerful regulatory functions in the Victorian Era and early 20th century. It was virtually dormant in the last third of 20th century. In 2017, it was revitalised as an advisory board headed by the International Trade Secretary who has nominally held the title of President of the Board of Trade, and who at present is the only privy counsellor of the board, the other m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Yolland
William Yolland CB, FRS FRSA (17 March 1810 – 4 September 1885) was an English military surveyor, astronomer and engineer, and was Britain's Chief Inspector of Railways from 1877 until his death. He was a redoubtable campaigner for railway safety, often in the face of strong opposition, at a time when railway investment was being directed towards the expansion of the networks rather than the prevention of accidents. He was a member of the three-man committee of inquiry into the Tay Bridge disaster.Vetch (2004) Career Yolland was born in Plympton St Mary, Devon, the son of the land agent to Lord Morley, Plymouth, and his father promoted the boy's interest in surveying and land management by enrolling him at a school specialising in mathematics. He was commissioned into the Royal Engineers in 1828 and completed his technical training at the Royal School of Military Engineering in Chatham, Kent, in 1831. Ordnance Survey After army service in Britain, Ireland and Canada he was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunstable Town Railway Station
Dunstable Town, also known as Dunstable Church Street, was a railway station on the Great Northern Railway's branch line from Welwyn which served Dunstable in Bedfordshire from 1858 to 1965. Against a background of falling passenger numbers and declining freight returns, the station closed to passengers in 1965 and to goods in 1964, a casualty of the Beeching Axe. The station site is now in use as part of the Luton to Dunstable Busway. History The Luton, Dunstable and Welwyn Junction Railway (LD&WJR) was authorised on 16 July 1855 and empowered the construction of a line from Dunstable to join the Great Northern Railway's (GNR) main line at Digswell. The line would run from a junction near the London and North Western Railway's (LNWR) Dunstable station across the road now known as the A5 to a second station in Dunstable at Church Street. Finding itself in financial difficulties, the LD&WJR merged with the Hertford and Welwyn Junction Railway on 28 June 1858, thereby creati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cowper-Temple, 1st Baron Mount Temple
William Francis Cowper-Temple, 1st Baron Mount Temple, PC (13 December 1811 – 16 October 1888), known as William Cowper (pronounced "Cooper") before 1869 and as William Cowper-Temple between 1869 and 1880, was a British Liberal statesman. Background and education Born at Brocket Hall, Hertfordshire, Cowper was the second son of Peter Cowper, 5th Earl Cowper, and the Hon. Emily Lamb, daughter of Peniston Lamb, 1st Viscount Melbourne (since his mother had several lovers there is some doubt about his true paternity). He was the younger brother of George Cowper, 6th Earl Cowper and nephew of Prime Minister Lord Melbourne. His father died in 1837 and in 1839 his mother married another Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, who became Cowper's stepfather. He was educated at Eton. After entering the Royal Horse Guards in 1830, he was promoted Captain five years later, eventually attaining the rank of brevet Major in 1852. Political career In 1835, Cowper was elected Liberal Member of Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luton Bute Street Station With The Cobbler (1964)
Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable and Houghton Regis, had a population of 258,018. It is the most populous town in the county, from the County Towns of Hertford, from Bedford and from London. The town is situated on the River Lea, about north-north-west of London. The town's foundation dates to the sixth century as a Saxon outpost on the River Lea, from which Luton derives its name. Luton is recorded in the Domesday Book as ''Loitone'' and ''Lintone'' and one of the largest churches in Bedfordshire, St Mary's Church, was built in the 12th century. There are local museums which explore Luton's history in Wardown Park and Stockwood Park. Luton was, for many years, widely known for hatmaking and also had a large Vauxhall Motors factory. Car production at the plant began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digswell Viaduct
The Digswell Viaduct, also called Welwyn Viaduct, is a railway viaduct that carries the East Coast Main Line over the River Mimram in the county of Hertfordshire in England. A prominent local landmark, it is located between Welwyn Garden City and Digswell. It is just to the south of Welwyn North railway station. The viaduct, of 40 arches, is a Grade II* listed structure. It was the longest and tallest viaduct on the Great Northern Railway's route. The viaduct is around long and comprises forty arches of span, and it is high from ground level to trackbed. It is built of red brick fired from clay quarried on site during construction, and took two years to build, including the construction of embankments at both ends which required the movement of around one million tons of earth by human and horse power. It was designed by William Cubitt and styled after a Roman aqueduct. It has been claimed that it was officially opened by Queen Victoria on 6 August 1850, but she was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)

