|
Hermann Steudner
Carl Theodor Hermann Steudner (1 September 1832 – 10 April 1863) was a botanist and an explorer of Africa. Education and early work Steudner was born in Greiffenberg, located in Silesia, but grew up in Görlitz. He studied botany, mineralogy, and medicine in Berlin and Würzburg. Among his professors were Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, Heinrich Wilhelm Dove, and Carl Ritter in Berlin; and Rudolf Virchow, Franz von Rinecker, and Albert von Kölliker in Würzburg, where he began his friendship with Ernst Haeckel. Having returned to Berlin, Steudner devoted himself to botany and published on Marantaceae. He was elected a member of the Berlin Society of Friends of Natural Science. Expedition to Africa Heinrich Barth of the ''Gesellschaft für Erdkunde zu Berlin'' convinced Steudner to participate in an African expedition to search for Eduard Vogel, whose traces had been lost in the Ouaddai Empire. This expedition was initiated by Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Society Of Friends Of Natural Science
The Berlin Society of Friends of Natural Science, (Gesellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin, in German) (GNF) is a scientific society founded in 1773. Apart from the Danziger Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, it is the oldest private natural society in Germany. At its foundation it had numerous prominent and influential members who were experts in the natural sciences - biologists in particular. The society exists still, and has its seat at the Institute for Zoology of the Free University of Berlin. Early Members * Friedrich Heinrich Wilhelm Martini (1729-1778) * Johann Gottlieb Gleditsch (1714-1786) * Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1743-1817) * Dietrich Ludwig Gustav Karsten (1768-1810) * Adelbert von Chamisso (1781-1838) * Alexander von Humboldt (1769-1859) * Otto Friedrich Müller (1730-1784) * Carl Eduard von Martens (1831-1904) * Hinrich Lichtenstein (1780-1857) * Christian Samuel Weiss (1780-1856) * Hermann Steudner Carl Theodor Hermann Steudner (1 September 1832 – 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilen People
The Bilen (also variously transcribed as Blin, and also formerly known as the Bogo, Bogos or North Agaw) are a Cushitic ethnic group in the Eritrea. They are primarily concentrated in central Eritrea, in and around the city of Keren and further south toward Asmara, the nation's capital. They are split into three sub-tribes; Bet Tarqe, Bet Tawqe and Bab Jengeren which are split into further clans known as Hissat. The Tawke has six whereas the Tarke has five which each are divided into smaller kinship groups. SF Nadel. (1944Races and tribes of Eritrea/ref> Origins Tradition establishes an apparent connection between the Eritrean Bilen and the Ethiopian Agaw which can be seen in linguistic similarities between Agaw and Bilen. The presence of many identical place names in the areas around Lasta and Bogos in central Eritrea further alludes to some historical connection between the two groups. According to local oral tradition, the Bilen lived to the Eritrean plateau from Lasta around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
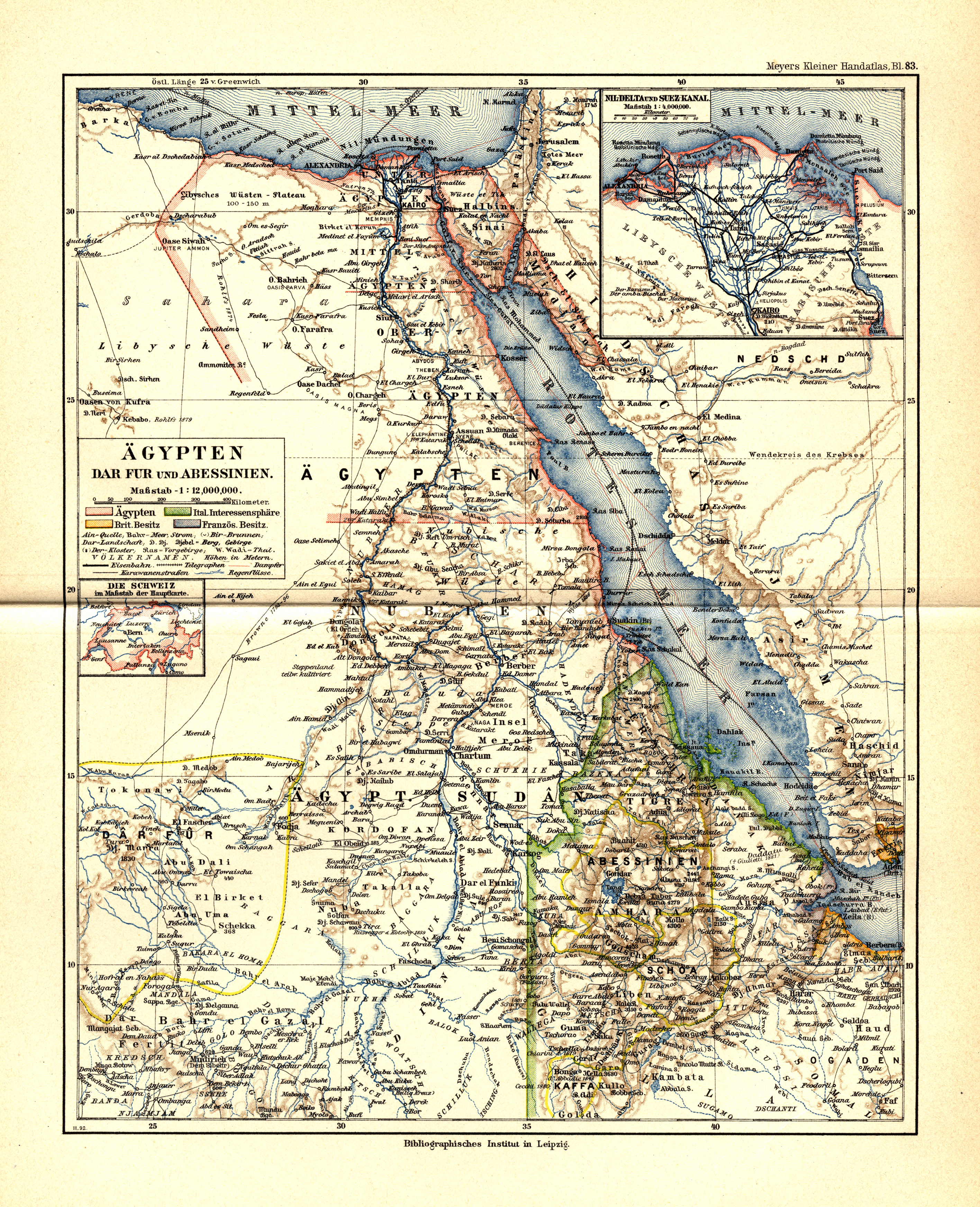
Keren, Eritrea
Keren (Tigrinya and Tigre: ), historically known as Sanhit,Shinn, David & al. "Hewitt Treaty" in the ''Historical Dictionary of Ethiopia''p. 214 is the second-largest city in Eritrea. It is situated around northwest of Asmara at an elevation of above sea-level. The city sprawls on a wide basin surrounded by granitic mountains on all sides. It serves as the capital of the Anseba Region, and is home to a number of ethnic groups including the Bilen people, Tigre people and Tigrinya people. History Keren grew around the Eritrean Railway to Asmara. The railway was later dismantled because of the war, although there are plans to rebuild it. It is an important commercial centre and was the scene of regular battles in both World War II and the Eritrean War of Independence. Keren was the site of a key battle between Italian and British troops in February – March 1941. Demographics As of 2016, Keren has a population of around 120,000 inhabitants. Residents belong to v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . It is sometimes called the Roof of Africa due to its height and large area. Most of the Ethiopian Highlands are part of central and northern Ethiopia, and its northernmost portion reaches into Eritrea. History In the southern parts of the Ethiopian Highlands once was located the Kingdom of Kaffa, a medieval early modern state, whence the coffee plant was exported to the Arabian Peninsula. The land of the former kingdom is mountainous with stretches of forest. The land is very fertile, capable of three harvests a year. The term ''coffee'' derives from the ar, قهوة, italic=no ()''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "coffee, ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1891. and is traced to Kaffa. Physical geography The Highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massawa
Massawa ( ; ti, ምጽዋዕ, məṣṣəwaʿ; gez, ምጽዋ; ar, مصوع; it, Massaua; pt, Maçuá) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahlak Archipelago.Matt Phillips, Jean-Bernard Carillet, ''Lonely Planet Ethiopia and Eritrea'', (Lonely Planet: 2006), p.340. It has been a historically important port for many centuries. Massawa was the capital of the Italian Colony of Eritrea until the seat of the colonial government was moved to Asmara in 1897. Massawa has an average temperature of nearly , which is one of the highest experienced in the world, and is "one of the hottest marine coastal areas in the world." History Massawa was originally a small seaside village, lying in lands coextensive with the Kingdom of Axum—also known as Kingdom of Zula in antiquity—and overshadowed by the nearby port of Adulis about to the south. Massawa has been ruled or occupied by a successi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also has exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. During the Hellenistic period, it was home to the Lighthouse of Alexandria, which ranked among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, as well as the storied Library of Alexandria. Today, the library is reincarnated in the disc-shaped, ultramodern Bibliotheca Alexandrina. Its 15th-century seafront Qaitbay Citadel is now a museum. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" by locals, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt, and is the largest city on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Von Heuglin
Martin Theodor von Heuglin (20 March 1824, Hirschlanden, Württemberg5 November 1876), was a German explorer and ornithologist. Biography Heuglin was born in Hirschlanden (now part of Ditzingen) in Württemberg. His father was a Protestant pastor, and he was trained to be a mining engineer. He was ambitious, however, to become a scientific investigator of unknown regions, and with that object studied the natural sciences, especially zoology. In 1850 he went to Egypt where he learnt Arabic, and visited the Red Sea and Sinai. In 1852 he accompanied Dr. Christian Reitz, Austrian consul at Khartoum, on a journey to Ethiopia, and after Reitz's death was appointed his successor in the consulate. While he held this post he travelled in Ethiopia and Kordofan, making a valuable collection of natural history specimens. In 1857 he journeyed through the coast lands of the African side of the Red Sea, and along the Somali coast. In 1860 he was chosen as leader of an expedition to search fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
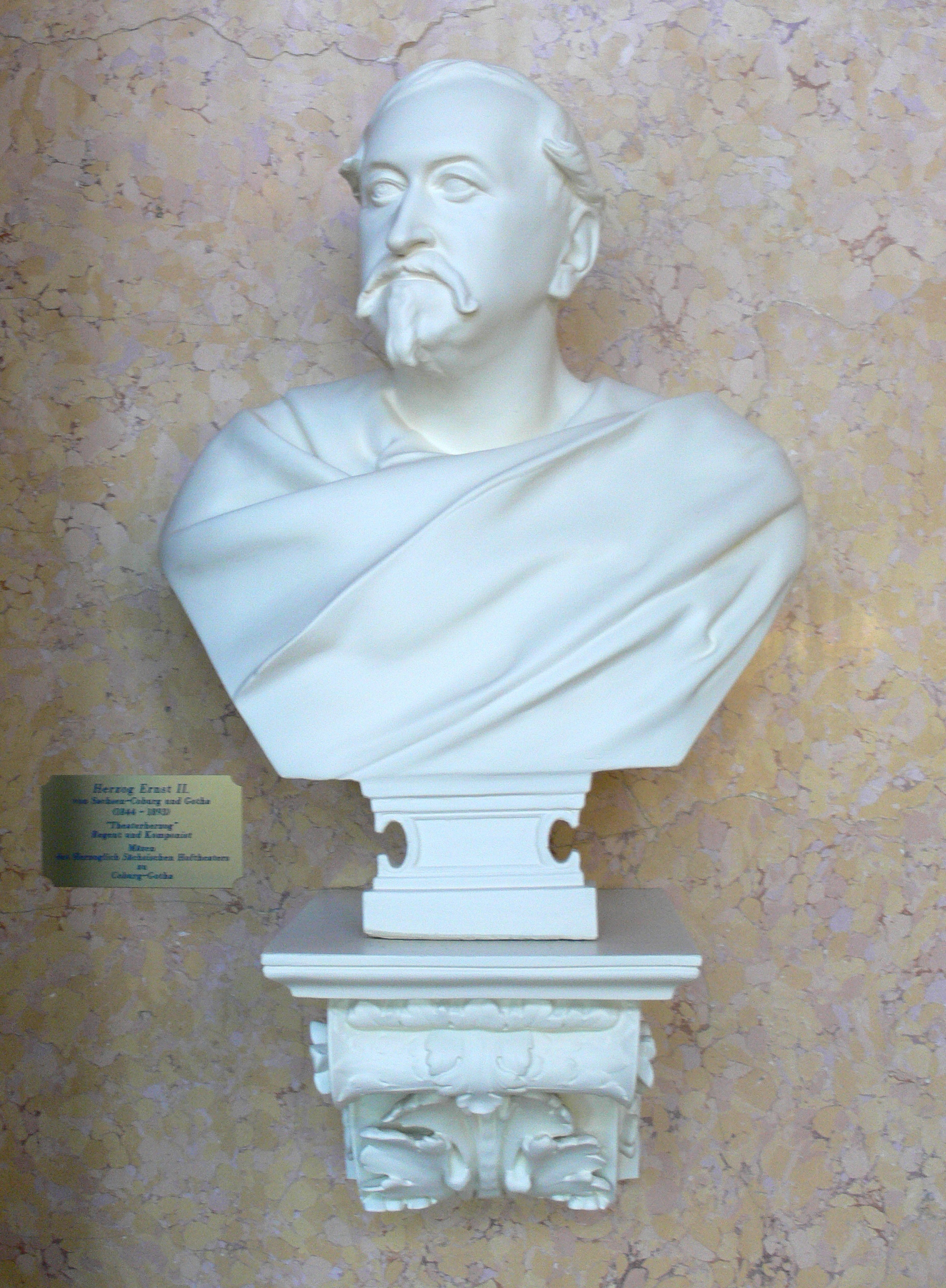
Ernest II, Duke Of Saxe-Coburg And Gotha
Ernest II (german: Ernst August Karl Johann Leopold Alexander Eduard, link=no; 21 June 181822 August 1893) was Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha from 29 January 1844 to his death in 1893. He was born in Coburg to Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, and Princess Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg. His father became Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (as Ernest I) in 1826 through an exchange of territories. In 1842, Ernest married Princess Alexandrine of Baden in what was to be a childless marriage. Two years later, he became Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha when his father died. Ernest supported the German Confederation in the Schleswig-Holstein Wars against Denmark, sending thousands of troops and becoming the commander of a German corps; he was instrumental in the 1849 victory at the battle of Eckernförde against Danish forces. After King Otto of Greece was deposed in 1862, the British government put Ernest's name forward as a possible successor. Negotiations concerning this failed for vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouaddai Empire
The Wadai Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة وداي ''Saltanat Waday'', french: royaume du Ouaddaï, Fur: ''Burgu'' or ''Birgu''; 1501–1912) was an African sultanate located to the east of Lake Chad in present-day Chad and the Central African Republic. It emerged in the seventeenth century under the leadership of the first sultan, Abd al-Karim, who overthrew the ruling Tunjur people of the area. It occupied land previously held by the Sultanate of Darfur (in present-day Sudan) to the northeast of the Sultanate of Baguirmi. History Origins Prior to the 1630s, Wadai, also known as Burgu to the people of Darfur, was a pre-Islamic Tunjur kingdom, established around 1501. The Arab migrants to the area which became Wadai claimed to be descendants of the Abbasid Caliphs, specifically from Salih ibn Abdallah ibn Abbas. Yame, an Abbasid leader, settled with Arab migrants in Debba, near the future capital of Ouara (Wara). In 1635, the Maba and other small groups in the region rallied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_signpost%2C_May_1941.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

