|
Hereditary Pyropoikilocytosis
Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis (HPP) is an autosomal recessive form of hemolytic anemia characterized by an abnormal sensitivity of red blood cells to heat and erythrocyte morphology similar to that seen in thermal burns or from prolonged exposure of a healthy patient's blood sample to high ambient temperatures. Patients with HPP tend to experience severe hemolysis and anemia in infancy that gradually improves, evolving toward typical elliptocytosis later in life. However, the hemolysis can lead to rapid sequestration and destruction of red cells. Splenectomy is curative when this occurs. HPP has been associated with a defect of the erythrocyte membrane protein spectrin and with spectrin deficiency. It was characterized in 1975. It is considered a severe form of hereditary elliptocytosis. Causes Mutations of the alphaspectrin gene causes this disease. HPP can be considered as a subset of hereditary elliptocytosis. Diagnosis Genetic testing for the presence of mutations in protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically (prosthetic valve damage). Hemolytic anemia accounts for 5% of all existing anemias. It has numerous possible consequences, ranging from general symptoms to life-threatening systemic effects. The general classification of hemolytic anemia is either intrinsic or extrinsic. Treatment depends on the type and cause of the hemolytic anemia. Symptoms of hemolytic anemia are similar to other forms of anemia ( fatigue and shortness of breath), but in addition, the breakdown of red cells leads to jaundice and increases the risk of particular long-term complications, such as gallstones and pulmonary hypertension. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of hemolytic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro. One cause of hemolysis is the action of hemolysins, toxins that are produced by certain pathogenic bacteria or fungi. Another cause is intense physical exercise. Hemolysins damage the red blood cell's cytoplasmic membrane, causing lysis and eventually cell death. Etymology From hemo- + -lysis, from , "blood") + , "loosening"). Inside the body Hemolysis inside the body can be caused by a large number of medical conditions, including some parasites (''e.g.'', ''Plasmodium''), some autoimmune disorders (''e.g.'', autoimmune haemolytic anaemia, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)), some genetic disorders (''e.g.'', Sickle-cell disease or G6PD deficiency), or blood with too low a solute conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cell production, and increased red blood cell breakdown. Causes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
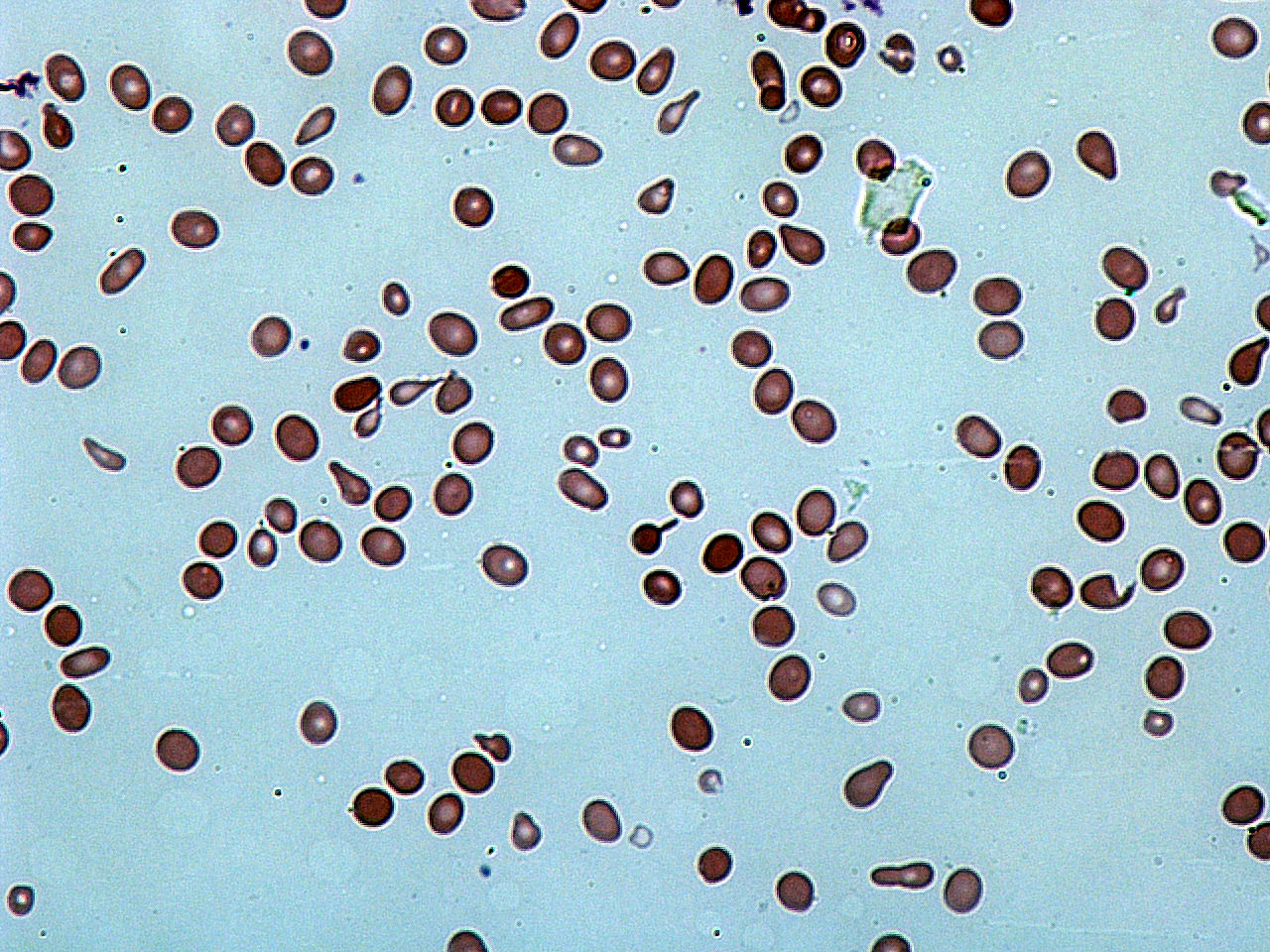
Elliptocytosis
Hereditary elliptocytosis, also known as ovalocytosis, is an inherited blood disorder in which an abnormally large number of the person's red blood cells are elliptical rather than the typical biconcave disc shape. Such morphologically distinctive erythrocytes are sometimes referred to as elliptocytes or ovalocytes. It is one of many red-cell membrane defects. In its severe forms, this disorder predisposes to haemolytic anaemia. Although pathological in humans, elliptocytosis is normal in camelids. Presentation RBCs are elleptical in shape rather than normal biconcave shape Most cases are asymptomatic with abnormalities in their peripherial blood film. Pathophysiology Common hereditary elliptocytosis A number of genes have been linked to common hereditary elliptocytosis (many involve the same gene as forms of Hereditary spherocytosis, or HS): These mutations have a common end result; they destabilise the cytoskeletal scaffold of cells. This stability is especially important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
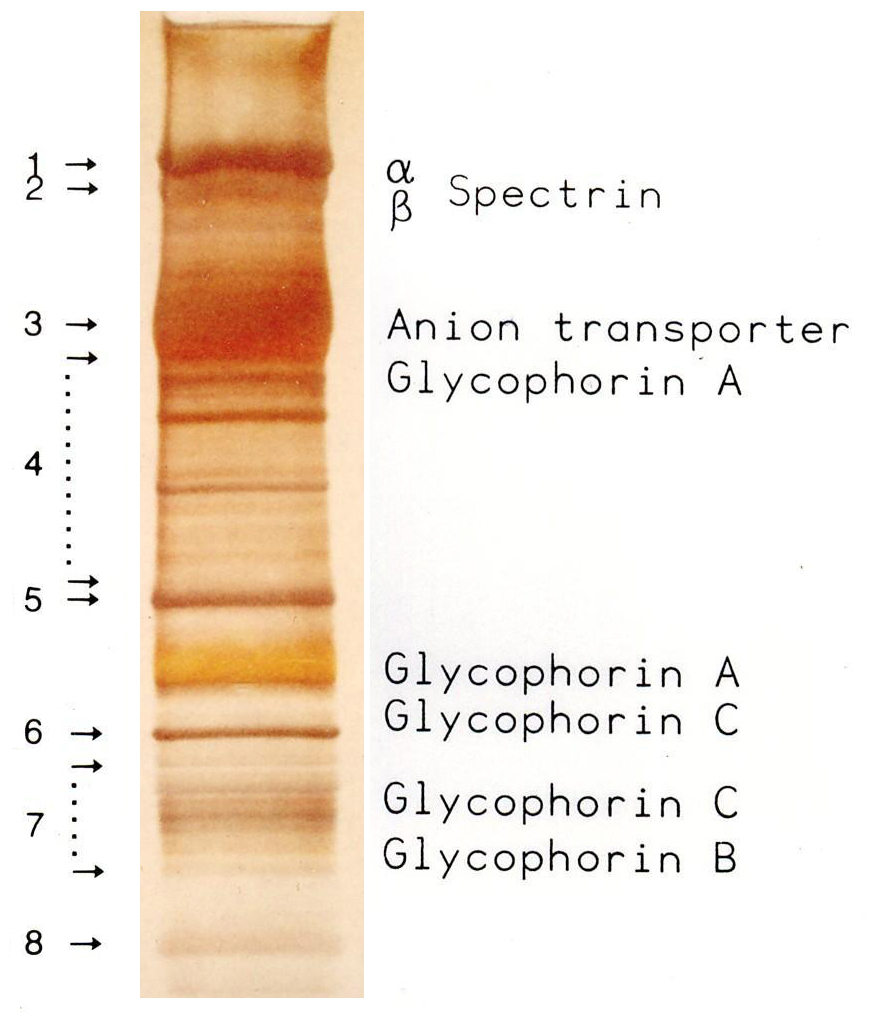
Spectrin
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrin Deficiency
Spectrin is a cytoskeletal protein that lines the intracellular side of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells. Spectrin forms pentagonal or hexagonal arrangements, forming a scaffold and playing an important role in maintenance of plasma membrane integrity and cytoskeletal structure. The hexagonal arrangements are formed by tetramers of spectrin subunits associating with short actin filaments at either end of the tetramer. These short actin filaments act as junctional complexes allowing the formation of the hexagonal mesh. The protein is named spectrin since it was first isolated as a major protein component of human red blood cells which had been treated with mild detergents; the detergents lysed the cells and the hemoglobin and other cytoplasmic components were washed out. In the light microscope the basic shape of the red blood cell could still be seen as the spectrin-containing submembranous cytoskeleton preserved the shape of the cell in outline. This became known as a red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Elliptocytosis
Hereditary elliptocytosis, also known as ovalocytosis, is an inherited blood disorder in which an abnormally large number of the person's red blood cells are elliptical rather than the typical biconcave disc shape. Such morphologically distinctive erythrocytes are sometimes referred to as elliptocytes or ovalocytes. It is one of many red-cell membrane defects. In its severe forms, this disorder predisposes to haemolytic anaemia. Although pathological in humans, elliptocytosis is normal in camelids. Presentation RBCs are elleptical in shape rather than normal biconcave shape Most cases are asymptomatic with abnormalities in their peripherial blood film. Pathophysiology Common hereditary elliptocytosis A number of genes have been linked to common hereditary elliptocytosis (many involve the same gene as forms of Hereditary spherocytosis, or HS): These mutations have a common end result; they destabilise the cytoskeletal scaffold of cells. This stability is especially important i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia. Common indications for splenectomy include trauma, tumors, splenomegaly or for hematological disease such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia. Indications The spleen is an organ located in the abdomen next to the stomach. It is composed of red pulp which filters the blood, removing foreign material, damaged and worn out red blood cells. It also functions as a storage site for iron, red blood cells and platelets. The rest (~25%) of the spleen is known as the white pulp and functions like a large lymph node bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poikilocytosis
Poikilocytosis is variation in the shapes of red blood cells. Poikilocytes may be oval, teardrop-shaped, sickle-shaped or irregularly contracted. Normal red blood cells are round, flattened disks that are thinner in the middle than at the edges. A ''poikilocyte'' is an abnormally-shaped red blood cell. Generally, poikilocytosis can refer to an increase in abnormal red blood cells of any shape, where they make up 10% or more of the total population of red blood cells. Types Membrane abnormalities # Acanthocytes or Spur/Spike cells # Codocytes or Target cells # Echinocytes and Burr cells # Elliptocytes and Ovalocytes # Spherocytes # Stomatocytes or Mouth cells # Drepanocytes or Sickle Cells # Degmacytes or "bite cells" Trauma # Dacrocytes or Teardrop Cells # Keratocytes # Microspherocytes and Pyropoikilocytes # Schistocytes # Semilunar bodies Diagnosis Poikilocytosis may be diagnosed with a test called a blood smear. During a blood smear, a medical technologist spreads a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |