|
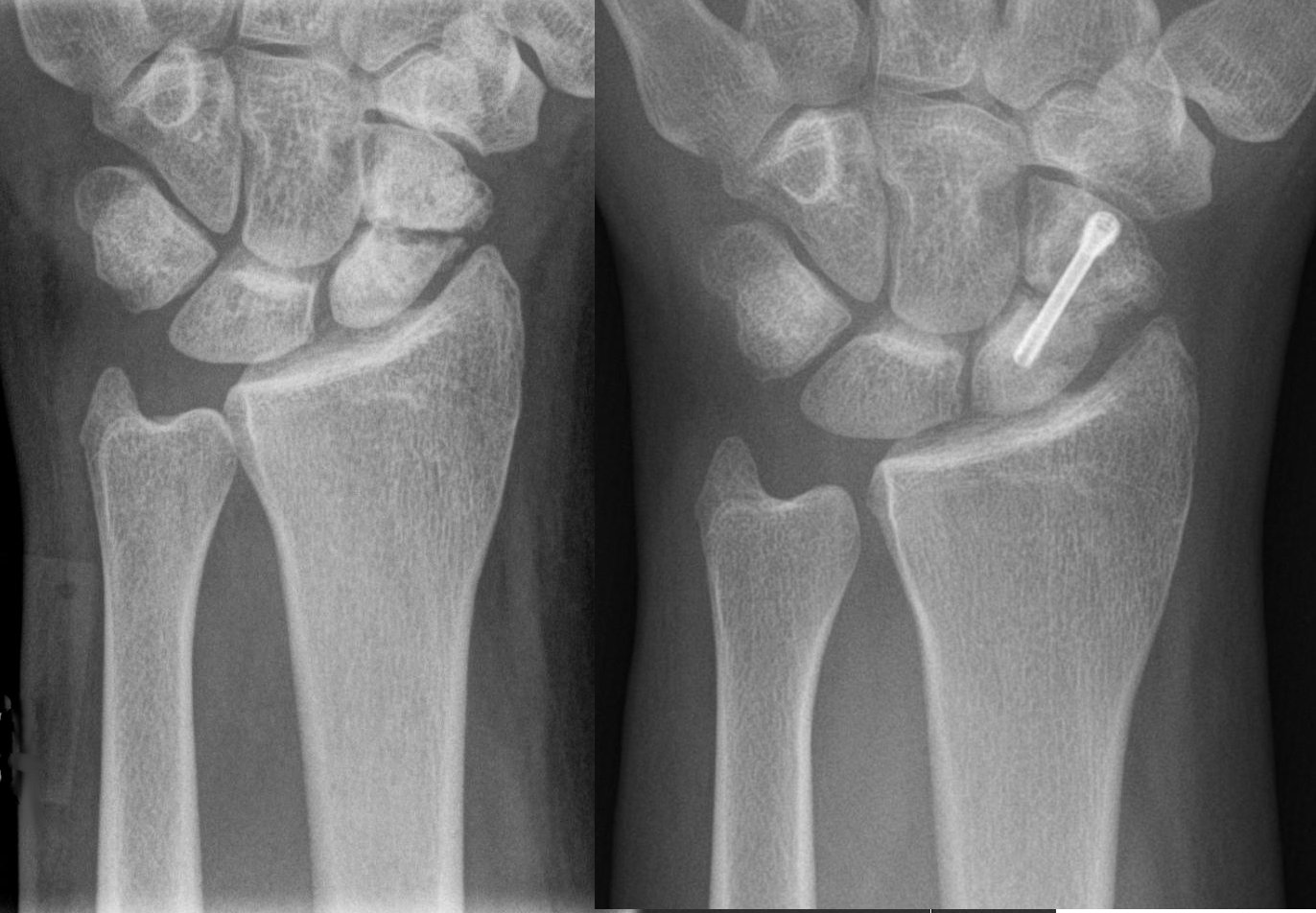
Herbert Screw
The Herbert screw (invented by Timothy Herbert) is a variable pitch cannulated screw typically made from titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resista ... for its biocompatible properties as the screw is normally intended to remain in the patient indefinitely. It became generally available in 1978. It is one of the earliest designs of headless compression screws which are used to achieve interfragmentary compression through its differential pitch between the threads at each end of the screw(distance between adjacent threads of screw). It is used in scaphoid, capitellum, radial head and in osteochondral fractures. Other uses include osteochondritis dissecans & small joint arthrodesis. References Orthopedic screws {{orthopedics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Herbert
Timothy James Herbert (born 11 July 1941) is an orthopaedic surgeon specializing in hand surgery. He was born in Sheffield (UK). He is known for his work with the scaphoid bone and related invention, the Herbert screw. He received his medical training at St Bartholomew's Hospital Medical School in London (1959–1964) and his specialty training at St George's Hospital in London, under Alan Graham Apley. Since 1975 he was with the Hand Surgery Unit at St. Luke's Hospital in Sydney Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ..., New South Wales, Australia and became Director of that section. He retired in 1996 at the age of 55.Buck-Gramcko, Dieter. Ein Leben für die Handchirurgie: 100 Lebensbilder. Darmstadt: Steinkopff, 2007. p.–99-101. References {{DEFAULTSORT:He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; plural or ) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces of a trocar needle thus extending the effective needle length by at least half the length of the original needle. Its size mainly ranges from 14 to 24 gauge. Different-sized cannula have different colours as coded. Decannulation is the permanent removal of a cannula (extubation), especially of a tracheostomy cannula, once a physician determines it is no longer needed for breathing. Medicine Cannulas normally come with a trocar inside. The trocar is a needle, which punctures the body in order to get into the intended space. Many types of cannulas exist: Intravenous cannulas are the most common in hospital use. A variety of cannulas are used to establish cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. A nasal cannula is a piece of plastic tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |