|
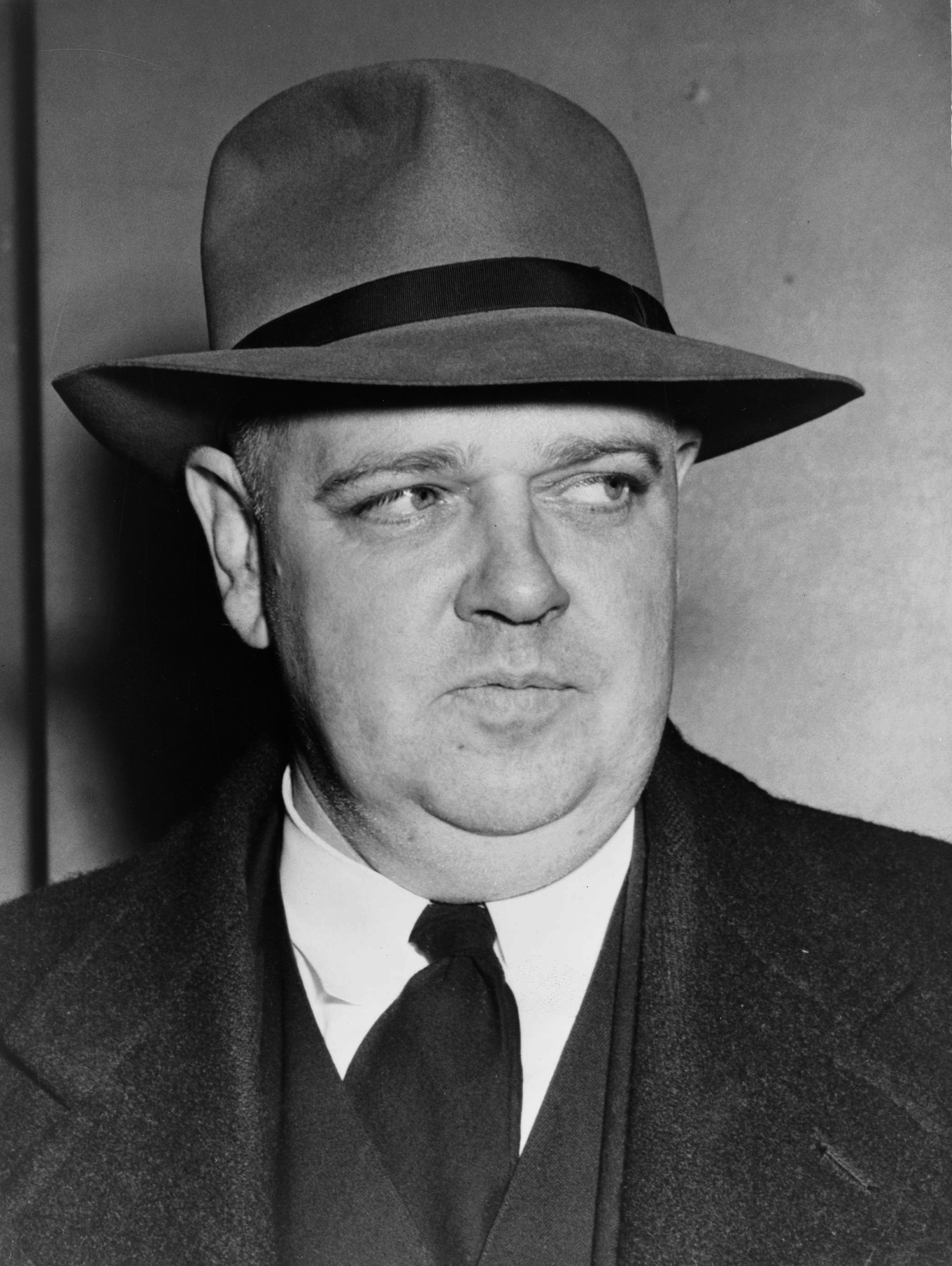
Herbert Fuchs (film Director)
Herbert Fuchs (1905–1988) was a former American Communist and federal government official who became a professor of law at the American University in Washington, D.C. in 1949, after which he became embroiled in anti-communist congressional hearings just after the peak of McCarthyism. Background Herbert Oscar Fuchs was born on September 20, 1905, in New York City. His parents Alfred Fuchs and Paula Hacker came from Vienna, Austria, and settled in Manhattan's Washington Heights, then home to many Germans-speakers. His father had been a lawyer in Vienna, but in New York he studied law at New York University and opened in law office in the " Yorkville" section on New York's Upper East Side. Fuchs had two brothers, Walter and Vernon. He attended Townsend Harris Hall (then on the campus of the City College of New York). In 1924, he graduated from City College with a BS in social sciences. In 1928, he graduated with a JD degree in law from New York University. Career Fuchs wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered around common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange which allocates products to everyone in the society.: "One widespread distinction was that socialism socialised production only while communism socialised production and consumption." Communist society also involves the absence of private property, social classes, money, and the state. Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance, but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a more libertarian approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers' self-management, and a more vanguardist or communist party-driven approach through the development of a constitutional socialist state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nye Committee
The Nye Committee, officially known as the Special Committee on Investigation of the Munitions Industry, was a United States Senate committee (April 12, 1934 – February 24, 1936), chaired by U.S. Senator Gerald Nye (R-ND). The committee investigated the financial and banking interests that underlay the United States' involvement in World War I and the operations and profits of the industrial and commercial firms supplying munitions to the Allies and to the United States. It was a significant factor in public and political support for American neutrality in the early stages of World War II. Background During the 1920s and 1930s, dozens of books and articles appeared about the high cost of war, and some argued that financiers and arms manufacturers had maneuvered the United States into entering World War I. One of the best-known was Smedley D. Butler, a retired Marine Corps general who had become a spokesman for left-wing anti-war elements. Historian Charles Callan Tansill's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Edison
Consolidated Edison, Inc., commonly known as Con Edison (stylized as conEdison) or ConEd, is one of the largest investor-owned energy companies in the United States, with approximately $12 billion in annual revenues as of 2017, and over $62 billion in assets. The company provides a wide range of energy-related products and services to its customers through its subsidiaries: *Consolidated Edison Company of New York, Inc. (CECONY), a regulated utility providing electric and gas service in New York City and Westchester County, New York, and steam service in the borough of Manhattan; *Orange and Rockland Utilities, Inc., a regulated utility serving customers in a area in southeastern New York and northern New Jersey; *Con Edison Solutions, an energy services company; *Con Edison Energy, a wholesale energy services company; *Con Edison Development, a company that owns and operates renewable and energy infrastructure projects, and, *Con Edison Transmission, Inc., which invests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurst Robins Anderson
Hurst Robins Anderson (September 16, 1904 – April 19, 1989) was president of American University from 1952 until 1968, during which he oversaw one of the institution's most important periods of growth and development. He was previously a faculty member of Allegheny College and president of Hamline University in Saint Paul, Minnesota. He received a BA from Ohio Wesleyan University, a law degree from the University of Michigan and master's degrees from Northwestern University and the University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chic ...."Hurst R. Anderson, 84; Leader of American University.", ''New York Times''m April 21, 1989 AU's largest residence hall is named after Anderson. References 1904 births 1989 deaths Leaders of American University Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party USA
The Communist Party USA, officially the Communist Party of the United States of America (CPUSA), is a communist party in the United States which was established in 1919 after a split in the Socialist Party of America following the Russian Revolution. The history of the CPUSA is closely related to the history of the Communists in the United States Labor Movement (1919–37), American labor movement and the history of communist parties worldwide. Initially operating underground due to the Palmer Raids which started during the First Red Scare, the party was influential in Politics of the United States, American politics in the first half of the 20th century and it also played a prominent role in the history of the labor movement from the 1920s through the 1940s, becoming known for Anti-racism, opposing racism and Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation after sponsoring the defense for the Scottsboro Boys in 1931. Its membership increased during the Great Depres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ware Group
The Ware Group was a covert organization of Communist Party USA operatives within the United States government in the 1930s, run first by Harold Ware (1889–1935) and then by Whittaker Chambers (1901–1961) after Ware's accidental death on August 13, 1935. History Background Harold Ware founded this group under the auspices of J. Peters by Summer 1933. Ware was a Communist Party (CP) official working for the federal government in Washington, D.C. The first known meeting of the Ware Group occurred in late 1933 with eight members: John Abt, Henry Collins, Alger Hiss, Victor Perlo, Lee Pressman, Nathaniel Weyl, and Nathan Witt. Initially, Peters instructed that members make "exceptional money sacrifices" to the Party, study Marxist theory and Party doctrine, observe "strictest secrecy," and to obtain "any government documents" available to them. (Known members later claimed that it was merely a Marxist study group.) Known active years By 1934, the group had grown to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Committee On Un-American Activities
The House Committee on Un-American Activities (HCUA), popularly dubbed the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC), was an investigative committee of the United States House of Representatives, created in 1938 to investigate alleged disloyalty and subversive activities on the part of private citizens, public employees, and those organizations suspected of having either fascist or communist ties. It became a standing (permanent) committee in 1945, and from 1969 onwards it was known as the House Committee on Internal Security. When the House abolished the committee in 1975, its functions were transferred to the House Judiciary Committee. The committee's anti-communist investigations are often associated with McCarthyism, although Joseph McCarthy himself (as a U.S. Senator) had no direct involvement with the House committee. McCarthy was the chairman of the Government Operations Committee and its Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations of the U.S. Senate, not the House. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dupont Circle
Dupont Circle (or DuPont Circle) is a traffic circle, park, neighborhood and historic district in Northwest Washington, D.C. The Dupont Circle neighborhood is bounded approximately by 16th Street NW to the east, 22nd Street NW to the west, M Street NW to the south, and Florida Avenue NW to the north. Much of the neighborhood is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. However, the local government Advisory Neighborhood Commission (ANC 2B) and the Dupont Circle Historic District have slightly different boundaries. The traffic circle is located at the intersection of Massachusetts Avenue NW, Connecticut Avenue NW, New Hampshire Avenue NW, P Street NW, and 19th Street NW. The circle is named for Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Du Pont. The traffic circle contains the Dupont Circle Fountain in its center. The neighborhood is known for its high concentration of embassies (many along Embassy Row) and think tanks (many along Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenleytown Aerial 2019
Tenleytown is a historic neighborhood in Northwest, Washington, D.C. History In 1790, locals began calling the neighborhood "Tennally's Town" after area tavern owner John Tennally. Over time, the spelling has evolved and by the 19th century the area was commonly known by its current name, although the spelling Tennallytown continued to be used for some time in certain capacities, including streetcars through the 1920s. The area is the site of Fort Reno, one of the forts that formed a ring around Washington, D.C. during the American Civil War to protect the capital against invasions. It proved to be the crucial lookout point for preventing a siege of Washington, because it is the highest natural elevation point in the District of Columbia. Fort Reno was decommissioned with the surrender of the Confederate army. The last remains of Fort Reno were removed about 1900, when the land owned by the Dyer family was being prepared for a reservoir. Due to its elevation it is also the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Senate Committee On Education And Labor
The United States Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions (HELP) generally considers matters relating to these issues. Its jurisdiction also extends beyond these issues to include several more specific areas, as defined by Senate rules. While currently known as the HELP Committee, the committee was originally founded on January 28, 1869, as the Committee on Education. Its name was changed to the Committee on Education and Labor on February 14, 1870, when petitions relating to labor were transferred to its jurisdiction from the Committee on Naval Affairs. The committee’s jurisdiction at the end of the 19th and early 20th centuries focused largely on issues relating to federal employees’ working conditions and federal education aid. Prominent action considered by the committee in the 1910s and 1920s included the creation of a national minimum wage, the establishments of a Department of Labor, a Department of Education, and a Children’s Bureau. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whittaker Chambers
Whittaker Chambers (born Jay Vivian Chambers; April 1, 1901 – July 9, 1961) was an American writer-editor, who, after early years as a Communist Party member (1925) and Soviet spy (1932–1938), defected from the Soviet underground (1938), worked for ''Time'' magazine (1939–1948), and then testified about the Ware Group in what became the Hiss case for perjury (1949–1950), often referred to as the trial of the century, all described in his 1952 memoir ''Witness''. Afterwards, he worked as a senior editor at ''National Review'' (1957–1959). US President Ronald Reagan awarded him the Presidential Medal of Freedom posthumously in 1984. Background Chambers was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and spent his infancy in Brooklyn. His family moved to Lynbrook, Long Island, New York State, in 1904, where he grew up and attended school. His parents were Jay Chambers and Laha Whittaker. He described his childhood as troubled because of his parents' separation and their ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alger Hiss
Alger Hiss (November 11, 1904 – November 15, 1996) was an American government official accused in 1948 of having spied for the Soviet Union in the 1930s. Statutes of limitations had expired for espionage, but he was convicted of perjury in connection with this charge in 1950. Before the trial Hiss was involved in the establishment of the United Nations, both as a U.S. State Department official and as a U.N. official. In later life he worked as a lecturer and author. On August 3, 1948, Whittaker Chambers, a former U.S. Communist Party member, testified under subpoena before the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) that Hiss had secretly been a communist while in federal service. Hiss categorically denied the charge and subsequently sued Chambers for libel. During the pretrial discovery process of the libel case, Chambers produced new evidence allegedly indicating that he and Hiss had been involved in espionage. A federal grand jury indicted Hiss on two counts of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)