|
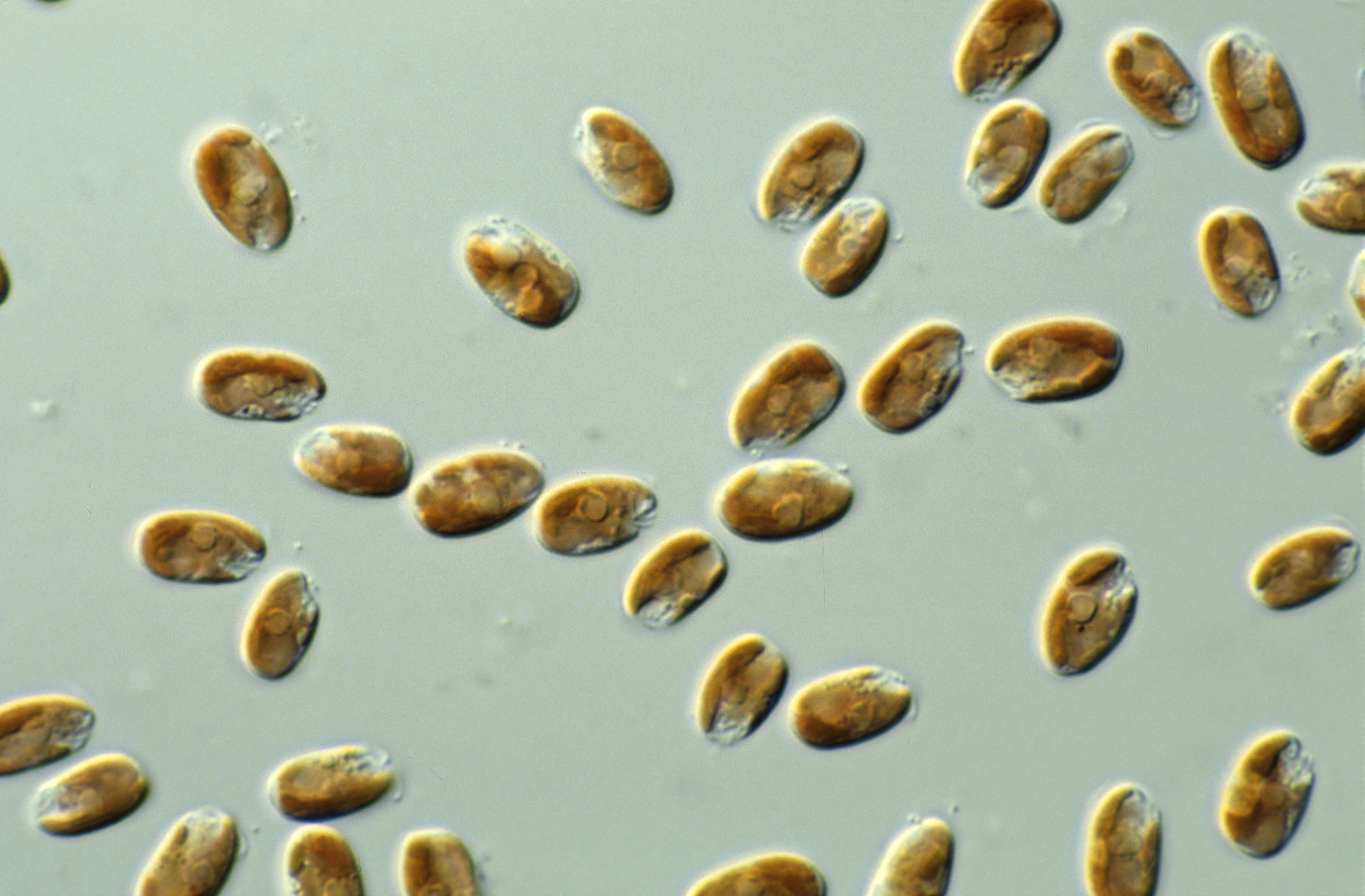
Hemiselmis
''Hemiselmis'' is a genus of cryptomonads. History of discovery It was first described by English biologist Mary Parke in 1949. She also described the first species in this genus, ''Hemiselmis rufescens.'' Morphology ''Hemiselmis'' are typically 4 to 9 micrometers long, free-swimming, biflagellate monads. They are generally bean-shaped with the flagella located between 1/3 and 1/2 the cell length from the anterior. A tubular gullet lined with usually two rows of ejectisomes is found to be in the posterior region of the cell. A single plastid and nucleomorph are present, with it possessing the biliprotein pigment Cr-phycoerythrin 555 or one of Cr-phycocyanin Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist w ..., 577, 612 and 630. For example, ''Hemiselmis pacifica'' possesses Cr-P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chroomonadaceae
Chroomonadaceae is a family of cryptomonads first recognized by Clay et al in 1999 as including genera ''Chroomonas'', '' Falcomonas'', and '' Komma''. Following a molecular phylogenic study in 2002, Hemiselmis was also placed within the Chroomonadaceae. Today, the family is generally recognized as sister to the Pyrenomonadaceae. They are one of only two groups of cryptomonads (alongside '' Rhinomonas'') to lack a rhizostyle. They are also distinguished by the lack of a cleavage furrow In cell biology, the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage, by which animal and some algal cells undergo cytokinesis, the final splitting of the membrane, in the process of cell division. ... and the presence of several phycocyanins and phycoerythrins not observed in any other cryptomonad taxa. Taxonomy Laza-Martinez, 2012 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q12620720 Cryptomonads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptophyta
The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some exhibit mixotrophy. Characteristics Cryptophytes are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectosomes or ejectisomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectosomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding. Except for '' Chilomonas'', which has leucoplasts, cryptophytes have one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptophyceae
The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some exhibit mixotrophy. Characteristics Cryptophytes are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectosomes or ejectisomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectosomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding. Except for '' Chilomonas'', which has leucoplasts, cryptophytes have one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. Characteristics Cryptomonads are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectosomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectosomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding. Except for the class ''Goniomonadea'',_which_lacks_plastids_entirely,_and_''Cryptomonas_paramecium''_(pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenomonadales
Pyrenomonadales is an order of Cryptophyta The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape .... References Cryptomonads Bikont orders {{Cryptomonad-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephroselmis
''Nephroselmis'' is a genus of green algae. It has been placed in the family Nephroselmidaceae, although a 2009 study suggests that it should be separated into its own class, Nephroselmidophyceae. One species can be an endosymbiont of ''Hatena arenicola''. Morphology The cell body is right-left flattened. On the ventral side are two heterodynamic unequal flagella, the shorter beats towards the anterior direction while the long trails behind. ''Nephroselmis'' have a single cup-shaped chloroplast that contains an eyespot in its anterior-ventral edge below the short flagellum and a pyrenoid with starch plates. Vacuole is located in the left-anterior side, nucleus is located in the right-posterior side. The flagellar root system consists of a rhizoplast and three microtubular roots, one of which is multilayered. All the cells surface area is covered with layers of unminerallized scales, while the surface of the flagella has hairs as well. The cell body surface is covered by two t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biliprotein
Biliproteins are pigment protein compounds that are located in photosynthesising organisms such as algae and certain insects. They refer to any protein that contains a bilin chromophore. In plants and algae, the main function of biliproteins is to make the process of light accumulation required for photosynthesis more efficient; while in insects they play a role in growth and development. Some of their properties: including light-receptivity, light-harvesting and fluorescence have made them suitable for applications in bioimaging and as indicators; while other properties such as anti-oxidation, anti-aging and anti-inflammation in phycobiliproteins have given them potential for use in medicine, cosmetics and food technology. While research on biliproteins dates back as far as 1950, it was hindered due to issues regarding biliprotein structure, lack of methods available for isolating individual biliprotein components, as well as limited information on lyase reactions (which are ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin (PE) is a red protein-pigment complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and cryptophytes, accessory to the main chlorophyll pigments responsible for photosynthesis.The red pigment is due to the prosthetic group, phycoerythrobilin, which gives phycoerythrin its red color. Like all phycobiliproteins, it is composed of a protein part covalently binding chromophores called phycobilins. In the phycoerythrin family, the most known phycobilins are: phycoerythrobilin, the typical phycoerythrin acceptor chromophore. Phycoerythrobilin is a linear tetrapyrrole molecule found in cyanobacteria, red algae, and cryptomonads. Together with other bilins such as phycocyanobilin it serves as a light-harvesting pigment in the photosynthetic light-harvesting structures of cyanobacteria called phycobilisomes. Phycoerythrins are composed of (αβ) monomers, usually organised in a disk-shaped trimer (αβ)3 or hexamer (αβ)6 (second one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is a pigment-protein complex from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble, so they cannot exist within the membrane like carotenoids can. Instead, phycobiliproteins aggregate to form clusters that adhere to the membrane called phycobilisomes. Phycocyanin is a characteristic light blue color, absorbing orange and red light, particularly near 620 nm (depending on which specific type it is), and emits fluorescence at about 650 nm (also depending on which type it is). Allophycocyanin absorbs and emits at longer wavelengths than phycocyanin C or phycocyanin R. Phycocyanins are found in cyanobacteria (also called blue-green algae). Phycobiliproteins have fluorescent properties that are used in immunoassay kits. Phycocyanin is from the Greek '' phyco'' meaning “algae” and ''cyanin'' is from the English word “cyan", which conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |