|
Hemiboeckella
''Hemiboeckella'' is a genus of crustacean in family Centropagidae Centropagidae is a family of copepods in the order Calanoida. Its members are particularly known as plankton in coastal waters and in fresh water in Australia and southern South America. They are also found on subantarctic islands and in lakes i .... It contains the following species: *'' Hemiboeckella andersonae'' Bayly, 1974 *'' Hemiboeckella powellensis'' Bayly, 1979 *'' Hemiboeckella searli'' G. O. Sars, 1912 References Centropagidae Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{copepod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiboeckella Powellensis
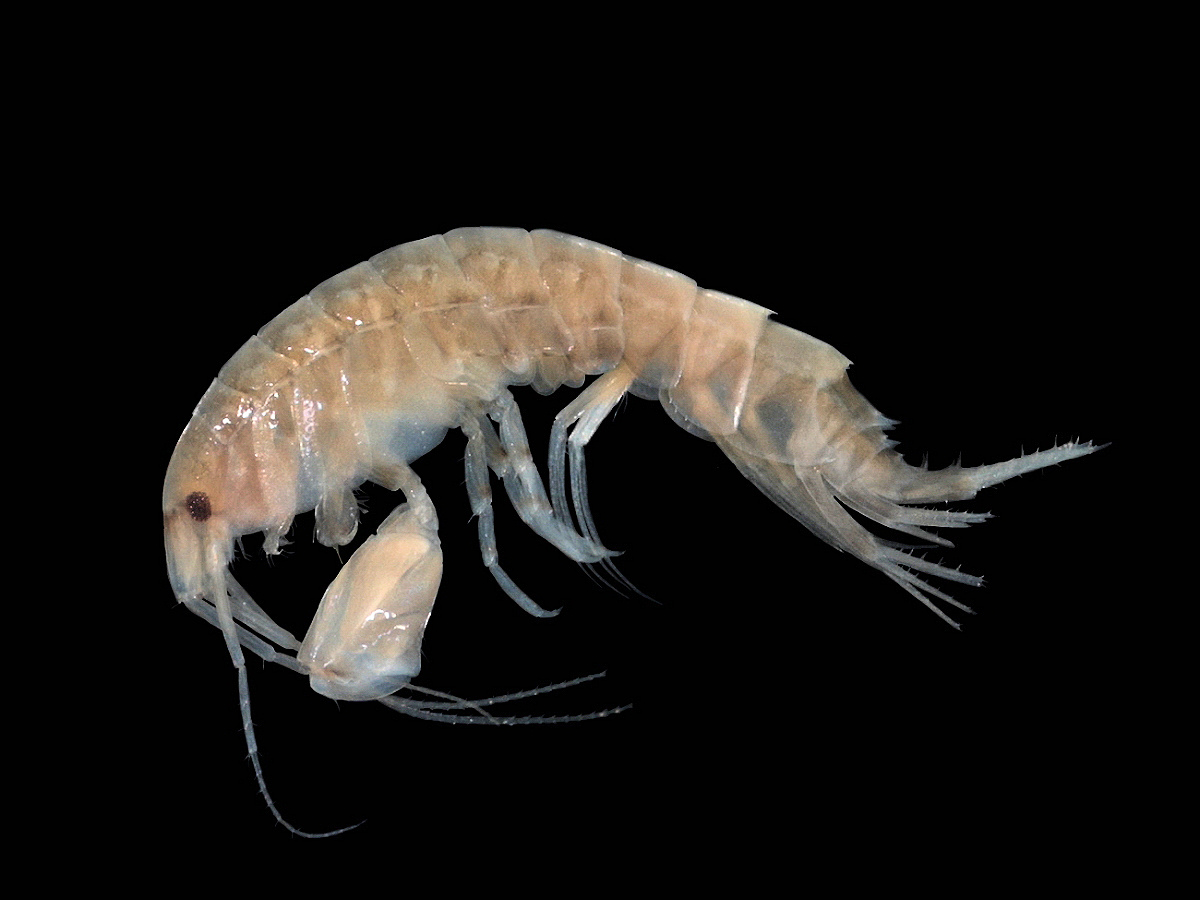
''Hemiboeckella powellensis'', is a zooplankton copepod of which only four of its kind have ever been observed. "Hemiboeckella" refers to this genus being a subvariant of Boeckella, whilst “powellensis” refers to Lake Powell in Western Australia, the region it is endemic to. Its existence was initially recorded in May and June of 1977, and has not been observed since. Description ''Hemiboeckella powellensis'' is a small crustacean that ranges from 0.67 to 1.16mm. Like all crustaceans, it has a segmented exoskeleton. It also has a copepod's characteristically round shaped body. The head consists of two setae on the anterior face, along with segmented maxillipeds. Protruding from its anterior, there are two antennae that are longer than its abdomen, with another smaller antennule. It has nautical eye, a characteristic trait of copepods. However, it does not appear to be used as a visual aid. It has four legs that are segmented three times, along with a curved claw on its rig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiboeckella Andersonae
''Hemiboeckella'' is a genus of crustacean in family Centropagidae. It contains the following species: *'' Hemiboeckella andersonae'' Bayly, 1974 *''Hemiboeckella powellensis ''Hemiboeckella powellensis'', is a zooplankton copepod of which only four of its kind have ever been observed. "Hemiboeckella" refers to this genus being a subvariant of Boeckella, whilst “powellensis” refers to Lake Powell in Western Aust ...'' Bayly, 1979 *'' Hemiboeckella searli'' G. O. Sars, 1912 References Centropagidae Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{copepod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiboeckella Searli
''Hemiboeckella'' is a genus of crustacean in family Centropagidae. It contains the following species: *''Hemiboeckella andersonae'' Bayly, 1974 *''Hemiboeckella powellensis ''Hemiboeckella powellensis'', is a zooplankton copepod of which only four of its kind have ever been observed. "Hemiboeckella" refers to this genus being a subvariant of Boeckella, whilst “powellensis” refers to Lake Powell in Western Aust ...'' Bayly, 1979 *'' Hemiboeckella searli'' G. O. Sars, 1912 References Centropagidae Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{copepod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centropagidae
Centropagidae is a family of copepods in the order Calanoida. Its members are particularly known as plankton in coastal waters and in fresh water in Australia and southern South America. They are also found on subantarctic islands and in lakes in Antarctica. Genera There are 14 genera recognised in the family Centropagidae, including over 130 species. *'' Boeckella'' De Guerne & Richard, 1889 — 49 species, freshwater *'' Calamoecia'' Brady, 1906 — 18 species, freshwater *''Centropages'' Krøyer, 1849 — 35 species, marine *'' Dussartopages'' Huys, 2009 — 1 species, marine *'' Gippslandia'' Bayly & Arnott, 1969 — 1 species, marine *'' Gladioferens'' Henry, 1919 — 6 species, marine *'' Guernella'' Giesbrecht in G & Schmeil, 1898 — 1 species, marine *'' Hemiboeckella'' G. O. Sars, 1912 — 3 species, freshwater *''Isias'' Boeck, 1865 — 4 species, marine *''Limnocalanus ''Limnocalanus'' is a genus of Centropagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillopoda
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calanoida
Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them. Description Calanoids can be distinguished from other planktonic copepods by having first antennae at least half the length of the body and biramous second antennae. However, their most distinctive anatomical trait is the presence of a joint between the fifth and sixth body segments. The largest specimens reach long, but most do not exceed long. Classification Calanoida contains the following families, as well as the genus '' Microdisseta'' (which is currently ''incertae sedis''); * Acartiidae * Aetideidae * Arctokonstantinidae * Arietellidae * Augaptilidae * Bathypontiidae * Calanidae * Calocalanidae * Candaciidae * Centropagidae * Clausocalanidae * Diaixidae * Diaptomidae * Discoidae * Epacteriscidae * Eucalanidae * Euchaetidae * Fosshageniidae * Heterorhabdidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Ossian Sars
Prof Georg Ossian Sars HFRSE (20 April 1837 – 9 April 1927) was a Norwegian marine and freshwater biologist. Life Georg Ossian Sars was born on 20 April 1837 in Kinn, Norway (now part of Flora), the son of Pastor Michael Sars and Maren Sars; the historian Ernst Sars was his elder brother, and the singer Eva Nansen was his younger sister.Google Translate He grew up in Manger, Hordaland, where his father was the local priest. He studied from 1852 to 1854 at Bergen Cathedral School, from 1854 at Christiania Cathedral School, and joined the university at Christiana (now the University of Oslo) in 1857. He indulged his interest in natural history while studying medicine; having collected water fleas in local lakes with Wilhelm Lilljeborg's works, he discovered new species, and this resulted in his first scientific publication. Georg Ossian Sars had a good memory and excellent drawing skills, and illustrated some of his father's zoological works. Sars was a founding investig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |