|
Hector (API)
Hector is a high-level client API for Apache Cassandra. Named after Hector, a warrior of Troy in Greek mythology, it is a substitute for the Cassandra Java Client, or Thrift, that is encapsulated by Hector. It also has Maven repository access. History As Cassandra is shipped with the low-level Thrift (protocol), there was a potential to develop a better protocol for application developers. Hector was developed by Ran Tavory as a high-level interface that overlays the shortcomings of Thrift. It is licensed with the MIT License that allows to use, modify, split and change the design. Features The high-level features of Hector are * A high-level object oriented interface to Cassandra: It is mainly inspired by the Cassandra-java-client. The API is defined in the Keyspace interface. * Connection pooling. As in high-scale applications, the usual pattern for DAOs is a large number of reads/writes. It is too expensive for clients to open new connections with each request. So, a client m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ran Tavory
RAN may refer to: * Radio access network, a part of a mobile telecommunication system * Rainforest Action Network * Ran (gene) (RAs-related Nuclear protein), also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran, a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene * Ran (Sufism), a concept of Sufism * RAN translation (Repeat Associated Non-AUG translation), an irregular mode of mRNA translation * Ran Online (stylized as ''RAN Online''), a massively multiplayer online role-playing game developed by Min Communications, Inc. * RAN Remote Area Nurse (TV series) * Rapid automatized naming, a predictor of reading ability * Ravenna Airport, an airport in Ravenna, Italy by IATA code * Régie du Chemin de Fer Abidjan-Niger, a railway in French West Africa, linking Côte d'Ivoire to Upper Volta (now called Burkina Faso) * Remote Area Nurse, in Australia * Royal Australian Navy, the naval branch of the Australian Defence Force * Rugby Americas North, the administrative body of rugby union in North Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thrift (protocol)
Thrift is an IDL (Interface Definition Language) and binary communication protocol used for defining and creating services for programming languages. It was developed by Facebook. Since 2020, it is an open source project in the Apache Software Foundation. It uses a remote procedure call (RPC) framework and combines a software stack with a code generation engine to build cross-platform services. Thrift can connect applications written in a variety of languages and frameworks, including ActionScript, C, C++, C#, Cocoa, Delphi, Erlang, Go, Haskell, Java, JavaScript, Objective-C, OCaml, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Elixir, Rust, Scala, Smalltalk, and Swift. The implementation was described in an April 2007 technical paper released by Facebook, now hosted on Apache. Architecture Thrift includes a complete stack for creating clients and servers. The top part is generated code from the Thrift definition. From this file, the services generate client and processor codes. In contrast t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers. The components of a distributed system communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to microservices to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. Distributed systems cost significantly more than monolithic architectures, primarily due to increased needs for additional hardware, servers, gateways, firewalls, new subnets, proxies, and so on. Also, distributed systems are prone to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hashtable
In computer science, a hash table is a data structure that implements an associative array, also called a dictionary or simply map; an associative array is an abstract data type that maps keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an ''index'', also called a ''hash code'', into an array of ''buckets'' or ''slots'', from which the desired value can be found. During lookup, the key is hashed and the resulting hash indicates where the corresponding value is stored. A map implemented by a hash table is called a hash map. Most hash table designs employ an imperfect hash function. Hash collisions, where the hash function generates the same index for more than one key, therefore typically must be accommodated in some way. In a well-dimensioned hash table, the average time complexity for each lookup is independent of the number of elements stored in the table. Many hash table designs also allow arbitrary insertions and deletions of key–value pairs, at amorti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Round-robin Scheduling
Round-robin (RR) is one of the algorithms employed by process and network schedulers in computing. Guowang Miao, Jens Zander, Ki Won Sung, and Ben Slimane, Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks, Cambridge University Press, , 2016. As the term is generally used, time slices (also known as time quanta) are assigned to each process in equal portions and in circular order, handling all processes without priority (also known as cyclic executive). Round-robin scheduling is simple, easy to implement, and starvation-free. Round-robin scheduling can be applied to other scheduling problems, such as data packet scheduling in computer networks. It is an operating system concept. The name of the algorithm comes from the round-robin principle known from other fields, where each person takes an equal share of something in turn. Process scheduling To schedule processes fairly, a round-robin scheduler generally employs time-sharing, giving each job a time slot or ''quantum'' (its allowa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Load Balancing (computing)
In computing, load balancing is the process of distributing a set of tasks over a set of resources (computing units), with the aim of making their overall processing more efficient. Load balancing can optimize response time and avoid unevenly overloading some compute nodes while other compute nodes are left idle. Load balancing is the subject of research in the field of parallel computers. Two main approaches exist: static algorithms, which do not take into account the state of the different machines, and dynamic algorithms, which are usually more general and more efficient but require exchanges of information between the different computing units, at the risk of a loss of efficiency. Problem overview A load-balancing algorithm always tries to answer a specific problem. Among other things, the nature of the tasks, the algorithmic complexity, the hardware architecture on which the algorithms will run as well as required error tolerance, must be taken into account. Therefore com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Java Management Extensions
Java Management Extensions (JMX) is a Java technology that supplies tools for managing and monitoring applications, system objects, devices (such as printers) and service-oriented networks. Those resources are represented by objects called MBeans (for '' Managed Bean''). In the API, classes can be dynamically loaded and instantiated. Managing and monitoring applications can be designed and developed using the Java Dynamic Management Kit. JSR 003 of the Java Community Process defined JMX 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2. JMX 2.0 was being developed under JSR 255, but this JSR was subsequently withdrawn. The JMX Remote API 1.0 for remote management and monitoring is specified by JSR 160. An extension of the JMX Remote API for Web Services was being developed under JSR 262. Adopted early on by the J2EE community, JMX has been a part of J2SE since version 5.0. "JMX" is a trademark of Oracle Corporation. Architecture JMX uses a three-level architecture: # The ''Probe'' level – also called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Failover
Failover is switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, hardware component or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, hardware component, or network in a computer network. Failover and switchover are essentially the same operation, except that failover is automatic and usually operates without warning, while switchover requires human intervention. History The term "failover", although probably in use by engineers much earlier, can be found in a 1962 declassified NASA report. The term "switchover" can be found in the 1950s when describing '"Hot" and "Cold" Standby Systems', with the current meaning of immediate switchover to a running system (hot) and delayed switchover to a system that needs starting (cold). A conference proceedings from 1957 describes computer systems with both Emergency Switchover (i.e. failover) and Scheduled Failover (for maintenance). Failover Systems designers usually pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Node (networking)
In Computer network, networking, a node (, ‘knot’) is either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint within telecommunication networks. A physical network node is an electronic device that is attached to a network, and is capable of creating, receiving, or transmitting information over a communication channel. In data communication, a physical network node may either be data communication equipment (such as a modem, Network hub, hub, Network bridge, bridge or Network switch, switch) or data terminal equipment (such as a digital telephone handset, a printer or a host computer). A Passivity (engineering), passive distribution point such as a distribution frame or patch panel is not a node. Computer networks In data communication, a physical network node may either be data communication equipment (DCE) such as a modem, Network hub, hub, Network bridge, bridge or Network switch, switch; or data terminal equipment (DTE) such as a digital telephone handset, a printe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Access Object
In software, a data access object (DAO) is a pattern that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or other persistence mechanism. By mapping application calls to the persistence layer, the DAO provides data operations without exposing database details. This isolation supports the single responsibility principle. It separates the data access the application needs, in terms of domain-specific objects and data types (the DAO's public interface), from how these needs can be satisfied with a specific DBMS (the implementation of the DAO). Although this design pattern is applicable to most programming languages, most software with persistence needs, and most databases, it is traditionally associated with Java EE applications and with relational databases (accessed via the JDBC API because of its origin in Sun Microsystems' best practice guidelines "Core J2EE Patterns". This object can be found in the Data Access layer of the 3-Tier Architecture. There are various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apache Maven
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects. Maven can also be used to build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages. The Maven project is hosted by The Apache Software Foundation, where it was formerly part of the Jakarta Project. Maven addresses two aspects of building software: how software is built and its dependencies. Unlike earlier tools like Apache Ant, it uses conventions for the build procedure. Only exceptions need to be specified. An XML file describes the software project being built, its dependencies on other external modules and components, the build order, directories, and required plug-ins. It comes with pre-defined targets for performing certain well-defined tasks such as compilation of code and its packaging. Maven dynamically downloads Java libraries and Maven plug-ins from one or more repositories such as the Maven 2 Central Repository, and stores them in a local cache. This local cache of downloaded arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
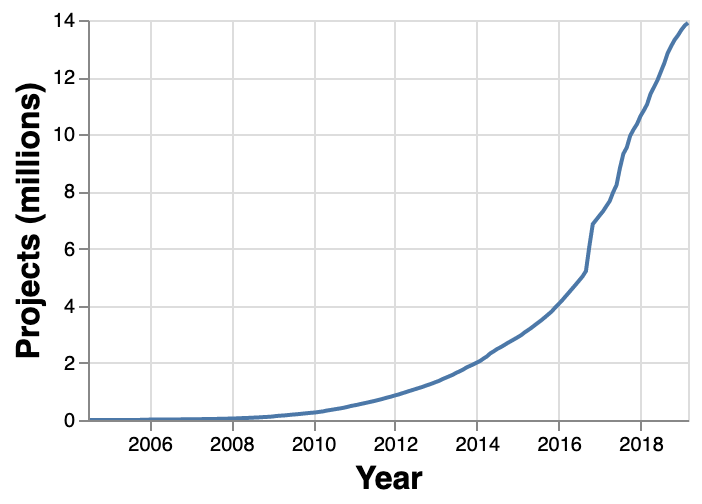
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |