|
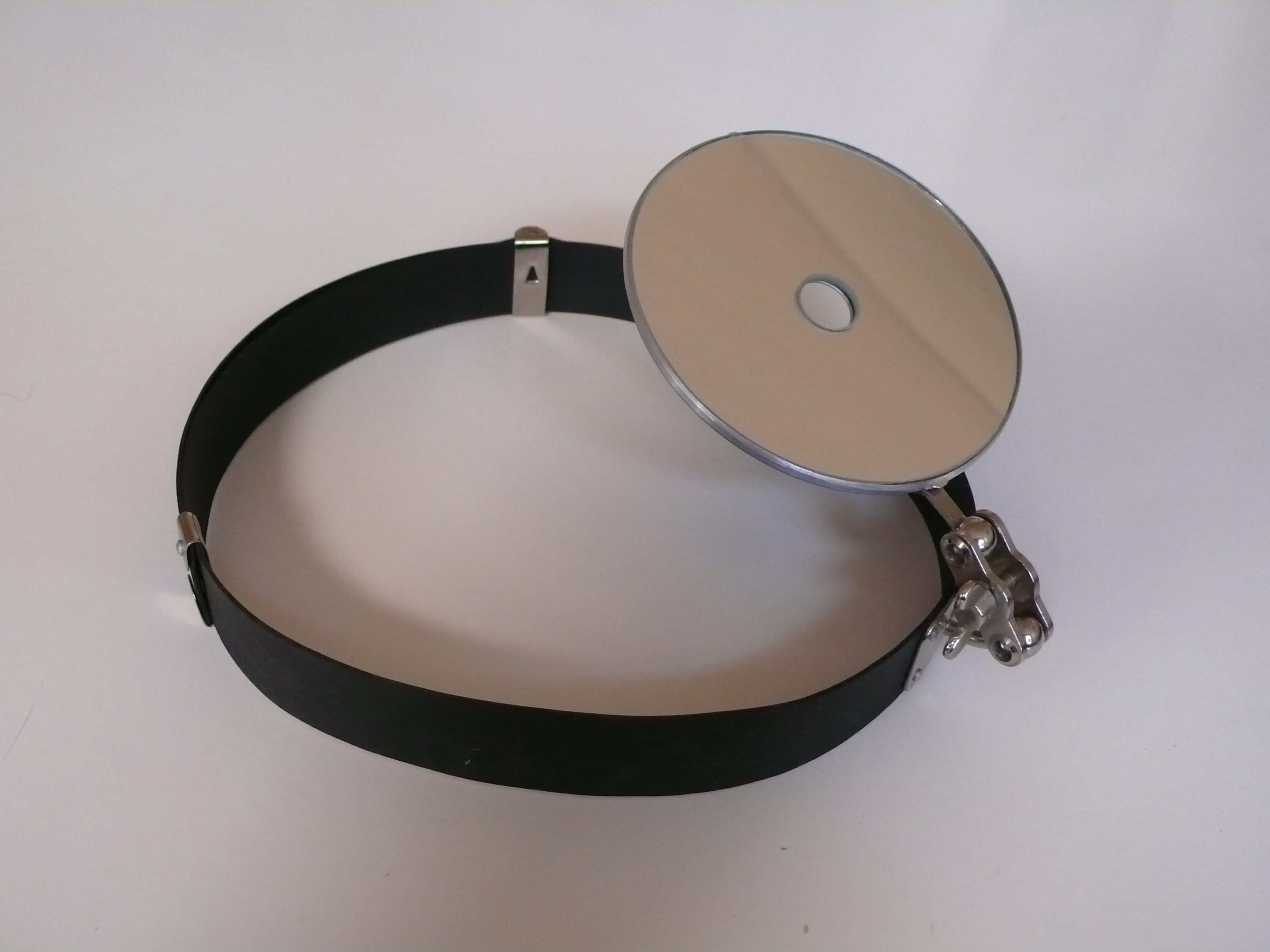
Head Mirror
A head mirror is a simple diagnostic device, stereotypically worn by physicians, but less so in recent decades as they have become somewhat obsolete. A head mirror is mostly used for examination of the ear, nose and throat. It comprises a circular concave mirror, with a small hole in the middle, and is attached to a head band. The mirror is worn over the physician's eye of choice, with the concave mirror surface facing outwards and the hole directly over the physician's eye, providing illumination like a ring light. In use, the patient sits and faces the physician. A bright lamp is positioned adjacent to the patient's head, pointing toward the physician's face and hence towards the head mirror. The light from the lamp reflects off the mirror, along the line of sight of the user, with the light being somewhat concentrated by the curvature of the mirror. When used properly, the head mirror thus provides excellent shadow-free illumination. Because they were once in common use, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Mirror In Use
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do, regardless of size. Heads develop in animals by an evolutionary trend known as cephalization. In bilaterally symmetrical animals, nervous tissue concentrate at the anterior region, forming structures responsible for information processing. Through biological evolution, sense organs and feeding structures also concentrate into the anterior region; these collectively form the head. Human head The human head is an anatomical unit that consists of the skull, hyoid bone and cervical vertebrae. The term "skull" collectively denotes the mandible (lower jaw bone) and the cranium (upper portion of the skull that houses the brain). Sculptures of human heads are generally based on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes are sometimes overgeneralized, inaccurate, and resistant to new information, but can sometimes be accurate. While such generalizations about groups of people may be useful when making quick decisions, they may be erroneous when applied to particular individuals and are among the reasons for prejudicial attitudes. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype refers to stereotypes that one is aware that one holds, and is aware that one is using to judge people. If person ''A ''is making judgments about a ''particular'' person ''B'' from a group ''G'', and person ''A'' has an explicit stereotype for group ''G'', their decision bias can be partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the ''science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or ''craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear, Nose And Throat
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concave Mirror
A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either ''convex'' (bulging outward) or ''concave'' (recessed inward). Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are sometimes used in optical devices. The most common non-spherical type are parabolic reflectors, found in optical devices such as reflecting telescopes that need to image distant objects, since spherical mirror systems, like spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberration. Distorting mirrors are used for entertainment. They have convex and concave regions that produce deliberately distorted images. They also provide highly magnified or highly diminished (smaller) images when the object is placed at certain distances. Convex mirrors A convex mirror or diverging mirror is a curved mirror in which the reflective surface bulges towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they are not used to focus light. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Light
A ring flash is a circular light that is often operated with a camera lens in the center to take photographs. Unlike point light sources, a ring flash can illuminate a subject with minimal shadows by closely and evenly surrounding the optical axis of the camera lens. This makes it a popular choice for various types of photography, including macro, portrait and fashion photography. Closely related to the ring flash is the continuous ring light, which can produce a consistent level of light for video recording or to see a live preview before capturing photographs. Continuous ring lights are popular for improving picture quality on video calls, social media selfies, and video blogging. For example, Cornell University offers a photo kiosk equipped with a continuous ring light and iPad to take social media profile pictures for students, faculty, staff, and alumni. Modern continuous ring lights frequently use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) because they are bright, energy-efficient, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of skull, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin classical compound, combini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the ''science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or ''craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirrors
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very Hardness (materials science), hard surface. A mirror is a Wave (physics), wave reflector. Light consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |