|
Head-marking Language
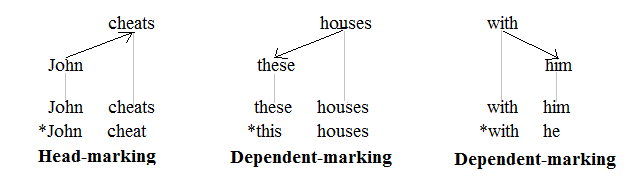
A language is head-marking if the grammatical marks showing agreement between different words of a phrase tend to be placed on the heads (or nuclei) of phrases, rather than on the modifiers or dependents. Many languages employ both head-marking and dependent-marking, and some languages double up and are thus double-marking. The concept of head/dependent-marking was proposed by Johanna Nichols in 1986 and has come to be widely used as a basic category in linguistic typology. In English The concepts of head-marking and dependent-marking are commonly applied to languages that have richer inflectional morphology than English. There are, however, a few types of agreement in English that can be used to illustrate these notions. The following graphic representations of a clause, a noun phrase, and a prepositional phrase involve agreement. The three tree structures shown are those of a dependency grammar (as opposed to those of a phrase structure grammar): :: Heads and dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and Grammar#Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency, Fluent speakers of a variety (linguistics), language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's First language, native language(s) – are language acquisition, acquired not by conscious study or language teaching, instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |