|
Hartwell, Buckinghamshire
Hartwell is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Stone with Bishopstone and Hartwell, in the Aylesbury Vale district, in central Buckinghamshire, England. It is to the south of Aylesbury, by the village of Stone. In 1961 the civil parish had a population of 100. The village name is Anglo Saxon in origin, and means "spring frequented by deer". In the Domesday Book of 1086 it was recorded as ''Herdewelle''. The ruined Hartwell Church was designed by the architect Henry Keene and completed in 1756. It is one of the most important early Gothic revival churches in England and is Grade II* listed. It has an octagonal centre with twin towers. In the north and south bays are rose windows, while other windows are represented as ogee arches. In the clerestory are quatrefoil windows. Inside, the church once had a plaster fan vault but this has now fallen in, and the church's windows are boarded. Today the building appears more as a garden folly, than a former p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone With Bishopstone And Hartwell
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the Earth's crust, crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid Earth's outer core, outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
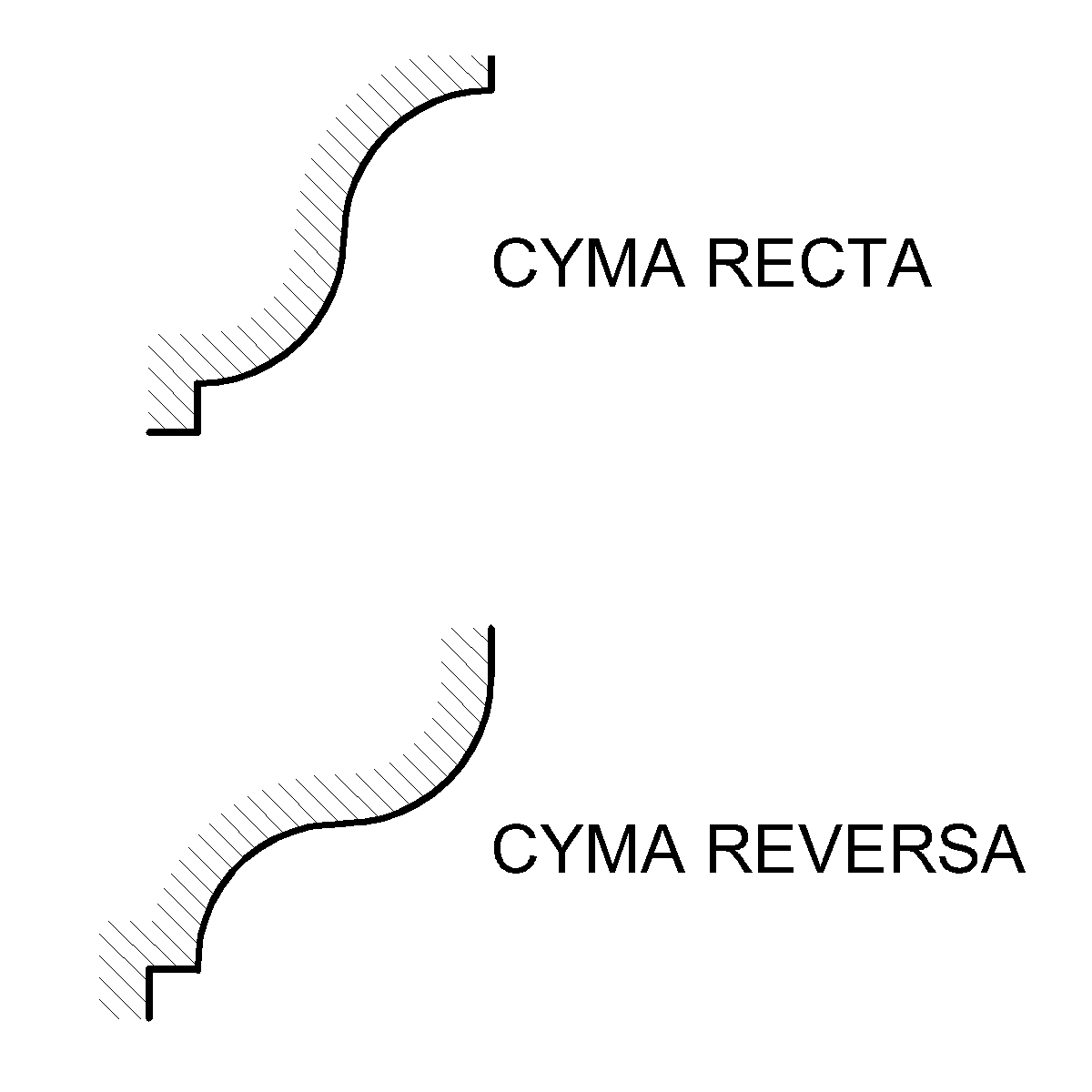
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic and Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the arch, and in decorative molding designs, where single ogees are common profiles (see opening image) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Greyhound Racing Club
The National Greyhound Racing Club was an organisation that governed Greyhound racing in the United Kingdom. History The National Greyhound Racing Club (NGRC) was formed in 1928 and this body would be responsible for regulation, licensing and the rules of racing that came into force on 23 April 1928. It consisted of twelve stewards, one of them senior and most of them with military or police backgrounds. Any greyhound track licensed under NGRC rules would have to adhere to all rules set by them. The National Greyhound Racing Society was a branch of the NGRC responsible for the promotion of the industry. By 1946 the Club employed a 300 strong security service to ensure fair play on its associated tracks. In 1972 the National Greyhound Racing Club and National Greyhound Racing Society amalgamated to form one controlling body called the National Greyhound Racing Club Ltd. In 1987 its secretary Fred Underhill received an O.B.E in recognition of his service from 1962–1988. Disba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyhound Racing In The United Kingdom
Greyhound racing is a sport in the United Kingdom. The industry uses a parimutuel betting tote system with on-course and off-course betting available. Attendances have declined in recent years, partly due to the decrease in evening fixtures with the majority of fixtures being held in the daytime. Attendances peaked in 1946 at around 70 million and totalisator turnover reaching £196,431,430. As of September 2022, there are 20 licensed stadiums in the United Kingdom (excluding Northern Ireland) and two independent stadiums (unaffiliated to a governing body). History Modern greyhound racing has evolved from a form of hunting called coursing, in which a dog runs after a live game animal – usually a rabbit or hare. The first official coursing meeting was held in 1776 at Swaffham, Norfolk. The rules of the Swaffham Coursing Society, started by Lord Orford, specified that only two greyhounds were to course a single hare. Coursing by proxy with an artificial lure was introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserves, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some areas including units that are noted for both biological and geological interest. Biological Biological SSSI/ASSIs may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Trust For Places Of Historic Interest Or Natural Beauty
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and independent National Trust for Scotland. The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the permanent preservation for the benefit of the Nation of lands and tenements (including buildings) of beauty or historic interest". It was given statutory powers, starting with the National Trust Act 1907. Historically, the Trust acquired land by gift and sometimes by public subscription and appeal, but after World War II the loss of country houses resulted in many such properties being acquired either by gift from the former owners or through the National Land Fund. Country houses and estates still make up a significant part of its holdings, but it is also known for its protection of wild lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XVIII
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in exile: during the French Revolution and the First French Empire (1804–1814), and during the Hundred Days. Until his accession to the throne of France, he held the title of Count of Provence as brother of King Louis XVI. On 21 September 1792, the National Convention abolished the monarchy and deposed Louis XVI, who was later executed by guillotine. When his young nephew Louis XVII died in prison in June 1795, the Count of Provence proclaimed himself (titular) king under the name Louis XVIII. Following the French Revolution and during the Napoleonic era, Louis XVIII lived in exile in Prussia, England, and Russia. When the Sixth Coalition finally defeated Napoleon in 1814, Louis XVIII was placed in what he, and the French royalists, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Cook Trust
The Ernest Cook Trust is a large educational charity in England. It was founded in 1952 by the philanthropist Ernest Cook, the grandson of Thomas Cook. Each year the Trustees distribute more than £1.25m in educational grants to benefit children and young people, notably to schools for improving their outdoor education and play areas. About Rooted in the conservation and management of the countryside, the Trust also actively encourages children and young people to learn from the land through hands-on educational opportunities on its estates and by offering grants. Estates The Trust currently owns and manages of landed estates across five counties in southern England. The trust owns of land and is responsible for the following estates: * Fairford Park, The Fairford Park Estate * Barnsley, Gloucestershire, The Barnsley Village Estate * Little Dalby, The Little Dalby Estate * Hartwell, Buckinghamshire, The Hartwell Estate * Boarstall, The Boarstall Estate * Slimbridge, The Slimbrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folly
In architecture, a folly is a building constructed primarily for decoration, but suggesting through its appearance some other purpose, or of such extravagant appearance that it transcends the range of usual garden buildings. Eighteenth-century English landscape gardening and French landscape gardening often featured mock Roman temples, symbolising classical virtues. Other 18th-century garden follies represented Chinese temples, Egyptian pyramids, ruined medieval castles or abbeys, or Tatar tents, to represent different continents or historical eras. Sometimes they represented rustic villages, mills, and cottages to symbolise rural virtues. Many follies, particularly during times of famine, such as the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in Ireland, were built as a form of poor relief, to provide employment for peasants and unemployed artisans. In English, the term began as "a popular name for any costly structure considered to have shown wikt:folly#Noun, folly in the builde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan Vault
A fan vault is a form of vault used in the Gothic style, in which the ribs are all of the same curve and spaced equidistantly, in a manner resembling a fan. The initiation and propagation of this design element is strongly associated with England. The earliest example, dating from about the year 1351, may be seen in the cloisters of Gloucester Cathedral. The largest fan vault in the world can be found in King's College Chapel, Cambridge. The fan vault is peculiar to England. The lierne vault of the cathedral of Barbastro in northern Spain closely resembles a fan vault, but it does not form a perfect conoid. Harvey (1978) suggests Catherine of Aragon as a possible source of English influence in Aragon. Birth of the fan vault The fan vault is attributed to development in Gloucester between 1351 and 1377, with the earliest known surviving example being the east cloister walk of Gloucester Cathedral. Harvey (1978) hypothesises that the east cloister at Gloucester was finish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |