|
Haplogroup Q-M323
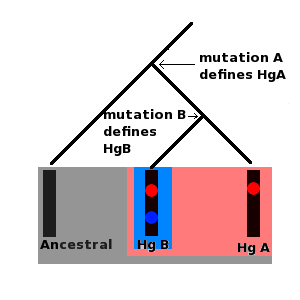
Haplogroup Q-M323 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q-M346. Haplogroup Q-M323 is defined by the presence of the M323 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-M323 was discovered in the Yemeni Jewish population. ''Q-M323 in 3/20 = 15% of a sample of Yemenite Jews.'' In the time since its discovery, it has not been detected in other populations. It could then be exclusive to this population. Associated SNP's Q-M323 is currently defined by the M323 SNP. Subgroups This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft treProposed Treefor haplogroup Q-M323. * Q-M346 M346, L56, L57, L474, L892, L942 ** Q-M323 M323 See also *Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of ... Y-DNA Q-M242 Subclades Y-DNA Backbone Tree Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M346 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M346 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q. Haplogroup Q-M346 is defined by the presence of the M346 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Origin and distribution Q-M346 was discovered in Central Asia and announced in Sengupta 2006. A latter paper suggested that its ancestral state was isolated to India, but this has since been refuted by its presence in West Asia, Europe and the Americas. Asia Q-M346 has a wide distribution across much of Asia. The Americas In the Americas, the founding paternal lineages include those who are Q-M346 but do not belong to the Q-M3 lineage. Associated SNPs Q-M346 is marked by the presence of the M346 SNP. Since the discovery of M346 several additional SNPs have been found to also be associated with Q-M346. These SNP's include: L56 and L57. These SNPs appear to be "parallel" to M346. Subgroups This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft treProposed Treefor haplogroup Q-M346. The first three levels of subclad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L53 (Y-DNA)
Q-L53 is a subclade of haplogroup Q-M346. Q-L53 is defined by the presence of the L53 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-L53 has descendants across much of Eurasia and in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is the parent of the major Haplogroup Q-L54 branch. Associated SNPs Q-L53 is currently defined by the L53 SNP as well as the L55, L213, L331, L475, and L476 SNPs. Subgroups This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft treProposed Treefor haplogroup Q-L53. It shows the first two branch points. * Q-L53 L53, L55, L213, L331, L475, L476 ** Q-L54 L54 *** Q-M3 M3, L341.2 *** Q-Z780 Z780 *** Q-L456 L456 *** Q-L568 L568, L569, L570, L571 *** Q-L330 L330, L334 *** Q-L804 L804, L805 See also *Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-P89
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-NWT01 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-NWT01 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q-MEH2. Haplogroup Q-NWT01 is defined by the presence of the NWT01 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-NWT01 has descendants in the Northwest Territories of modern Canada. It was in these populations that it was discovered. The Americas Q-NWT01 is present in pre-Columbian populations in the Canadian Northwest. It also has been found in a specimen of the Saqqaq culture of prehistoric Greenland.YFull Haplogroup YTree v6.03.05 at 20 July 2018. Accessed July 20, 2018.Monika Karmin, Lauri Saag, Mário Vicente, ''et al.'' (2015), "A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture." ''Genome Research'' 25:1–8. Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; ISSN 1088-9051/15; www.genome.org. A ...
|
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA)
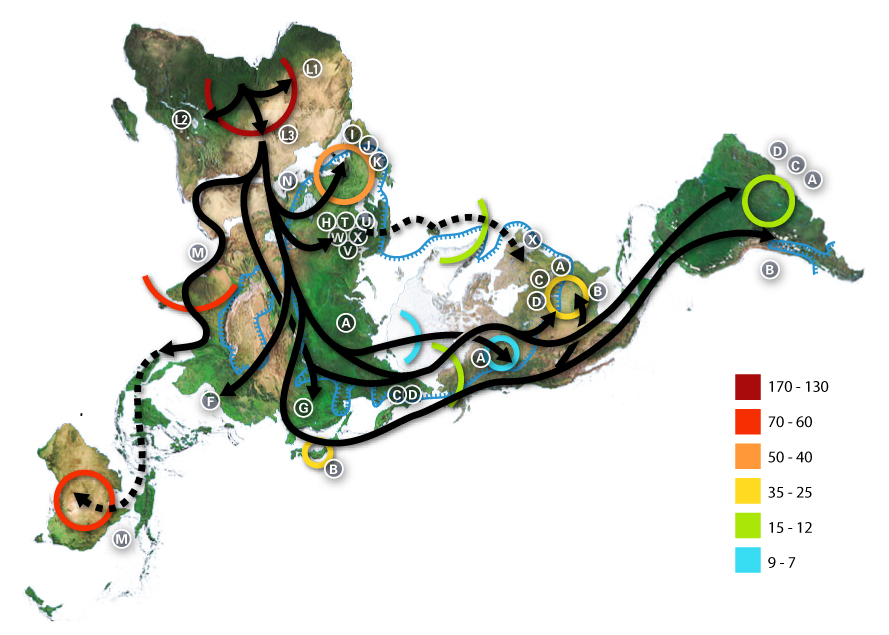
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346. In 1996 the research group at Stanford University headed by Dr. Peter Underhill first discovered the SNP that was to become known as M3. At the time, it was called DYS191. Later studies completed the genetic bridge by determining that Q-M3 was related to Q-M242-bearing populations who traveled through Central Asia to East Asia. Origin and distribution Haplogroup Q-M3 is one of the Y-Chromosome haplogroups linked to the indigenous peoples of the Americas (over 90% of indigenous people in Meso & South America). Today, such lineages also include other Q-M242 branches ( Q-M346, Q-L54, Q-P89.1, Q-NWT01, and Q-Z780), haplogroup C-M130 branches ( C-M217 and C-P39), and R-M207, which are almost exclusively found in the North America. Haplogroup Q-M3 is defined by the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M25 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M25, also known as Q1a1b is a subclade or branch of human Y-DNA haplogroup Q-F1096 (Q1a1), which is, in turn, a subclade of Q-MEH2 ( Q1a). In human genetics, each Y-DNA haplogroup constitutes a biological paternal lineages back to a shared common male ancestor. Distribution Q-M25 has descendants in modern populations across all of Eurasia. Only one detailed study on the Y-DNA on Turkmens from Turkmenistan has taken place. Haplogroup Q is found in minority Turkmen tribes living in Afghanistan at percentages of about 32%,J D Cristofaro et al., 2013, "Afghan Hindu Kush: Where Eurasian Sub-Continent Gene Flows Converge", http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0076748 and another study found that 42.6% of Iranian Turkmens have haplogroup Q-M25 (also known as Q1a1b). The Americas Q-M25 has not been detected in pre-Columbian populations in the Americas. Asia Q-M25 has been detected in the Northeast of East Asia, in South Asia, and across Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M120 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M120, also known as Q1a1a1, is a Y-DNA haplogroup. It is the only primary branch of haplogroup Q1a1a (F746/NWT01). The lineage is most common amongst modern populations in north-east Eurasia. Distribution Q-M120 has descendants in modern populations across eastern Eurasia. The Americas One of the 1K Genomes samples, HG01944, from Peruvians in Lima, Peru belongs to Q-M120. Q-M120 is the other branch under Q-F746. It is best known as an East Asian branch of Q. This is intriguing; if it is not a result of post-colonial admixture, it will mark a fourth or fifth Q lineage in the Americas. The branch of Q-M120 including this sample has a calculated TMRCA of 5,000 to 7,000 years, meaning that it may be the result of a later pre-Columbian immigration from North or East Asia. Asia Q-M120 is present in Eastern Asia and may trace its origin to East Asia. It has been found at low frequency in samples of Han Chinese, Dungans, Hmong Daw in Laos,Cai X, Qin Z, Wen B, Xu S, Wan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L54 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-L54 is a subclade of Y-DNA haplogroup Q-L53. Q1a3a-L54 is defined by the presence of the L54 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-L54 has descendants across Western and Central Europe, the North and East of Asia, and the Americas. It includes two of the major pre-Columbian paternal lineages in the Americas: Q-M3 and Q-M971. The boy Anzick-1, who lived 12,600 years ago and was found in the state of Montana, has a Y-chromosome that refers to haplogroup Q-M971 (Q-L54*(xM3)). Q-L54 descendant lines also include two Eurasian paternal lineages, the Central Asian Q-L330 lineage and the Scandinavian Q-L804. Q-L330 is also found in some men with Romaniote Jewish paternal lines from Greece. Q-L804 is Scandinavian and the TMRCA is just over 3000 years. Haplogroup Q‐L54 is dominant in two North Siberian populations, the Kets Kets (russian: Кеты; Ket: Ostygan) are a tribe of Yeniseian speaking people in Siberia. During the Russian Empire, they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L940 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L717 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L330 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |