|
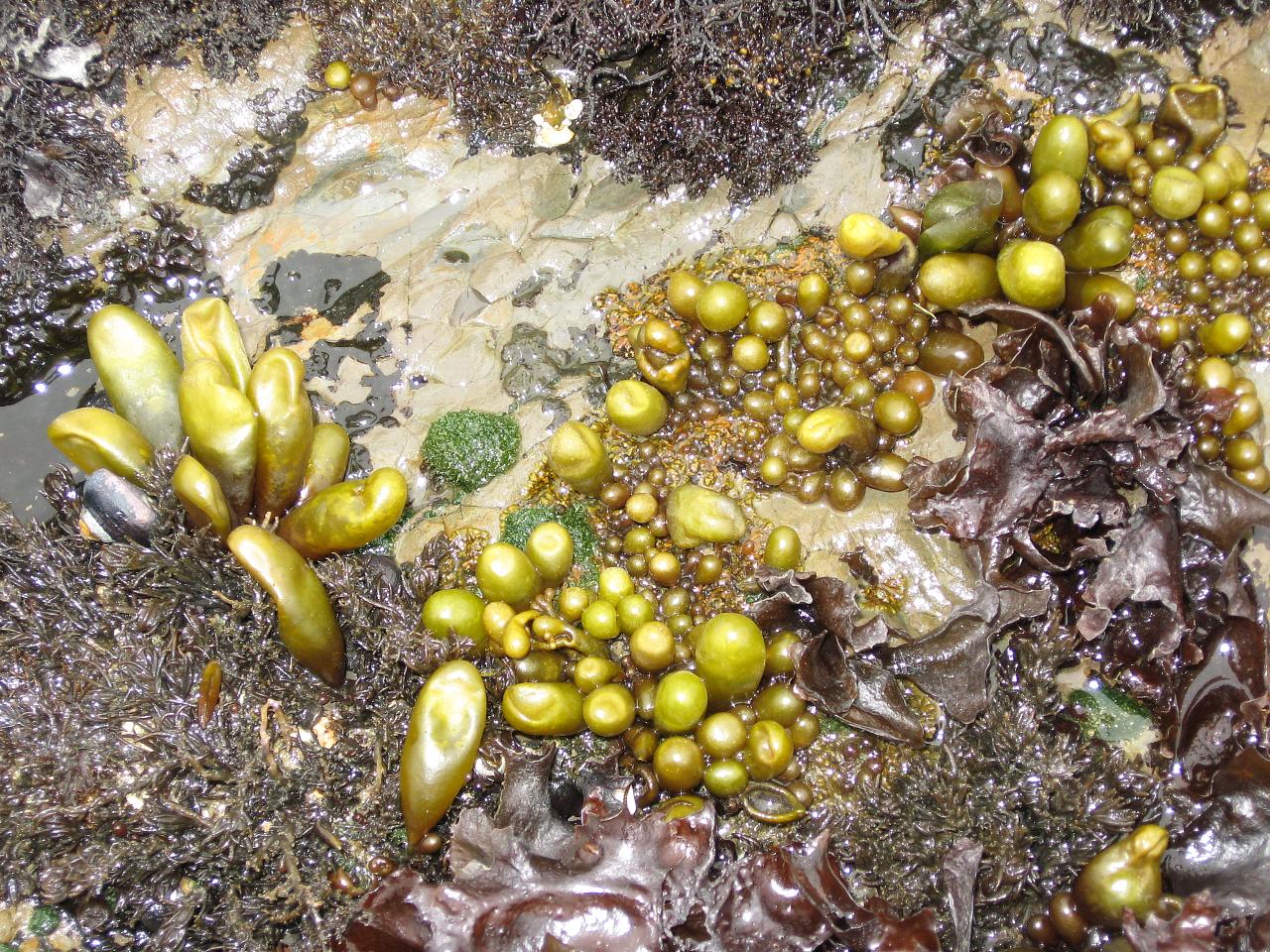
Halosaccion Glandiforme
''Halosaccion glandiforme,'' also known as sea sacs or sea grapes, is a species of red algae.Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2019). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Halosaccion glandiforme (S.G.Gmelin) Ruprecht, 1850. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=372579 on 2019-12-29 It was first described to science by S. G. Gmelin in 1768, in what is arguably the first book to focus on marine biology, ''Historia Fucorum''. Franz Josef Ruprecht is responsible for the current taxonomic description. The type specimen was collected in Kamchatka, Russia. Description The thallus, or body, of this algae is a hollow, torpedo-shaped sac. This ellipsoid shape has low drag through the water allowing the algae to inhabit areas with significant wave and current energy. The sac is reddish-purple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring. German zoologists Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. Humans In human fertilization, a released ovum (a haploid secondary oocyte with replicate chromosome copies) and a haploid sperm cell (male gamete) combine to form a single diploid cell called the zygote. Once the single sperm fuses with the oocyte, the latter completes the division of the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpogonium
The carpogonium (plural ''carpogonia'') is the female organ in the Red Algae (Rhodophyta) which have a highly specialized type of reproduction. It contains the reproductive nucleus. It may contain a number of cells usually without chloroplasts. It shows an elongated process which is the receptive organ for the male gametes. It gives birth to the carpospore A carpospore is a diploid spore produced by red algae. After fertilization, the alga's carpogonium The carpogonium (plural ''carpogonia'') is the female organ in the Red Algae (Rhodophyta) which have a highly specialized type of reproduction. It c ...s. It may also have hairlike structures called ''trichogynes'' which receive sperm before fertilization takes place."trichogyne". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House, Inc. 14 Sep. 2017. Dictionary.com http://www.dictionary.com/browse/trichogyne References Red algae {{rhodophyta-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in fish to line the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller type—called a sperm. Sperm cells or spermatozoa are small and motile due to the flagellum, a tail-shaped structure that allows the cell to propel and move. In contrast, each egg cell or ovum is relatively large and non-motile. In short a gamete is an egg cell (female gamete) or a sperm (male gamete). In animals, ova mature in the ovaries of females and sperm develop in the testes of males. During fertilization, a spermatozoon and ovum unite to form a new diploid organism. Gametes carry half the genetic information of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrasporaphyte
The tetrasporaphyte is a phase in the life history of algae which bear tetrasporangia. This phase is usually morphologically similar to the gametophyte A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has on ... phase.Round, F.E. 1965. ''The Biology of the Algae''.p.32. Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd References Algae {{algae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the Sexual reproduction of plants, sexual phase in the life cycle of plants and algae. It develops sex organs that produce gametes, haploid sex cells that participate in fertilization to form a diploid zygote which has a double set of chromosomes. Cell division of the zygote results in a new diploid multicellular organism, the second stage in the life cycle known as the sporophyte. The sporophyte can produce haploid spores by meiosis that on germination produce a new generation of gametophytes. Algae In some multicellular green algae (''Ulva lactuca'' is one example), red algae and brown algae, sporophytes and gametophytes may be externally indistinguishable (isomorphic). In ''Ulva (genus), Ulv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neorhodomela Larix
''Neorhodomela larix'', commonly known as black pine, is a species of red algae native to coastal areas of the North Pacific, from Mexico to the Bering Sea to Japan. It forms dense mats on semi-exposed rocks in intertidal areas. The thallus is dark brown to black in color with whorled branches resembling a bottlebrush. Ecology The brown alga ''Soranthera ulvoidea'' is commonly found as an epiphyte An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphytes grow are called phoroph ... on '' Neorhodomela'' species, especially ''N. larix'' Postels, A. & Ruprecht, F. (1840). pp. -vi iv, 1-28 -2, index atin: iv 22, -2, index 40 pls. Petropoli t. Petersburg Typis Eduardi Pratz. Isabella Abbott notes that individuals of '' Soranthera'' growing on ''Neorhodomela'' species as a host differ from those found on ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corallina Vancouveriensis
''Corallina'' is a genus of red seaweeds with hard, abrasive calcareous skeletons in the family Corallinaceae. They are stiff, branched plants with articulations. Species # ''Corallina aberrans'' (Yendo) K.R.Hind & G.W.Saunders # '' Corallina abundans'' Me.Lemoine # '' Corallina arbuscula'' Postels & Ruprecht # '' Corallina armata'' J.D.Hooker & Harvey # '' Corallina bathybentha'' E.Y.Dawson # '' Corallina berteroi'' Montagne ex Kützing # ''Corallina bifurca'' Kützing # '' Corallina binangonensis'' Ishijima # ''Corallina confusa'' Yendo # ''Corallina cossmannii'' Me.Lemoine # '' Corallina crassisima'' (Yendo) K.Hind & G.W.Saunders # ''Corallina declinata'' (Yendo) K.Hind & G.W.Saunders # ''Corallina ferreyrae'' E.Y.Dawson, Acleto & Foldvik # '' Corallina goughensis'' Y.M.Chamberlain # ''Corallina hombronii'' (Montagne) Montagne ex Kützing # ''Corallina maxima'' (Yendo) K.R.Hind & G.W.Saunders # ''Corallina melobesioides'' (Segawa) Martone, S.C.Lindstrom, K.A.Miller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
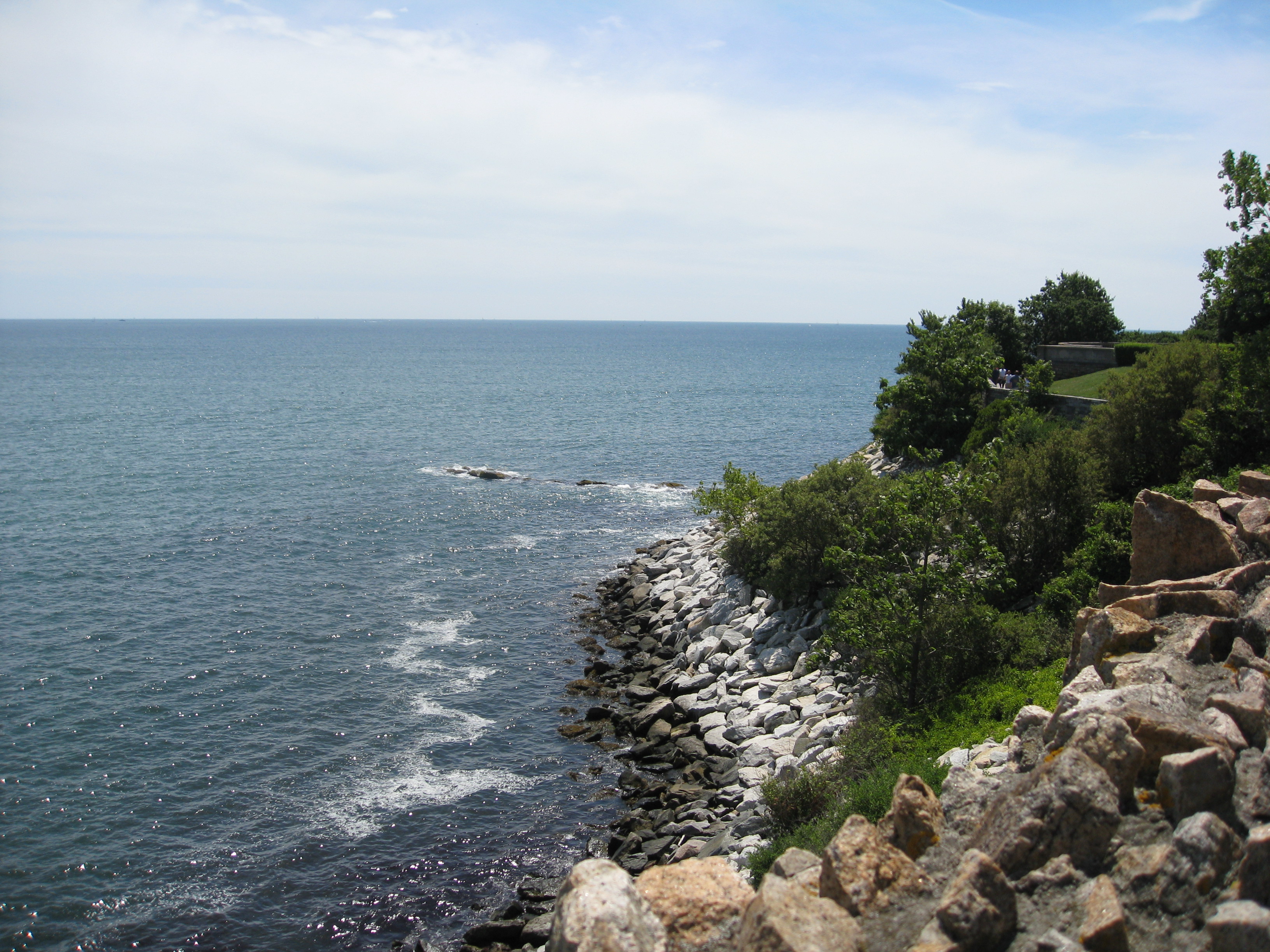
Intertidal Zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of habitats with various species of life, such as seastars, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the ''littoral zone'' or '' seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The well-known area also includes steep rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast mudflats). The area can be a narrow strip, as in Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in the intertidal zone are adapted to an environment of harsh extremes, living in water pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |