|
Haloferax Mediterranei
''Haloferax mediterranei'' is a species of archaea in the family Haloferacaceae. Discovery ''Haloferax mediterranei'' was discovered in 1983 in marine salterns in the village of Santa Pola, Spain. The species was initially named ''Halobacterium mediterranei'', then renamed ''Haloferax mediterranei'' in 1986. Haloferax mediterranei is the fastest-growing known member of the Halobacteriales under optimal laboratory conditions, but it is relatively rare in the environment. The full genome of ''H. mediterranei'' was sequenced in 2012. Metabolism and Growth Conditions ''Haloferax mediterranei'' is the fastest-growing archaeon in the Halobacteriales family, with generation times as low as 1.2 hours reported under optimal laboratory growth conditions. ''Haloferax mediterranei'' is able to use a variety of compounds as carbon and energy sources, and can accumulate materials to serve as a source of carbon and energy, as well as use organic and inorganic nitrogen sources. ''H. mediterrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Sammlung Von Mikroorganismen Und Zellkulturen
The Leibniz Institute DSMZ - German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH (German: ''Leibniz-Institut DSMZ-Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH''), located in Braunschweig, is a research infrastructure in the Leibniz Association. Also the DSMZ is the world's most diverse collection of bioresources (status 2021: 75,000 bioresources). These include microorganisms (including more than 32,000 bacterial strains, 690 archaeal strains, 7,000 strains of yeasts and fungi) as well as more than 840 human and animal cell cultures, over 1. 500 plant viruses, over 940 bacteriophages, and 250 plasmids (status 2021). Since 2010, the scientific director of the Leibniz Institute DSMZ has been Jörg Overmann, a microbiologist with a PhD. He holds a professorship in microbiology at the Technical University of Braunschweig. Since August 2018, he has led the institute in a dual leadership with Bettina Fischer as administrative director. History Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferacaceae
''Haloferacaceae'' is a family of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the order ''Haloferacales.'' The type genus of this family is ''Haloferax.'' Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order ''Haloferacales.'' The name ''Haloferacaceae'' is derived from the Latin term ''Haloferax,'' referring to the type genus of the family and the suffix "-ceae", an ending used to denote a family. Together, ''Haloferacaceae'' refers to a family whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Haloferax.'' Taxonomy and molecular signatures As of 2021, ''Haloferacaceae'' contains 10 validly published genera. This family can be molecularly distinguished from other Halobacteria by the presence of five conserved signature proteins (CSPs) and four conserved signature indels (CSIs) present in the following proteins: thermosome, ribonuclease BN and hypothetical proteins. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Pola
Santa Pola (Valencian and Spanish: ) is a coastal town located in the comarca of Baix Vinalopó in the Valencian Community, Spain, by the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of and has a population of 30,000 inhabitants of whom 10,000 are residents of the nearby town of Gran Alacant. The town has an important salt evaporation pond known as the ''salines'' which remains in business, additionally, most of it is recognized as the Natural Park of Salines de Santa Pola, an important Ramsar site. The town was settled over the ruins of a Roman village called ''Portus Ilicitanus'' (literally, ''Harbour of Elche''); after being abandoned for decades, then a castle was constructed in the 16th century which marked the repopulation of Santa Pola. The town has an archeological museum covering these phases. Santa Pola is, at present, a coastal fishing and tourist town. Population more than doubles during the summer, with people coming mostly from the rest of the Alicante province, and als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferax Volcanii
''Haloferax volcanii'' is a species of organism in the genus ''Haloferax'' in the Archaea. Description and significance Microbiologist Benjamin Elazari Volcani first discovered ''Haloferax volcanii'', a self-named extremophile, in the 1930s. ''H. volcanii'' is a halophilic mesophile archaeon that can be isolated from hypersaline environments such as: the Dead Sea, the Great Salt Lake, and oceanic environments with high sodium chloride concentrates. ''Haloferax volcanii'' is noteworthy because it can be cultured without much difficulty, rare for an extremophile. ''H. volcanii'' is chemoorganotrophic, metabolizing sugars as a carbon source. It is primarily aerobic, but is capable of anaerobic respiration under anoxic conditions. Recently an isolate of this species was studied by researchers at University of California, Berkeley, as part of a project on the survival of haloarchaea on Mars. Genome structure The genome of ''H. volcanii'' consists of a large (4 Mb), multicopy chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FtsZ
FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ''ftsZ'' gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division (also called the Z ring). FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z." The hypothesis was that cell division mutants of '' E. coli'' would grow as filaments due to the inability of the daughter cells to separate from one another. FtsZ is found in almost all bacteria, many archaea, all chloroplasts and some mitochondria, where it is essential for cell division. FtsZ assembles the cytoskeletal scaffold of the Z ring that, along with additional proteins, constricts to divide the cell in two. History In the 1960s scientists screened for temperature sensitive mutations that blocked cell division at 42 °C. The mutant cells divided normally at 30°, but failed to divide at 42°. Continued growth without division produced long filamentous cells (Filamenting temperature s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
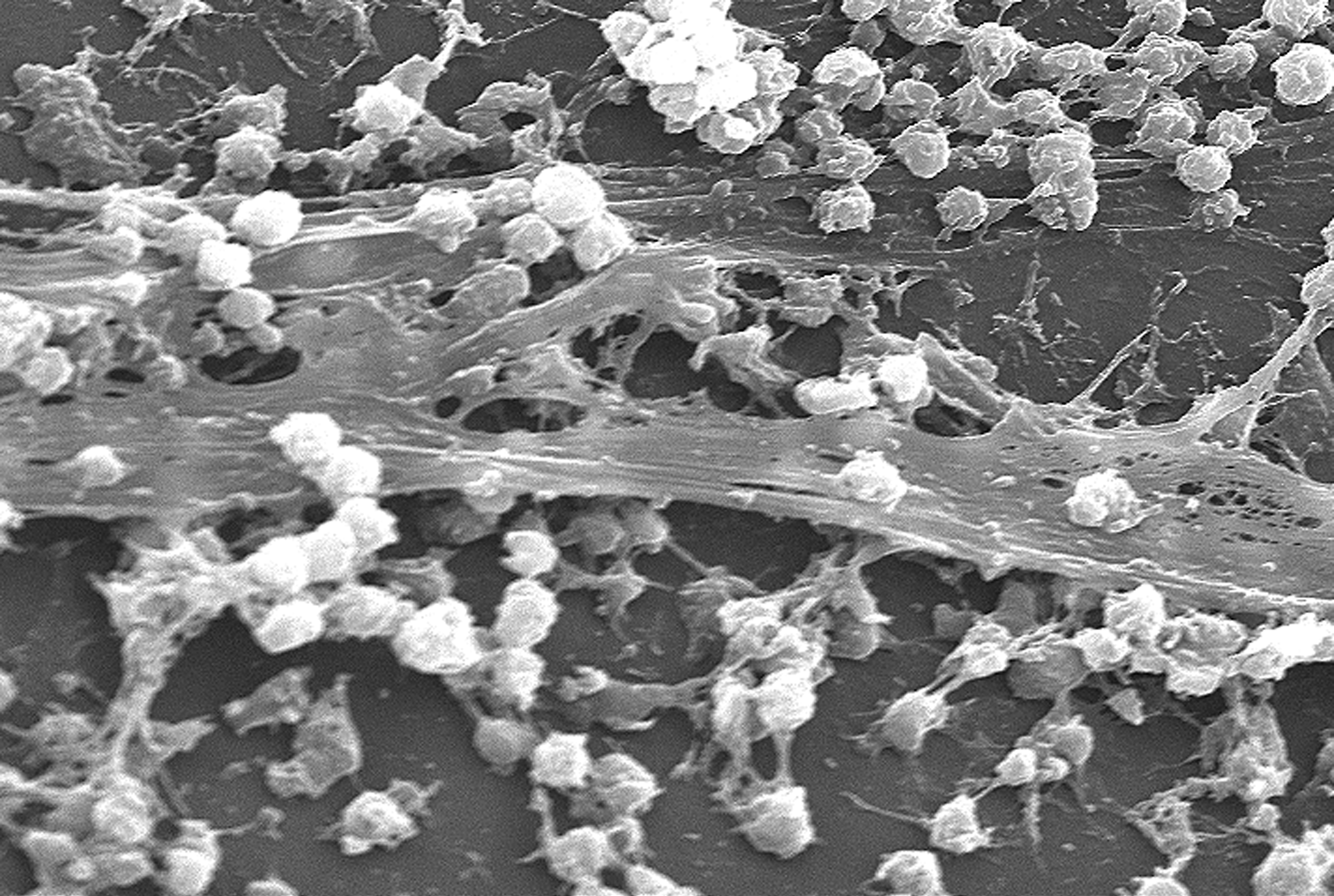
Biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhydroxyalkanoates
Polyhydroxyalkanoates or PHAs are polyesters produced in nature by numerous microorganisms, including through bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids. When produced by bacteria they serve as both a source of energy and as a carbon store. More than 150 different monomers can be combined within this family to give materials with extremely different properties. These plastics are biodegradable and are used in the production of bioplastics. They can be either thermoplastic or elastomeric materials, with melting points ranging from 40 to 180 °C. The mechanical properties and biocompatibility of PHA can also be changed by blending, modifying the surface or combining PHA with other polymers, enzymes and inorganic materials, making it possible for a wider range of applications. Biosynthesis To induce PHA production in a laboratory setting, a culture of a micro-organism such as '' Cupriavidus necator'' can be placed in a suitable medium and fed appropriate nutrients so that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacterium Salinarum
''Halobacterium salinarum'', formerly known as ''Halobacterium cutirubrum'' or ''Halobacterium halobium'', is an extremely halophilic marine obligate aerobic archaeon. Despite its name, this is not a bacterium, but a member of the domain Archaea. It is found in salted fish, hides, hypersaline lakes, and salterns. As these salterns reach the minimum salinity limits for extreme halophiles, their waters become purple or reddish color due to the high densities of halophilic Archaea. ''H. salinarum'' has also been found in high-salt food such as salt pork, marine fish, and sausages. The ability of ''H. salinarum'' to survive at such high salt concentrations has led to its classification as an extremophile. Cell morphology and metabolism Halobacteria are single-celled, rod-shaped microorganisms that are among the most ancient forms of life and appeared on Earth billions of years ago. The membrane consists of a single lipid bilayer surrounded by an S-layer. The S-layer is made of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
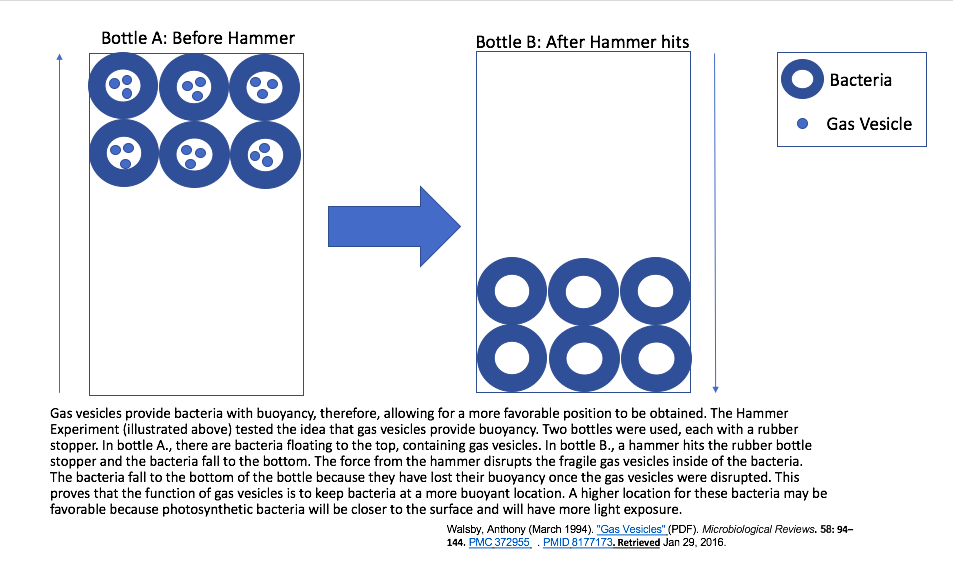
Gas Vesicle
Gas vesicles, also known as gas vacuoles, are nanocompartments in certain prokaryotic organisms, which help in buoyancy. Gas vesicles are composed entirely of protein; no lipids or carbohydrates have been detected. Function Gas vesicles occur primarily in aquatic organisms as they are used to modulate the cell's buoyancy and modify the cell's position in the water column so it can be optimally located for photosynthesis or move to locations with more or less oxygen. Organisms that could float to the air–liquid interface out competes other aerobes that cannot rise in a water column, through using up oxygen in the top layer. In addition, gas vesicles can be used to maintain optimum salinity by positioning the organism in specific locations in a stratified body of water to prevent osmotic shock. High concentrations of solute will cause water to be drawn out of the cell by osmosis, causing cell lysis. The ability to synthesize gas vesicles is one of many strategies that allow h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacteria
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)