|
Haloferacales
''Haloferacales'' is an order of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the class Haloarchaea. The type genus of this order is ''Haloferax.'' The name ''Haloferacales'' is derived from the Latin term ''Haloferax,'' referring to the type genus of the order and the suffix "-ales," an ending used to denote an order. Together, ''Haloferacales'' refers to an order whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Haloferax.'' Biochemical Characteristics and Molecular Signatures Members are halophiles and can be chemoorganotrophs or heterotrophs and are isolated from high-salt environments such as marine solar salterns and the Dead Sea. Some members are motile and contain gas vesicles. Morphology is variable, including rod, coccus or flat square shapes. Members of this order grow optimally in neutral pH. The DNA G+C content for this order ranges between 55-66 mol%. This order can be reliably distinguished from other Halobacteria by the presence of five conserved signatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halorubraceae
''Halorubraceae'' is a family of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the order ''Haloferacales.'' The type genus of this family is ''Halorubrum''. Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order ''Haloferacales.'' The name ''Halorubraceae'' is derived from the Latin term ''Halorubrum,'' referring to the type genus of the family and the suffix "-ceae," an ending used to denote a family. Together, ''Halorubraceae'' refers to a family whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Halorubrum.'' Current taxonomy and molecular signatures As of 2021, ''Halorubraceae'' contains nine validly published genera. This family can be distinguished from other Halobacteria by the presence of four conserved signature proteins (CSPs). Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Note: * Halorubraceae See also * List of Archaea ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferacaceae
''Haloferacaceae'' is a family of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic or heterotrophic archaea within the order ''Haloferacales.'' The type genus of this family is ''Haloferax.'' Its biochemical characteristics are the same as the order ''Haloferacales.'' The name ''Haloferacaceae'' is derived from the Latin term ''Haloferax,'' referring to the type genus of the family and the suffix "-ceae", an ending used to denote a family. Together, ''Haloferacaceae'' refers to a family whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Haloferax.'' Taxonomy and molecular signatures As of 2021, ''Haloferacaceae'' contains 10 validly published genera. This family can be molecularly distinguished from other Halobacteria by the presence of five conserved signature proteins (CSPs) and four conserved signature indels (CSIs) present in the following proteins: thermosome, ribonuclease BN and hypothetical proteins. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacteria
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacteriales
In taxonomy, the Halobacteriales are an order of the Halobacteria, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. They are also called halophiles, though this name is also used for other organisms which live in somewhat less concentrated salt water. They are common in most environments where large amounts of salt, moisture, and organic material are available. Large blooms appear reddish, from the pigment bacteriorhodopsin. This pigment is used to absorb light, which provides energy to create ATP. Halobacteria also possess a second pigment, halorhodopsin, which pumps in chloride ions in response to photons, creating a voltage gradient and assisting in the production of energy from light. The process is unrelated to other forms of photosynthesis involving electron transport; however, and halobacteria are incapable of fixing carbon from carbon dioxide. Halobacteria can exist in salty environments because although they are aerobes they have a separate and different way o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natrialbales
''Natrialbales'' is an order of halophilic, chemoorganotrophic archaea within the class Haloarchaea. The type genus of this order is ''Natrialba.'' The name ''Natrialbales'' is derived from the Latin term ''Natriabla,'' referring to the type genus of the order and the suffix "-ales", an ending used to denote an order. Together, ''Natrialbales'' refers to an order whose nomenclatural type is the genus ''Natrialba.'' Biochemical characteristics and molecular signatures Members are halophilic chemoorganotrophs and are mainly isolated from high-salt environments such as saline lakes, soda lakes and salted hides. Some members are motile. Morphology is variable, including rod, coccus or pleomorphic shapes. Majority of the class are able to grow optimally in alkaline pH and do not possess gas vesicles. The DNA G+C content for this order ranges between 60-70 mol%. This order can be reliably distinguished from other orders within the phylum Euryarchaeota by the presence of eight conser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloferax
In taxonomy, ''Haloferax'' (common abbreviation: ''Hfx.'') is a genus of the Haloferacaceae. Genetic exchange Cells of ''H. mediterranei'' and cells of the related species '' H. volcanii'' can undergo a process of genetic exchange between two cells which involves cell fusion resulting in a heterodiploid cell (containing two different chromosomes in one cell). Although this genetic exchange ordinarily occurs between two cells of the same species, it can also occur at a lower frequency between an ''H. mediterranei'' and an ''H. volcani'' cell. These two species have an average nucleotide sequence identity of 86.6%. During this exchange process, a diploid cell is formed that contains the full genetic repertoire of both parental cells, and genetic recombination is facilitated. Subsequently, the cells separate, giving rise to recombinant cells. Taxonomy As of 2022, 13 species are validly published under the genus ''Haloferax''. ;Proposed species Several species and novel binomial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetyl-CoA Synthetase
Acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) or Acetate—CoA ligase is an enzyme () involved in metabolism of acetate. It is in the ligase class of enzymes, meaning that it catalyzes the formation of a new chemical bond between two large molecules. Reaction The two molecules joined together that make up Acetyl CoA are acetate and coenzyme A (CoA). The complete reaction with all the substrates and products included is: : ATP + Acetate + CoA AMP + Pyrophosphate + Acetyl-CoA Once acetyl-CoA is formed it can be used in the TCA cycle in aerobic respiration to produce energy and electron carriers. This is an alternate method to starting the cycle, as the more common way is producing acetyl-CoA from pyruvate through the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The enzyme's activity takes place in the mitochondrial matrix so that the products are in the proper place to be used in the following metabolic steps. Acetyl Co-A can also be used in fatty acid synthesis, and a common function of the synthetase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
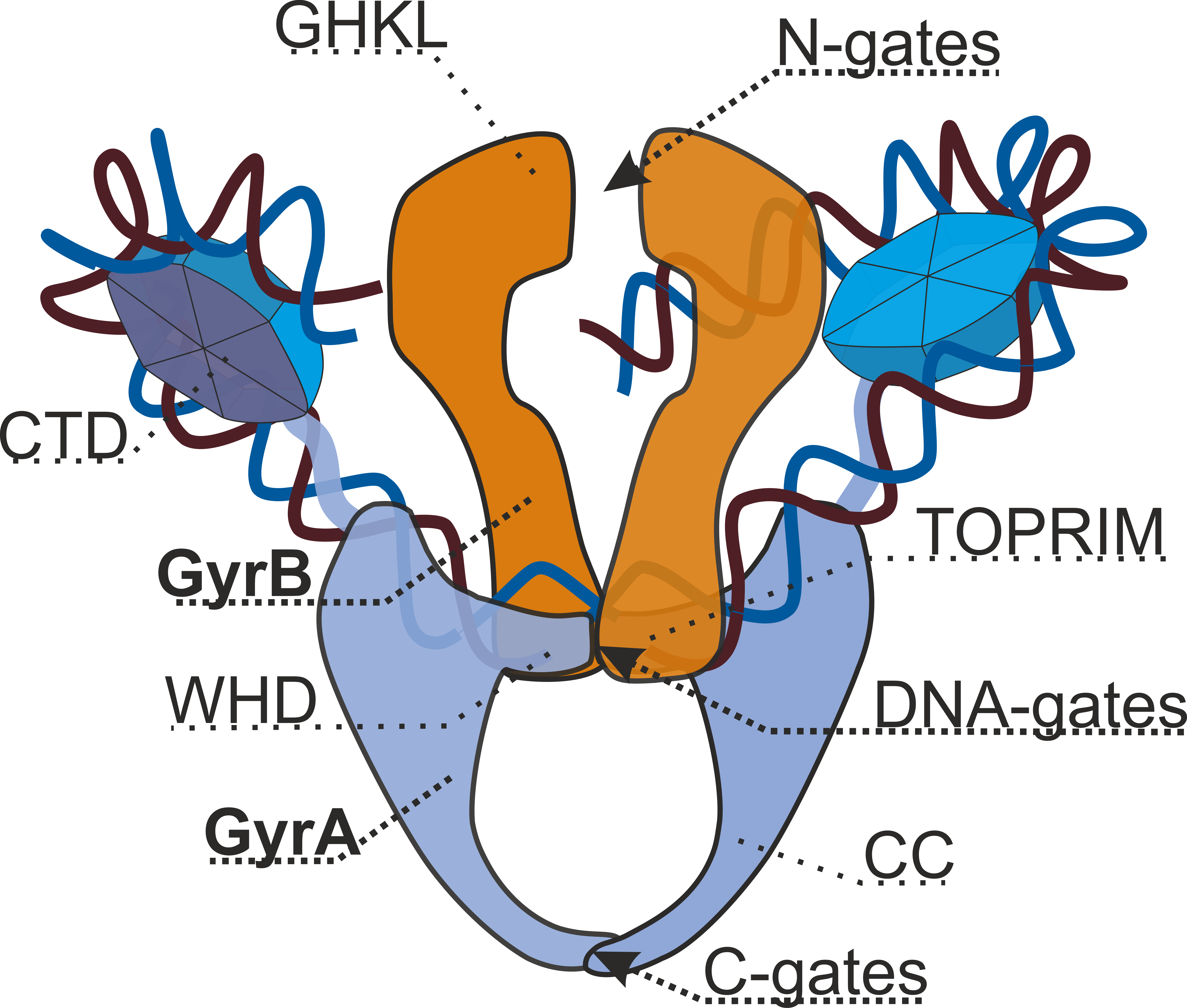
DNA Gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ... within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA polymerase, RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing DNA replication#Replication fork, replication fork. The enzyme causes negative DNA supercoil, supercoiling of the DNA or relaxes positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template so as to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in bacteria, whose single circular DNA is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conserved Signature Indels
Conserved signature inserts and deletions (CSIs) in protein sequences provide an important category of molecular markers for understanding phylogenetic relationships. CSIs, brought about by rare genetic changes, provide useful phylogenetic markers that are generally of defined size and they are flanked on both sides by conserved regions to ensure their reliability. While indels can be arbitrary inserts or deletions, CSIs are defined as only those protein indels that are present within conserved regions of the protein. The CSIs that are restricted to a particular clade or group of species, generally provide good phylogenetic markers of common evolutionary descent. Due to the rarity and highly specific nature of such changes, it is less likely that they could arise independently by either convergent or parallel evolution (i.e. homoplasy) and therefore are likely to represent synapomorphy. Other confounding factors such as differences in evolutionary rates at different sites or among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology in describing the food chain. Heterotrophs may be subdivided according to their energy source. If the heterotroph uses chemical energy, it is a chemoheterotroph (e.g., humans and mushrooms). If it uses light for energy, then it is a photoheterotroph (e.g., green non-sulfur bacteria). Heterotrophs represent one of the two mechanisms of nutrition (trophic levels), the other being autotrophs (''auto'' = self, ''troph'' = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)