|
Halobacterium Cutirubrum
''Halobacterium salinarum'', formerly known as ''Halobacterium cutirubrum'' or ''Halobacterium halobium'', is an extremely halophile, halophilic ocean, marine obligate aerobic archaeon. Despite its name, this is not a bacteria, bacterium, but a member of the domain Archaea. It is found in salted fish, Hide (skin), hides, hypersaline lakes, and salterns. As these salterns reach the minimum salinity limits for extreme halophiles, their waters become purple or reddish color due to the high densities of halophilic Archaea. ''H. salinarum'' has also been found in high-salt food such as salt pork, marine fish, and sausages. The ability of ''H. salinarum'' to survive at such high salt concentrations has led to its classification as an extremophile. Cell morphology and metabolism Halobacteria are single-celled, rod-shaped microorganisms that are among the most ancient forms of life and appeared on Earth billions of years ago. The membrane consists of a single lipid bilayer surrounded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate Aerobe
An obligate aerobe is an organism that requires oxygen to grow. Through cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to metabolise substances, like sugars or fats, to obtain energy. In this type of respiration, oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor for the electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration has the advantage of yielding more energy ( adenosine triphosphate or ATP) than fermentation or anaerobic respiration, but obligate aerobes are subject to high levels of oxidative stress."Obligate aerobe - definition from Biology-Online.org." ''Biology Online.'' Biology-Online, n.d. Web. 12 Dec 2009. Examples Among organisms, almost all animals, most fungi, and several bacteria are obligate aerobes. Examples of obligately aerobic bacteria include ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (acid-fast), ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' (Gram-negative), ''Bacillus'' (Gram-positive), and ''Nocardia asteroides'' (Gram-positive). With the exception of the yeasts, most fungi are obligate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriorhodopsin Chemiosmosis
Bacteriorhodopsin is a protein used by Archaea, most notably by haloarchaea, a class of the Euryarchaeota. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move protons across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting proton gradient is subsequently converted into chemical energy. Function Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven H+ ion transporter found in some haloarchaea, most notably '' Halobacterium salinarum'' (formerly known as syn. ''H. halobium''). The proton-motive force generated by the protein is used by ATP synthase to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By expressing bacteriorhodopsin, the archaea cells are able to synthesise ATP in the absence of a carbon source. Structure Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27 kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectric Point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). However, pI is also used. For brevity, this article uses pI. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons (H+). Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface charge-determining ions are H+/HO−, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. The pI value can affect the solubility of a molecule at a given pH. Such molecules have minimum solubility in water or salt solutions at the pH that corresponds to their pI and often precipitate out of solution. Biological amphoteric molecules such as proteins contain both acidic and basic function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Precipitation
Protein precipitation is widely used in downstream processing of biological products in order to concentrate proteins and purify them from various contaminants. For example, in the biotechnology industry protein precipitation is used to eliminate contaminants commonly contained in blood. The underlying mechanism of precipitation is to alter the solvation potential of the solvent, more specifically, by lowering the solubility of the solute by addition of a reagent. General principles The solubility of proteins in aqueous buffers depends on the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic amino acid residues on the protein's surface. Hydrophobic residues predominantly occur in the globular protein core, but some exist in patches on the surface. Proteins that have high hydrophobic amino acid content on the surface have low solubility in an aqueous solvent. Charged and polar surface residues interact with ionic groups in the solvent and increase the solubility of a protein. Knowledge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Transport
In cellular biology, ''active transport'' is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement. There are two types of active transport: primary active transport that uses adenosine triphosphate ( ATP), and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. Some examples of active transport include: * Phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages * Movement of calcium ions out of cardiac muscle cells * Transportation of amino acids across the intestinal lining in the human gut * Secretion of proteins such as enzymes, peptide hormones, and antibodies from various cells * Functioning of white blood cells to defend invading diseases Active cellular transportation (ACT) Unlike passive transport, which uses the kinetic energy and natural entropy of molecules moving down a gradient, active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Equilibrium
Molecular diffusion, often simply called diffusion, is the thermal motion of all (liquid or gas) particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size (mass) of the particles. Diffusion explains the net flux of molecules from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. Once the concentrations are equal the molecules continue to move, but since there is no concentration gradient the process of molecular diffusion has ceased and is instead governed by the process of self-diffusion, originating from the random motion of the molecules. The result of diffusion is a gradual mixing of material such that the distribution of molecules is uniform. Since the molecules are still in motion, but an equilibrium has been established, the result of molecular diffusion is called a "dynamic equilibrium". In a phase with uniform temperature, absent external net forces acting on the particles, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste. Potassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. KCl is used as a fertilizer, in medicine, in scientific applications, domestic water softeners (as a substitute for sodium chloride salt), and in food processing, where it may be known as E number additive E508. It occurs naturally as the mineral sylvite, and in combination with sodium chloride as sylvinite. Uses Fertilizer The majority of the potassium chloride produced is used for making fertilizer, called potash, since the growth of many plants is limited by potassium availability. Potassium chloride sold as fertilizer is known as muriate of potash (MOP). The vast majority of potash fertilizer worldwide is sold as MOP. Medical use Potassium is vital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compatible Solutes
Osmoprotectants or compatible solutes are small organic molecules with neutral charge and low toxicity at high concentrations that act as osmolytes and help organisms survive extreme osmotic stress. Osmoprotectants can be placed in three chemical classes: betaines and associated molecules, sugars and polyols, and amino acids. These molecules accumulate in cells and balance the osmotic difference between the cell's surroundings and the cytosol. In plants, their accumulation can increase survival during stresses such as drought. In extreme cases, such as in bdelloid rotifers, tardigrades, brine shrimp, and nematodes, these molecules can allow cells to survive being completely dried out and let them enter a state of suspended animation called cryptobiosis. Intracellular osmoprotectant concentrations are regulated in response to environmental conditions such as osmolarity and temperature via regulation of specific transcription factors and transporters. They have been shown to play a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
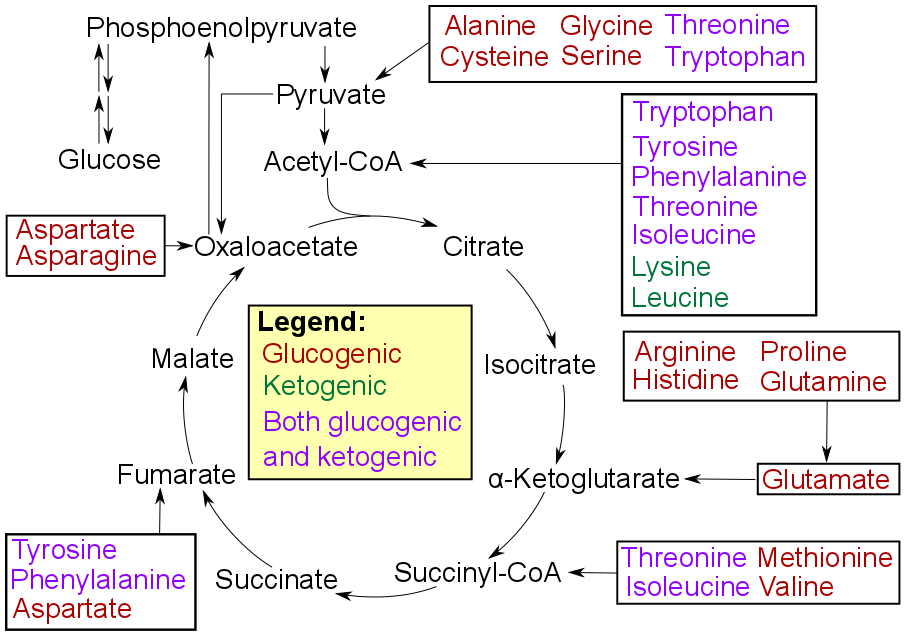
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or intermediates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)