|
Halipegus Eccentricus
''Halipegus eccentricus'' is a monoecious, digenea parasitic trematode commonly found in true frogs in North America. It was first described in 1939. ''H. eccentricus'' is mainly found in the Eustachian tubes of a variety of frog species, its definitive host, although its life cycle involves other hosts, as is common for trematodes. Earlier research proposed that its life cycle involved two other species of hosts (ostracods and snails); however, subsequent research has revealed that the nymph form of the damselfly is also involved. Population dynamics and distribution There is a positive correlation between numbers of ''H. eccentricus'' and frog size and age. The maximum infrapopulation density that a single frog can support is twelve, although most infected frogs have only five or six worms. Seasonal patterns of prevalence of the parasite in one of its intermediate hosts, ''Physa gyrina'', have been observed to peak in May through July and to decline in autumn, which coincides w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington, Texas
Arlington is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, located in Tarrant County. It forms part of the Mid-Cities region of the Dallas–Fort Worth–Arlington metropolitan statistical area, and is a principal city of the metropolis and region. The city had a population of 394,266 in 2020, making it the second-largest city in the county after Fort Worth. Arlington is the 50th-most populous city in the United States, the seventh-most populous city in the state of Texas, and the largest city in the state that is not a county seat. Arlington is home to the University of Texas at Arlington, a major urban research university, the Arlington Assembly plant used by General Motors, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission Region IV, Texas Health Resources, Mensa International, and D. R. Horton. Additionally, Arlington hosts the Texas Rangers at Globe Life Field, the Dallas Cowboys at AT&T Stadium, the Arlington Renegades at Choctaw Stadium, the Dallas Wings at College Park Center, the Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planorbella Trivolvis
''Planorbella trivolvis'' is a species of freshwater air-breathing snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails, or planorbids, which all have sinistral or left-coiling shells. Description All species within family Planorbidae have sinistral shells. The width of the shell of this species is up to 18 mm. Distribution This pond snail is native to North America, from the Arctic areas of Canada all the way south to Florida. It has also been introduced in other parts of the world. * PeruParaense W. L. (September 2003) "Planorbidae, Lymnaeidae and Physidae of Peru (Mollusca: Basommatophora)". ''Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz'' 98(6): 767-771PDF/ref> * DominicaReeves W. K., Dillon Jr. R. T. & Dasch G. A. (2008). "Freshwater snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from the Commonwealth of Dominica with a discussion of their roles in the transmission of parasites". ''American Malacological Bulletin'' 24: 59-63. PDF. Habitat This specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypridopsis
''Cypridopsis'' is a genus of ostracods, belonging to the family Cyprididae. The genus was described in 1867 by George Stewardson Brady. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. Species include: * ''Cypridopsis bamberi'' Henderson, 1986 * ''Cypridopsis elephantiasis'' Hu & Tao, 2008 * ''Cypridopsis sinensis ''Cypridopsis'' is a genus of ostracods, belonging to the family Cyprididae. The genus was described in 1867 by George Stewardson Brady. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution. Species include: * ''Cypridopsis bamberi'' Henderson, 1986 * ''Cyp ...'' Hu & Tao, 2008 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4544301 Cyprididae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damselflies
Damselflies are flying insects of the suborder Zygoptera in the order Odonata. They are similar to dragonflies, which constitute the other odonatan suborder, Anisoptera, but are smaller and have slimmer bodies. Most species fold the wings along the body when at rest, unlike dragonflies which hold the wings flat and away from the body. An ancient group, damselflies have existed since at least the Lower Permian, and are found on every continent except Antarctica. All damselflies are predatory insects; both nymphs and adults actively hunt and eat other insects. The nymphs are aquatic, with different species living in a variety of freshwater habitats including acidic bogs, ponds, lakes and rivers. The nymphs moult repeatedly, at the last moult climbing out of the water to undergo metamorphosis. The skin splits down the back, they emerge and inflate their wings and abdomen to gain their adult form. Their presence on a body of water indicates that it is relatively unpolluted, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halipegus Occidualis
''Halipegus'' is a genus of trematode Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host ... in the family Derogenidae. The status of ''H. eccentricus'' has been disputed. In 1998, it was suggested that it be regarded as a junior synonym of ''H. occidualis'', but this was rejected in 1999. Species The following species are accepted within ''Halipegus'': * '' Halipegus africanus'' Dollfus, 1950 * '' Halipegus alhaussaini'' Saoud & Roshdy, 1970 * '' Halipegus ambalensis'' Gupta & Chopra, 1987 * '' Halipegus barabankiensis'' Choudhary, Ray & Agrawal, 2019 * '' Halipegus bulla'' (Fain, 1953) Skrjabin & Gushanskaja, 1955 * '' Halipegus ctenopomi'' Jones, 1982 * '' Halipegus dubius'' Klein, 1905 * '' Halipegus eccentricus'' Thomas, 1939 * '' Halipegus eschi'' Zelmer & Brooks, 2000 * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
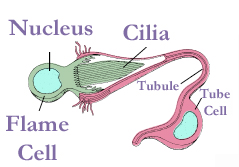
Flame Cell
A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in the simplest freshwater invertebrates, including flatworms, rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney, removing waste materials. Bundles of flame cells are called protonephridia. The flame cell has a nucleus (biology), nucleated cell body, with a "cup-shaped" projection, with flagella covering the inner surface of the cup. The beating of these flagella resemble a flame, giving the cell its name. The cup is attached to a tube cell, whose inner surface is also coated in cilia, which help to move liquid through the tube cell. The tube opens externally through a ''nephropore'', or, in the trematoda, into an excretory Urinary bladder, bladder. The function of these cells is to regulate the osmotic pressure of the worm, and maintain its ionic balance. Microvilli in the tube cell may be used to reabsorb some ions. Molecules enter the tubule in tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The American Midland Naturalist
''The American Midland Naturalist'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering natural history. It was established in 1909 by Julius Nieuwland and is published by the University of Notre Dame. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2013 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 0.621. References External links * History of the journal* {{DEFAULTSORT:American Midland Naturalist Biology journals English-language journals Publications established in 1909 Quarterly journals Academic journals published by universities and colleges of the United States 1909 establishments in Indiana University of Notre Dame academic journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physa Gyrina
''Physa'' is a genus of small, left-handed or sinistral, air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Physinae of the family Physidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Physa Draparnaud, 1801. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=181551 on 2021-06-26 These snails eat algae, diatoms and detritus. Anatomy Members of the freshwater pulmonate family Physidae possess a complex of muscles that is unique amongst gastropods. This complex was given the name "physid musculature". The physid musculature has two main components, the physid muscle ''sensu stricto'' and the fan muscle. The physid musculature is responsible for a unique ability of physids to rapidly flick their shells from side to side — a reaction that frequently enables them to escape predation. Shell description These small snails, like all the species in the family Physidae, have shells that are sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damselfly
Damselflies are flying insects of the suborder Zygoptera in the order Odonata. They are similar to dragonflies, which constitute the other odonatan suborder, Anisoptera, but are smaller and have slimmer bodies. Most species fold the wings along the body when at rest, unlike dragonflies which hold the wings flat and away from the body. An ancient group, damselflies have existed since at least the Lower Permian, and are found on every continent except Antarctica. All damselflies are predatory insects; both nymphs and adults actively hunt and eat other insects. The nymphs are aquatic, with different species living in a variety of freshwater habitats including acidic bogs, ponds, lakes and rivers. The nymphs moult repeatedly, at the last moult climbing out of the water to undergo metamorphosis. The skin splits down the back, they emerge and inflate their wings and abdomen to gain their adult form. Their presence on a body of water indicates that it is relatively unpolluted, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and the Digenea. Aspidogastrea is the smaller subclass, comprising 61 species. These flukes mainly infect bivalves and bony fishes.https://www.biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.3918.3.2 Digenea — which comprise the majority of trematodes — ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are typically tied to a specific place or landform, and are usually depicted as maidens. They were not necessarily immortal, but lived much longer than human beings. They are often divided into various broad subgroups, such as the Meliae (ash tree nymphs), the Dryads (oak tree nymphs), the Naiads (freshwater nymphs), the Nereids (sea nymphs), and the Oreads (mountain nymphs). Nymphs are often featured in classic works of art, literature, mythology, and fiction. Since the Middle Ages, nymphs have been sometimes popularly associated or even confused with fairies. Etymology The Greek word has the primary meaning of "young woman; bride, young wife" but is not usually associated with deities in particular. Yet the etymology of the noun remains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)