|
Hajdu–Cheney Syndrome
Hajdu–Cheney syndrome, also called acroosteolysis with osteoporosis and changes in skull and mandible, arthrodentoosteodysplasia and Cheney syndrome, is an extremely rare autosomal dominant congenital disorder of the connective tissue characterized by severe and excessive bone resorption leading to osteoporosis and a wide range of other possible symptoms. Mutations in the ''NOTCH2'' gene, identified in 2011, cause HCS. HCS is so rare that only about 50 cases have been reported worldwide since the discovery of the syndrome in 1948 Signs and symptoms Hajdu–Cheney syndrome causes many issues with an individual's connective tissues. Some general characteristics of an individual with Hajdu–Cheney syndrome include bone flexibility and deformities, short stature, delayed acquisition of speech and motor skills, dolichocephalic skull, Wormian bone, small maxilla, hypoplastic frontal sinuses, basilar impression, joint laxity, bulbous finger tips and severe osteoporosis. Wormian bone oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid human genome, genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY syndrome, XYY, Klinefelter syndrome, XXY, Triple X syndrome, XXX, XXXX syndrome, XXXX, XXXXX syndrome, XXXXX or XXYY syndrome, XXYY, among Aneuploidy, other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits (eyes), or orbital hypertelorism. In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as well as the distance between the pupils is greater than normal. Hypertelorism should not be confused with telecanthus, in which the distance between the inner eye corners is increased but the distances between the outer eye corners and the pupils remain unchanged.Michael L. Bentz: ''Pediatric Plastic Surgery''; Chapter 9 Hypertelorism by Renato Ocampo, Jr., MD/ John A. Persing, MD Hypertelorism is a symptom in a variety of syndromes, including Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), 1q21.1 duplication syndrome, basal cell nevus syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome and Loeys–Dietz syndrome. Hypertelorism can also be seen in Apert syndrome, Autism spectrum disorder, craniofrontonasal dysplasia, Noonan syndrome, neurofibromatosis, LEOPARD syndrome, Crouzon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant Disorders
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphanet
Orphanet is a knowledge base dedicated to rare diseases as well as corresponding diagnosis, orphan drugs, clinical trials and expert networks The website is managed by a network of academic establishments from 40 countries, led by Inserm. It contains content both for physicians and for patients. Its administrative office is in Paris and its official medical journal is the ''Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases'' published on their behalf by BioMed Central. As of October 2020, the site provides information about over 6100 rare diseases and 5400 genes. Functions available Orphanet is an online database with the aspiration of gathering, providing and improving knowledge on rare diseases and to improve the diagnosis, care and treatment of patients with rare diseases. By listing rare diseases, and maintaining a standard nomenclature of rare diseases (ORPHAcodes) Orphanet makes a contribution in making them more visible in health and research information systems. The information is ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they have two phosphonate () groups. They are thus also called diphosphonates ('' bis-'' or '' di-'' + ''phosphonate''). Evidence shows that they reduce the risk of fracture in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis. Bone tissue undergoes constant remodeling and is kept in balance (homeostasis) by osteoblasts creating bone and osteoclasts destroying bone. Bisphosphonates inhibit the digestion of bone by encouraging osteoclasts to undergo apoptosis, or cell death, thereby slowing bone loss. The uses of bisphosphonates include the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease of bone, bone metastasis (with or without hypercalcemia), multiple myeloma, primary hyperparathyroidism, osteogenesis imperfecta, fibrous dysplasia, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
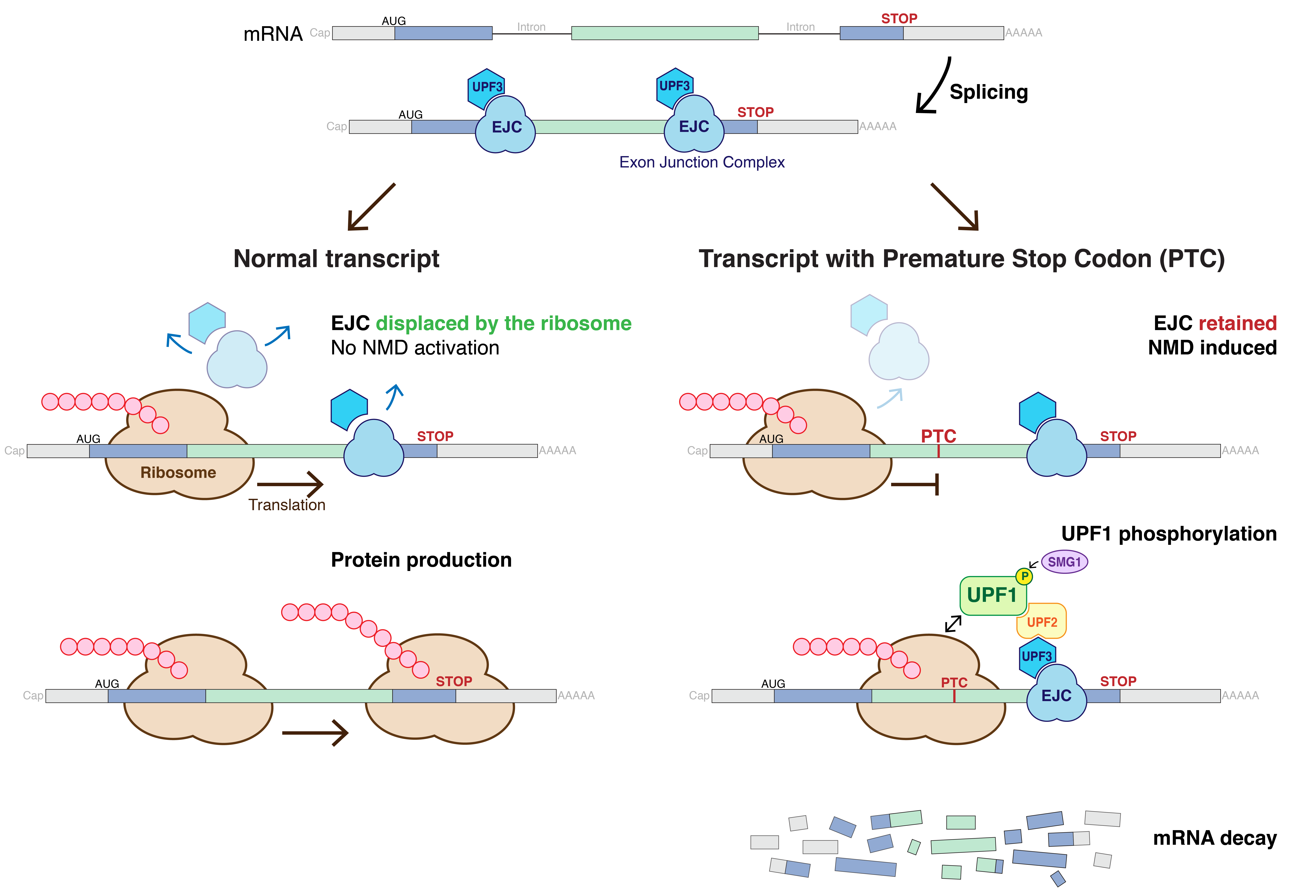
Nonsense-mediated MRNA Decay
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins. NMD was first described in human cells and in yeast almost simultaneously in 1979. This suggested broad phylogenetic conservation and an important biological role of this intriguing mechanism. NMD was discovered when it was realized that cells often contain unexpectedly low concentrations of mRNAs that are transcribed from alleles carrying nonsense mutations. Nonsense mutations code for a premature stop codon which causes the protein to be shortened. The truncated protein may or may not be functional, depending on the severity of what is not translated. In human genetics, NMD has the possibility to not only limit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEST Sequence
A PEST sequence is a peptide sequence that is rich in proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T). This sequence is associated with proteins that have a short intracellular half-life; therefore, it is hypothesized that the PEST sequence acts as a signal peptide for protein degradation. This protein degradation may be mediated via the proteasome or calpain A calpain (; , ) is a protein belonging to the family of calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine proteases (protease, proteolytic enzymes) expressed ubiquitously in mammals and many other organisms. Calpains constitute the C2 family of proteas .... Other signals thought to identify proteins for degradation include cyclin destruction boxes, which are amino acid sequences that mark cell-cycle proteins for destruction. References Peptide sequences Proteins Post-translational modification {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant - En
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromosome e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiocephaly
Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. A mild and widespread form is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head caused by remaining in a supine position for prolonged periods. Plagiocephaly is a diagonal asymmetry across the head shape. Often it is a flattening which is to one side at the back of the head and there is often some facial asymmetry. Depending on whether synostosis is involved, plagiocephaly divides into two groups: synostotic, with one or more fused cranial sutures, and non-synostotic (deformational). Surgical treatment of these groups includes the deference method; however, the treatment of deformational plagiocephaly is controversial. Brachycephaly describes a very wide head shape with a flattening across the whole back of the head. Causes Slight plagiocephaly is routinely diagnosed at birth and may be the result of a restrictive intrau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wormian Bone
Wormian bones, also known as intrasutural bones or sutural bones, are extra bone pieces that can occur within a suture (joint) in the skull. These are irregular isolated bones that can appear in addition to the usual centres of ossification of the skull and, although unusual, are not rare. They occur most frequently in the course of the lambdoid suture, which is more tortuous than other sutures. They are also occasionally seen within the sagittal and coronal sutures. A large wormian bone at lambda is often called an Inca bone (''os incae''), due to the relatively high frequency of occurrence in Peruvian mummies. Another specific Wormian bone, the pterion ossicle, sometimes exists between the sphenoidal angle of the parietal bone and the great wing of the sphenoid bone. They tend to vary in size and can be found on either side of the skull. Usually, not more than several are found in a single individual, but more than one hundred have been once found in the skull of a hydrocephali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolichocephalic
Dolichocephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek δολιχός 'long' and κεφαλή 'head') is a condition where the head is longer than would be expected, relative to its width. In humans, scaphocephaly is a form of dolichocephaly. Dolichocephalic dogs (such as German Shepherds) have elongated noses. This makes them vulnerable to fungal diseases of the nose such as aspergillosis. In humans the anterior–posterior diameter (length) of dolichocephaly head is more than the transverse diameter (width). It can be present in cases of Sensenbrenner syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Sotos syndrome, CMFTD as well as Marfan syndrome. See also * Brachycephaly * Cephalic index * Plagiocephaly Plagiocephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a condition characterized by an asymmetrical distortion (flattening of one side) of the skull. A mild and widespread form is characterized by a flat spot on the back or one side of the head cause ... References External links Congenital d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(14582377398).jpg)