|
Haemophilia C
Haemophilia C (also known as plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA) deficiency or Rosenthal syndrome) is a mild form of haemophilia affecting both sexes, due to factor XI deficiency. It predominantly occurs in Ashkenazi Jews. It is the fourth most common coagulation disorder after von Willebrand's disease and haemophilia A and B. In the United States, it is thought to affect 1 in 100,000 of the adult population, making it 10% as common as haemophilia A. Signs and symptoms In terms of the signs/symptoms of haemophilia C, unlike individuals with Haemophilia A and B, people affected by it are not ones to bleed spontaneously. In these cases, haemorrhages tend to happen after a major surgery or injury. However, people affected with haemophilia C might experience symptoms closely related to those of other forms of haemophilia such as the following: Cause Haemophilia C is caused by a deficiency of coagulation factor XI and is distinguished from haemophilia A and B by the fact it does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding Diathesis
In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability (a condition of irregular and slow blood clotting), in turn caused by a coagulopathy (a defect in the system of coagulation). Therefore, this may result in the reduction of platelets being produced and leads to excessive bleeding. Several types of coagulopathy are distinguished, ranging from mild to lethal. Coagulopathy can be caused by thinning of the skin (Cushing's syndrome), such that the skin is weakened and is bruised easily and frequently without any trauma or injury to the body. Also, coagulopathy can be contributed by impaired wound healing or impaired clot formation. Signs and symptoms Complications Following are some complications of coagulopathies, some of them caused by their treatments: Causes While there are several possible causes, they generally result in excessive bleeding and a lack of clotting. Acquired Acquired causes of coagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUDs
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC). One study found that female family planning providers choose LARC methods more often (41.7%) than the general public (12.1%). Among birth control methods, IUDs, along with other contraceptive implants, result in the greatest satisfaction among users. IUDs are safe and effective in adolescents as well as those who have not previously had children. Once an IUD is removed, even after long-term use, fertility returns to normal rapidly. Copper devices have a failure rate of about 0.8% while hormonal ( levonorgestrel) devices fail about 0.2% of the time within the first year of use. In comparison, male sterilization and male condoms have a failure rate of about 0.15% and 15%, respectively. Copper IUDs can also be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresh Frozen Plasma
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is a blood product made from the liquid portion of whole blood. It is used to treat conditions in which there are low blood clotting factors (INR > 1.5) or low levels of other blood proteins. It may also be used as the replacement fluid in plasma exchange. Using ABO compatible plasma, while not required, may be recommended. Use as a volume expander is not recommended. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Side effects include nausea and itchiness. Rarely there may be allergic reactions, blood clots, or infections. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe for the baby. Greater care should be taken in people with protein S deficiency, IgA deficiency, or heart failure. Fresh frozen plasma is made up of a complex mixture of water, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. When frozen it lasts about a year. Plasma first came into medical use during the Second World War. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from major trauma, postpartum bleeding, surgery, tooth removal, nosebleeds, and heavy menstruation. It is also used for hereditary angioedema. It is taken either orally or by injection into a vein. Mechanism of action Tranexamic acid is a synthetic analog of the amino acid lysine. It serves as an antifibrinolytic by reversibly binding four to five lysine receptor sites on plasminogen. This decreases the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, preventing fibrin degradation and preserving the framework of fibrin's matrix structure. Tranexamic acid has roughly eight times the antifibrinolytic activity of an older analogue, ε-aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid also directly inhibits the activity of plasmin with weak potency ( IC50 = 87 mM), and it can block the active-site of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) with high specificity ( Ki = 2 mM), one of the highest among all the serine proteases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranexamic Acid Ball-and-stick
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from major trauma, postpartum bleeding, surgery, tooth removal, nosebleeds, and heavy menstruation. It is also used for hereditary angioedema. It is taken either orally or by injection into a vein. Mechanism of action Tranexamic acid is a synthetic analog of the amino acid lysine. It serves as an antifibrinolytic by reversibly binding four to five lysine receptor sites on plasminogen. This decreases the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, preventing fibrin degradation and preserving the framework of fibrin's matrix structure. Tranexamic acid has roughly eight times the antifibrinolytic activity of an older analogue, ε-aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid also directly inhibits the activity of plasmin with weak potency ( IC50 = 87 mM), and it can block the active-site of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) with high specificity ( Ki = 2 mM), one of the highest among all the serine proteas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixing Study
Mixing studies are tests performed on blood plasma of patients or test subjects to distinguish factor deficiencies from factor inhibitors, such as lupus anticoagulant, or specific factor inhibitors, such as antibodies directed against factor VIII. The basic purpose of these tests is to determine the cause of prolongation of Prothrombin Time (PT), Partial Thromboplastin Time, or sometimes of thrombin time (TT). Mixing studies take advantage of the fact that factor levels that are 50 percent of normal should give a normal Prothrombin time (PT) or Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) result. Factor deficient plasmas (Adsorbed Plasma & Aged Plasma, etc.) are used in mixing studies. Plasma with known factor deficiencies are commercially available but are very expensive, so they are often prepared in the laboratory and can then be used for mixing experiments. Test method Fresh normal plasma has all the blood coagulation factors with normal levels. Plasma from patients on oral anticoagulan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
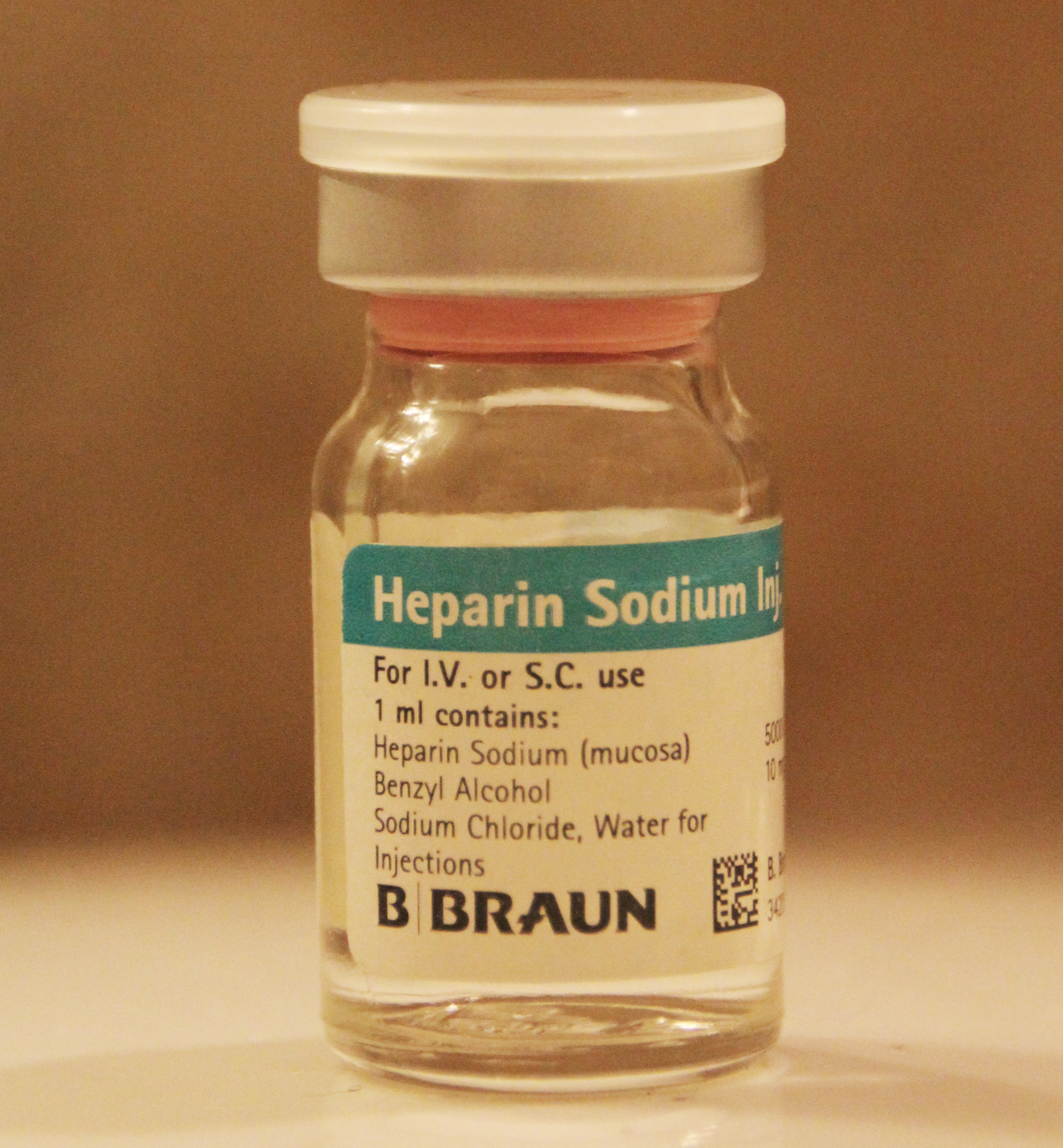
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Anticoagulant
Lupus anticoagulant is an immunoglobulin that binds to phospholipids and proteins associated with the cell membrane. Its name is a partial misnomer, as it is actually a prothrombotic antibody ''in vivo''. Lupus anticoagulant in living systems causes a decrease in clotting time. The name derives from their properties ''in vitro'', as these antibodies increase coagulation times in laboratory tests such as the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Investigators speculate that the antibodies interfere with phospholipids used to induce in vitro coagulation. In vivo, the antibodies are thought to interact with platelet membrane phospholipids, increasing adhesion and aggregation of platelets, which accounts for the in vivo prothrombotic characteristics. The condition was first described by hematologist C. Lockard Conley in 1952. Terminology Both words in the term "lupus anticoagulant" can be misleading: * Most patients with a lupus anticoagulant do not actually have lupus erythem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)