|
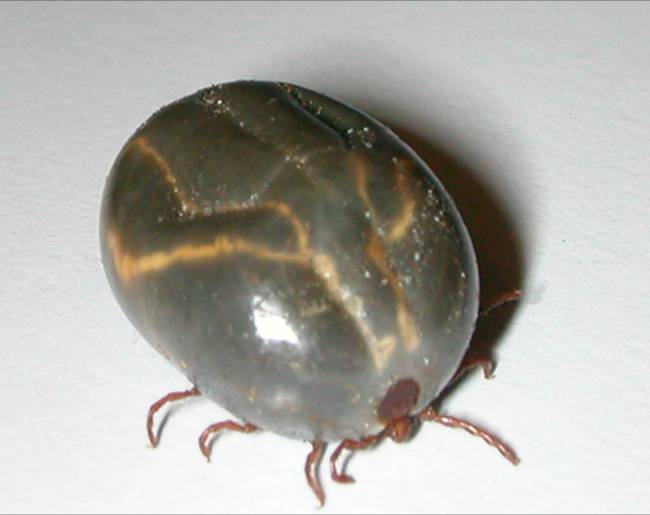
Haemaphysalis Longicornis
''Haemaphysalis longicornis'', the Asian longhorned tick, longhorned tick, bush tick, Asian tick, or cattle tick, is a parasitic arachnid belonging to the tick family Ixodidae. The Asian longhorned tick is a known livestock pest, especially in New Zealand, and can transmit a disease called theileriosis to cattle but not to humans. However, the tick has been associated with several other tickborne diseases in humans. An unfed female is typically 2.0–2.6 mm long and 1.5–1.8 mm wide, and grows to 9.8 mm long and 8.2 mm wide with engorgement. Distinguishing a specimen from other members of the genus ''Haemaphysalis'' requires microscopic examination of minor physical characteristics. Geographic distribution The Asian longhorned tick is native to temperate areas of East and Central Asia, including China, Korea, and Japan, as well as Pacific islands including Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, and Hawaii, to name a few.Rachel Can''Haemaphysalis longicornis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longhorned Tick (Haemaphysalis Longicornis)
''Haemaphysalis longicornis'', the Asian longhorned tick, longhorned tick, bush tick, Asian tick, or cattle tick, is a Parasitism, parasitic arachnid belonging to the tick family Ixodidae. The Asian longhorned tick is a known livestock pest, especially in New Zealand, and can transmit a disease called tropical theileriosis, theileriosis to cattle but not to humans. However, the tick has been associated with several other tickborne diseases in humans. An unfed female is typically 2.0–2.6 mm long and 1.5–1.8 mm wide, and grows to 9.8 mm long and 8.2 mm wide with engorgement. Distinguishing a specimen from other members of the genus ''Haemaphysalis'' requires microscopic examination of minor physical characteristics. Geographic distribution The Asian longhorned tick is native to temperate areas of East and Central Asia, including China, Korea, and Japan, as well as Pacific islands including Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, and Hawaii, to name a few.Rachel Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Des Helmore
Desmond W. Helmore (born 1940) is a New Zealand artist and illustrator, known both for his fine art and for his scientific work depicting insects, not least illustrating the New Zealand Arthropod Collection. One of the country's most noted and prolific biological illustrators, over 1000 of his illustrations of insects were published in research papers from 1976 to 2006. Life and education Helmore was born in Takapau, Hawke's Bay Region, Hawkes Bay, New Zealand, and lived there on a farm until age 12. Interested in drawing since childhood, he attended Christ's College, Christchurch, Christ's College in Christchurch, and then the Ilam School of Fine Arts at the University of Canterbury from 1959 to 1962, where he was taught by Rudolf Gopas, Rudi Gopas, Russell Clark (artist), Russell Clark, and Bill Sutton (artist), Bill Sutton. His fellow students at Ilam included Dick Frizzell, Tony Fomison, and John Panting. In his survey of New Zealand art, Frizzell described Helmore as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
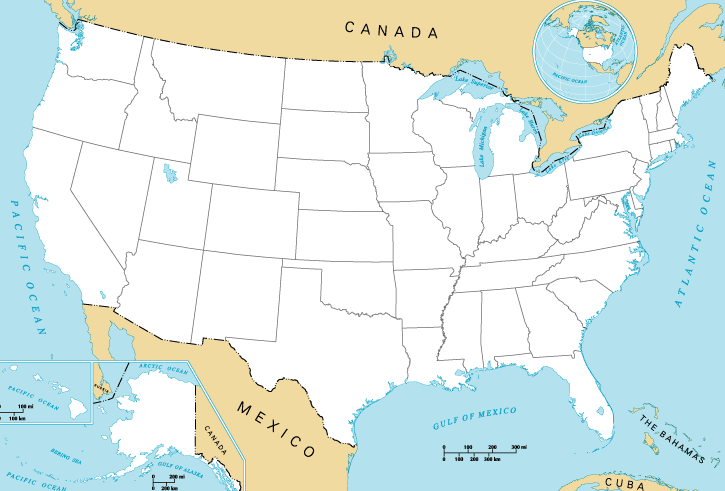
Mainland United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii (also the last ones admitted to the Union), and all other offshore insular areas, such as American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term "Lower48" is used also, especially in relation to just Alaska (Hawaii is farther south). The related but distinct term continental United States includes Alaska (which is also on the continent of North America but separated from the 48 states by British Columbia and Yukon of Canada), but excludes the Hawaiian Islands and all U.S. territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The greatest distance (on a great-circle route) entirely within the contiguous U.S. is 2,802 miles (4,509 km), between Florida and the State of Washington; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneuploid
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a ''euploid'' cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of some genetic disorders. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. About 68% of human solid tumors are aneuploid. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells (nondisjunction). Most cases of aneuploidy in the autosomes result in miscarriage, and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18 and 13. Chromosome abnormalities are detected in 1 of 160 live human births. Autosomal aneuploidy is more dangerous than sex chromosome aneuploidy, as autosomal aneuploidy is almost always lethal to embryos that cease develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryos occur in a gamete (egg or sperm) without combining with another gamete (e.g., egg and sperm fusing). In animals, parthenogenesis means development of an embryo from an unfertilized Gametophyte, egg cell. In plants, parthenogenesis is a component process of apomixis. In algae, parthenogenesis can mean the development of an embryo from either an individual sperm or an individual egg. Parthenogenesis occurs naturally in some plants, algae, invertebrate animal species (including nematodes, some tardigrades, water fleas, some scorpions, aphids, some mites, some bees, some Phasmatodea and parasitic wasps) and a few vertebrates (such as some fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds). This type of reproduction has been induced artificially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes ( diploid). This is typical in animals, though the number of chromosome sets and how that number changes in sexual reproduction varies, especially among plants, fungi, and other eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction is the most common life cycle in multicellular eukaryotes, such as animals, fungi and plants. Sexual reproduction also occurs in some unicellular eukaryotes. Sexual reproduction does not occur in prokaryotes, unicellular organisms without cell nuclei, such bacteria and archaea. However, some process in bacteria may be considered analogous to sexual reproduction in that they incorporate new genetic information, including bacterial conjugation, transformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemaphysalis Longicornis 1
''Haemaphysalis'' is a genus of ticks, containing these species: *'' Haemaphysalis aborensis'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aciculifer'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aculeata'' Lavarra, 1904 *'' Haemaphysalis adleri'' Feldman-Muhsam, 1951 *'' Haemaphysalis anomala'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis anomaloceraea'' Teng & Cui, 1984 *'' Haemaphysalis anoplos'' Hoogstraal, Uilenberg & Klein, 1967 *'' Haemaphysalis aponommoides'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis asiatica'' (Supino, 1897) *'' Haemaphysalis atheruri'' Hoogstraal, Trapido & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bancrofti'' Nuttall & Warburton, 1915 *'' Haemaphysalis bandicota'' Hoogstraal & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bartelsi'' Schulze, 1938 *'' Haemaphysalis bequaerti'' Hoogstraal, 1956 *'' Haemaphysalis birmaniae'' Supino, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bispinosa'' Neumann, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bochkovi'' Apanaskevich & Tomlinson, 2019Dmitry Apanaskevich and Jackson A. Tomlinson. 2019. Description of four new species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also reports on related subjects such as technology, communications, science, politics, and law. It is based in Jersey City, New Jersey. Competitors in the national business magazine category include ''Fortune'' and ''Bloomberg Businessweek''. ''Forbes'' has an international edition in Asia as well as editions produced under license in 27 countries and regions worldwide. The magazine is well known for its lists and rankings, including of the richest Americans (the Forbes 400), of the America's Wealthiest Celebrities, of the world's top companies (the Forbes Global 2000), Forbes list of the World's Most Powerful People, and The World's Billionaires. The motto of ''Forbes'' magazine is "Change the World". Its chair and editor-in-chief is Steve Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


