|
HU-210
HU-210 is a synthetic cannabinoid that was first chemical synthesis, synthesized in 1988 from (1R,5S)-myrtenol by a group led by Raphael Mechoulam at the Hebrew University. HU-210 is 100 to 800 times more potent than natural Tetrahydrocannabinol, THC from cannabis (drug), cannabis and has an extended duration of action. HU-210 has a binding affinity of 0.061nM at CB1 and 0.52nM at CB2 in cloned human cannabinoid receptors. Compared to Delta-9-THC of 40.7nM at CB1. HU-210 is the (–)-1,1-dimethylheptyl analog of 11-hydroxy- Δ8- tetrahydrocannabinol; in some references it is called 1,1-dimethylheptyl- 11-hydroxytetrahydrocannabinol. The abbreviation "HU" stands for Hebrew University. Effects and research HU-210, the (–) enantiomer of 11-OH-D8-THC-DMH, has almost all of the cannabinoid activity, while the (+) enantiomer, known as HU-211, is inactive as a cannabinoid and instead acts as an NMDA antagonist having neuroprotective effects. HU-210 promotes cell proliferation, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Cannabinoid
Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of designer drug molecules that bind to the same receptors to which cannabinoids (THC, CBD and many others) in cannabis plants attach. These novel psychoactive substances should not be confused with synthetic phytocannabinoids (THC or CBD obtained by chemical synthesis) or synthetic endocannabinoids from which they are in many aspects distinct. Typically, synthetic cannabinoids are sprayed onto plant matter and are usually smoked, although they have also been ingested as a concentrated liquid form in the US and UK since 2016. They have been marketed as herbal incense, or "herbal smoking blends", and sold under common names like K2, spice, and synthetic marijuana. They are often labeled "not for human consumption" for liability defense. A large and complex variety of synthetic cannabinoids are designed in an attempt to avoid legal restrictions on cannabis, making synthetic cannabinoids designer drugs. Most synthetic cannabinoids are agonists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HU-211
Dexanabinol (HU-211 or ETS2101) is a synthetic cannabinoid derivative in development by e-Therapeutics plc. It is the "unnatural" enantiomer of the potent cannabinoid agonist HU-210. Unlike other cannabinoid derivatives, HU-211 does not act as a cannabinoid receptor agonist, but instead has NMDA antagonist effects. It therefore does not produce cannabis-like effects, but is anticonvulsant and neuroprotective, and is widely used in scientific research as well as currently being studied for applications such as treating head injury, stroke, or cancer. It was shown to be safe in clinical trials and is currently undergoing Phase I trials for the treatment of brain cancer and advanced solid tumors. Clinical trials Dexanabinol has been studied in IV administration and oral dosing. e-Therapeutics is evaluating the compound in clinical trials for brain and solid cancers. Phase II studies are planned based on the results of the current trials. A phase 1b study for hepatocellular carci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
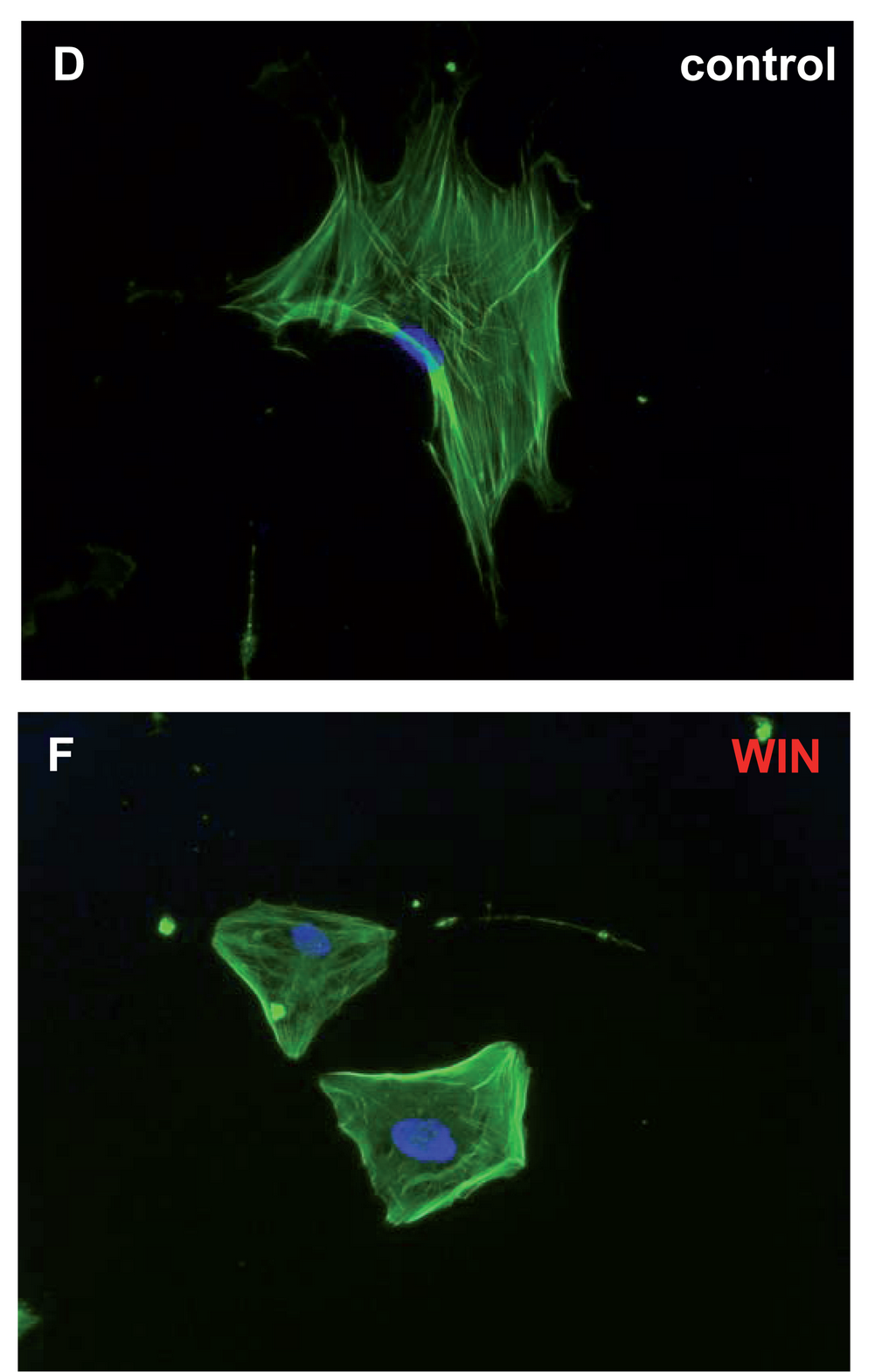
WIN 55,212-2
WIN 55,212-2 is a chemical described as an aminoalkylindole derivative, which produces effects similar to those of cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) but has an entirely different chemical structure. WIN 55,212-2 is a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist that has been found to be a potent analgesic in a rat model of neuropathic pain. It activates p42 and p44 MAP kinase via receptor-mediated signaling. At 5 μM WIN 55,212-2 inhibits ATP production in sperm in a CB1 receptor-dependent fashion. WIN 55,212-2, along with HU-210 and JWH-133, may prevent the inflammation caused by amyloid beta proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease, in addition to preventing cognitive impairment and loss of neuronal markers. This anti-inflammatory action is induced through agonist action at cannabinoid receptors, which prevents microglial activation that elicits the inflammation. WIN 55,212-2 is a full agonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor ( ''K''i = 1.9 nM) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JWH-133
JWH-133 (Dimethylbutyl-deoxy-Delta-8-THC) is a potent selective CB2 receptor agonist with a Ki of 3.4nM and selectivity of around 200x for CB2 over CB1 receptors. It was discovered by and named after, John W. Huffman. It's important to note that JWH-133 has been confused with other analogs of Delta-8-THC in professionally published peer-reviewed literature. Including being confused with Dimethylpentyl-Delta-8-THC as well as Dimethylbutyl-Delta-8-THC. Including confusing the chemical name with Dimethylbutyl-Delta-8-THC itself. Including confusing it with the Delta-9 isomer Including using the structural image of Dimethylbutyl-Delta-8-THC instead of Dimethylbutyl-deoxy-Delta-8-THC. It's important to note that 3-(1',1'-Dimethylbutyl)-1-deoxy-delta-8-THC is a selective CB2 agonist, binding 677nM at Cb1 and 3.4nM at CB2 while 3-(1',1'-Dimethylbutyl)-delta-8-THC itself binds 65nM at CB1. Structurally the only difference between JWH-133 and dimethylbutyl-D8-THC is that JWH-133 lacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Antagonist
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown medical history and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor
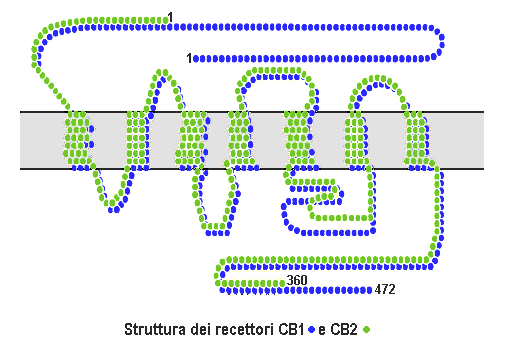
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: endocannabinoids; plant cannabinoids (such as Tetrahydrocannabinol, produced by the cannabis plant); and synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All of the endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (plant based cannabinoids) are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% similar. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is a lipid found in cannabis and, like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, it is assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress. THC was first discovered and isolated by Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam in Israel in 1964. It was found that, when smoked, THC is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to endocannabinoid receptors located in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. These are the parts of the brain responsible for thinking, memory, pleasure, coordination a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexanabinol
Dexanabinol (HU-211 or ETS2101) is a synthetic cannabinoid derivative in development by e-Therapeutics plc. It is the "unnatural" enantiomer of the potent cannabinoid agonist HU-210. Unlike other cannabinoid derivatives, HU-211 does not act as a cannabinoid receptor agonist, but instead has NMDA antagonist effects. It therefore does not produce cannabis-like effects, but is anticonvulsant and neuroprotective, and is widely used in scientific research as well as currently being studied for applications such as treating head injury, stroke, or cancer. It was shown to be safe in clinical trials and is currently undergoing Phase I trials for the treatment of brain cancer and advanced solid tumors. Clinical trials Dexanabinol has been studied in IV administration and oral dosing. e-Therapeutics is evaluating the compound in clinical trials for brain and solid cancers. Phase II studies are planned based on the results of the current trials. A phase 1b study for hepatocellular carci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), also known as cannabinoid receptor 1, is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR1'' gene. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by: endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG); plant phytocannabinoids, such as the compound THC which is an active ingredient of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and, synthetic analogs of THC. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. Structure The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The receptor may exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK/ERK Pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway (also known as the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway) is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. The signal starts when a signaling molecule binds to the receptor on the cell surface and ends when the DNA in the nucleus expresses a protein and produces some change in the cell, such as cell division. The pathway includes many proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), originally called extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), which communicate by adding phosphate groups to a neighboring protein ( phosphorylating it), thereby acting as an "on" or "off" switch. When one of the proteins in the pathway is mutated, it can become stuck in the "on" or "off" position, a necessary step in the development of many cancers. In fact, components of the MAPK/ERK pathway were first discovered in cancer cells, and drugs that reverse the "on" or "off" switch are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |